Comprehensive Dietary Strategies for Effective Management of Type 2 Diabetes
An in-depth guide on managing type 2 diabetes through a tailored nutritional plan, emphasizing fiber-rich foods, healthy fats, and lifestyle changes. Learn effective dietary strategies to stabilize blood sugar, improve insulin sensitivity, and prevent complications with expert tips and food recommendations tailored for long-term health.

Comprehensive Dietary Strategies for Effective Management of Type 2 Diabetes
Managing type 2 diabetes effectively hinges significantly on adopting an appropriate and well-structured nutritional plan. An effective diet can help regulate blood sugar levels, improve insulin sensitivity, and reduce the risk of complications associated with diabetes. While individual nutritional needs may vary based on health status, age, gender, and lifestyle, certain core principles remain universal. Implementing these dietary strategies requires a deep understanding of food choices, portion control, and meal timing. This comprehensive guide explores key aspects of creating a diabetes-friendly diet, actionable tips, and nutritious food options to support optimal health outcomes.
Core Principles of a Diabetes-Optimized Diet
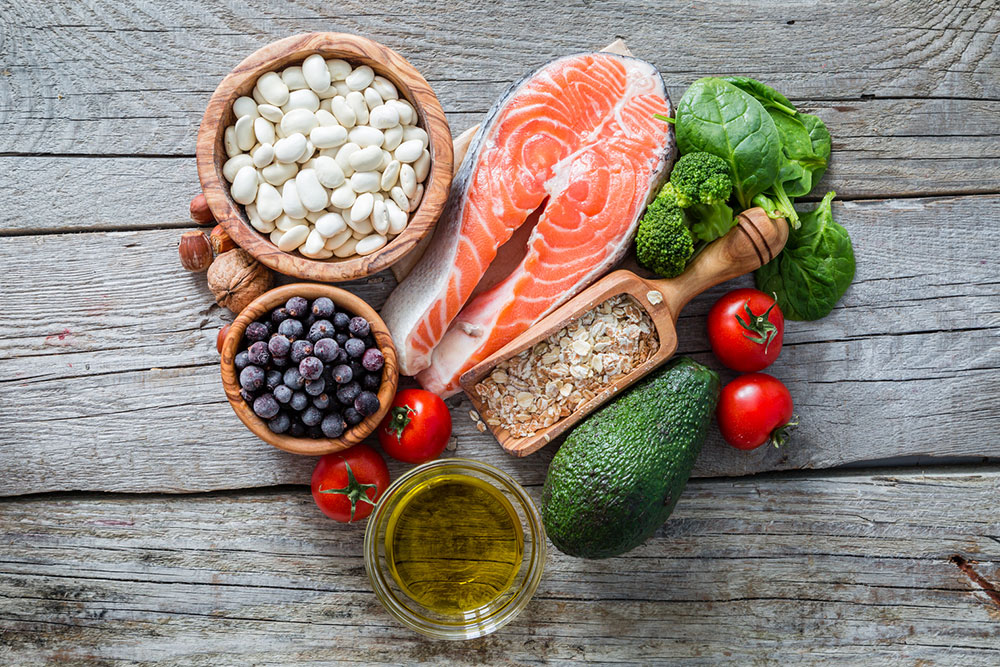
Prioritizing high-fiber foods, limiting processed items, and reducing intake of unhealthy fats and sugars form the foundation of a diet suitable for managing type 2 diabetes. These principles aim to stabilize blood glucose levels, enhance metabolic health, and prevent disease progression.
Essential Food Choices for Managing Diabetes
Whole grains: Incorporate foods like oats, barley, quinoa, wild rice, and brown rice, which are rich in dietary fiber and complex carbohydrates that help slow glucose absorption.
Fruits: Opt for berries such as strawberries, blackberries, and raspberries, as well as citrus fruits like oranges and grapefruits, which provide vitamins, antioxidants, and fiber.
Vegetables: Emphasize non-starchy vegetables such as leafy greens, carrots, cauliflower, broccoli, and asparagus. These foods are low in calories and carbs while being rich in vital nutrients.
Plant-based proteins: Incorporate beans, lentils, peas, and nuts like almonds, walnuts, and pecans (in moderation). These are excellent sources of protein, fiber, and healthy fats.
Animal-based proteins: Include fatty fish such as salmon, tuna, herring, and sardines, which are high in omega-3 fatty acids that support cardiovascular health.
Healthy fats: Use sources like extra virgin olive oil, peanut oil, flaxseeds, and avocados sparingly to provide beneficial monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats.
Dairy products: Choose low-fat or non-fat options like yogurt and milk to obtain calcium and protein without excess saturated fats.
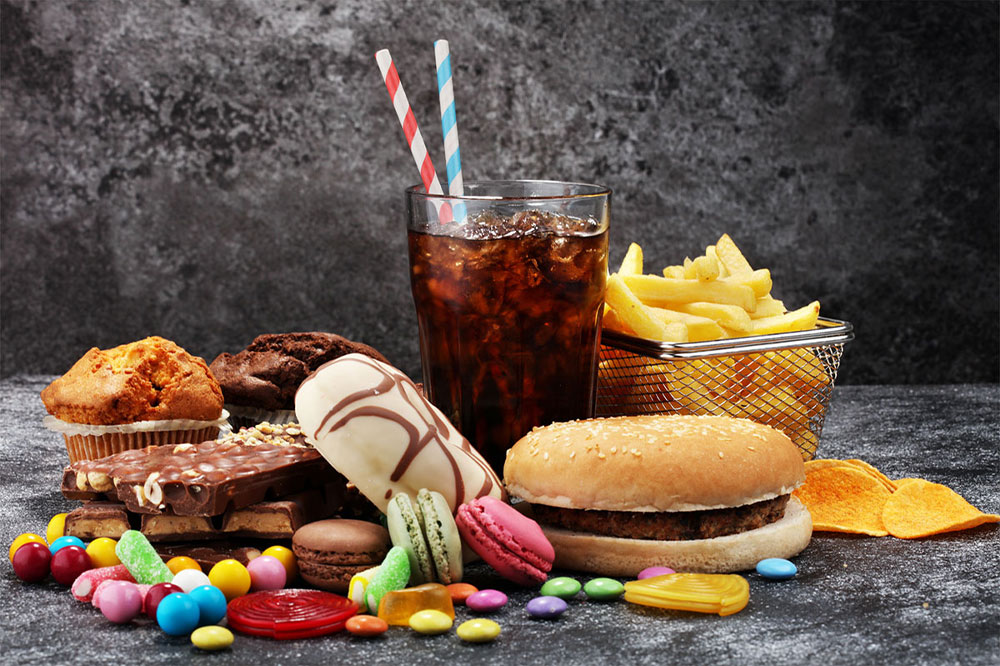
Foods and Ingredients to Limit or Avoid
Refined flours and processed foods, which can cause rapid spikes in blood sugar.
Full-fat dairy products that are high in saturated fats.
White rice, pasta, and other refined grains lacking fiber.
Red and processed meats which have been linked to increased inflammation and cardiovascular risks.
Starchy vegetables such as potatoes and corn when consumed in excess.
Sugary drinks like sodas, fruit-flavored beverages, and sweetened teas.
Trans fats and excessive saturated fats found in many fried and commercially baked goods.
High-sodium foods, processed snacks, and preserved foods that can elevate blood pressure.
Fried foods that contribute to unhealthy fat consumption and weight gain.
Additional Tips for Success
Maintain consistent meal times to prevent blood sugar fluctuations.
Eat a variety of foods to ensure comprehensive nutrient intake and prevent dietary monotony.
Monitor salt intake to help manage blood pressure and reduce cardiovascular risks.
Incorporate dietary fiber gradually and in appropriate amounts to enhance satiety, improve digestion, and support heart health.
Practice portion control and avoid overeating to aid in weight management, which is crucial for improving insulin sensitivity.
Complementing a balanced diet with regular physical activity can significantly enhance blood sugar control. Engaging in activities like walking, swimming, or cycling not only improves glycemic levels but also supports cardiovascular health, mental well-being, and overall fitness. While dietary modifications and exercise can sometimes reduce reliance on medication, it’s imperative to consult healthcare professionals for personalized treatment plans tailored to individual health conditions and goals.