Comprehensive Personalized Nutrition Strategies to Manage Type 2 Diabetes Effectively
This comprehensive guide offers personalized dietary strategies for managing type 2 diabetes effectively. It emphasizes the importance of balanced nutrition, including carbohydrates, proteins, healthy fats, and fiber, tailored to individual needs. The article highlights practical tips for selecting suitable foods like whole grains, lean proteins, vegetables, and healthy fats, aiming to stabilize blood sugar levels and prevent complications. Managing diabetes through customized nutrition plans is key to improving health outcomes and maintaining a balanced lifestyle. Perfect for those seeking sustainable ways to control their condition and enhance their quality of life.

Individualized Dietary Approaches for Better Control of Type 2 Diabetes
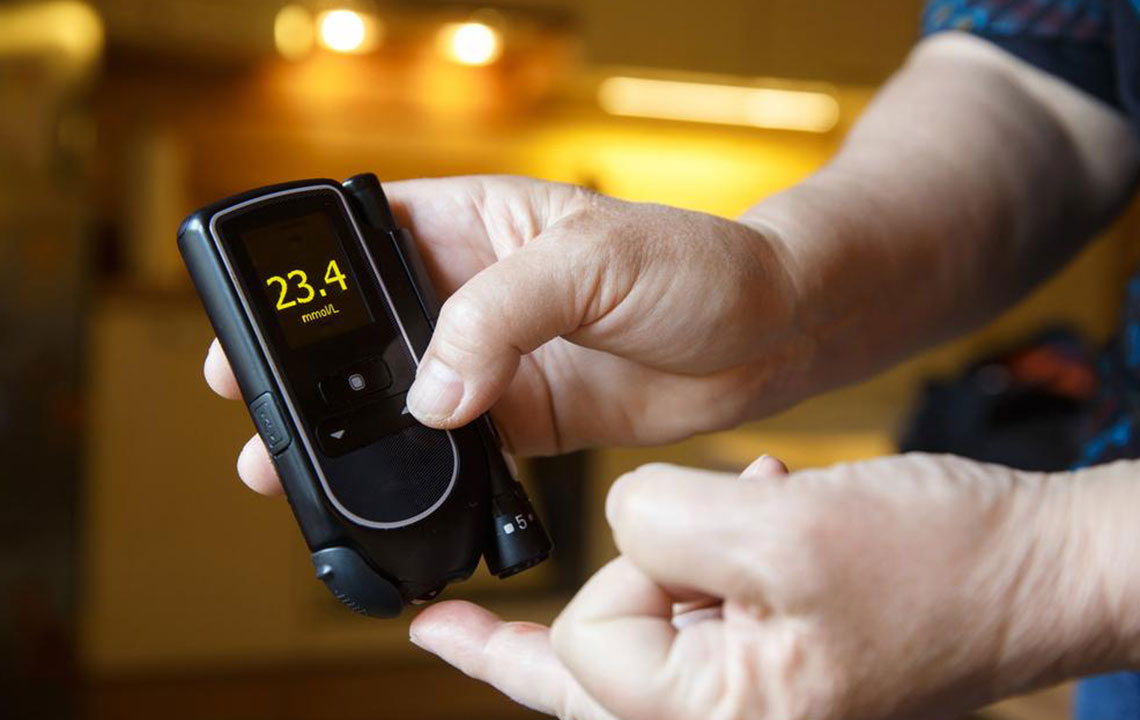
Maintaining optimal energy levels and overall health hinges on the foods we consume daily. For individuals diagnosed with type 2 diabetes, understanding the role of nutrition is crucial, as their bodies face challenges in efficiently processing glucose. When the body cannot effectively utilize insulin, the resulting inability to absorb glucose from the bloodstream leads to various health concerns, including fatigue, cardiovascular risks, and nerve damage.
Insulin, a vital hormone produced by the pancreas, plays a critical role in ferrying glucose into cells across different tissues like the brain, muscles, and fat tissues. However, in type 2 diabetes, insulin production is often inadequate, or the body's cells become resistant to its effects, rendering glucose absorption inefficient. This inefficiency causes glucose to build up in the bloodstream, resulting in chronic high blood sugar levels—a hallmark of diabetes.
If left unmanaged, persistently elevated blood sugar can lead to serious health complications, including nerve damage, kidney failure, vision loss, and cardiovascular disease. Over time, cells may become resistant to insulin, prompting the pancreas to produce even more insulin in an attempt to compensate. This vicious cycle exacerbates hyperglycemia and underscores the importance of effective management strategies.
To prevent the progression of insulin resistance and manage blood sugar effectively, personalized dietary modifications are essential. A diet tailored to an individual's needs can help maintain blood glucose levels within a safe range, reduce the risk of complications, and improve quality of life. Such a diet balances the intake of carbohydrates, vitamins, proteins, fats, salt, and dietary fiber, all of which influence blood sugar and overall health.
What constitutes a diabetic-friendly diet?
A well-structured, balanced diet forms the cornerstone of diabetes management. The primary goal is to ensure adequate nutrition while preventing blood sugar spikes. Understanding how different nutrients affect glycemic control is vital for creating an effective eating plan. The key is to monitor and regulate food consumption meticulously to achieve stable blood glucose levels.
Carbohydrates
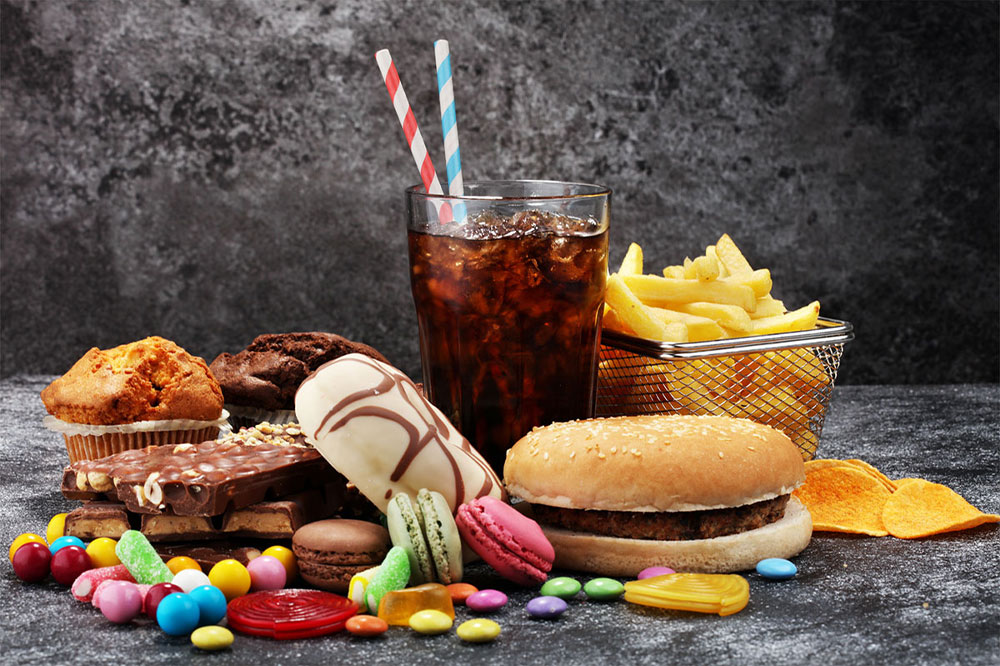
Carbohydrates are the body's main energy source; however, their impact on blood sugar necessitates careful selection and portion control. Enjoy fruits, whole grains, cereals, dairy products like milk and yogurt, and starchy vegetables such as potatoes, beans, and corn. Emphasize whole grains, which are rich in vital nutrients, fiber, and phytochemicals, and avoid processed refined grains like white flour that can cause rapid blood sugar rises. Incorporating complex carbohydrates with a low glycemic index helps sustain energy levels and maintain glycemic stability throughout the day.
Proteins
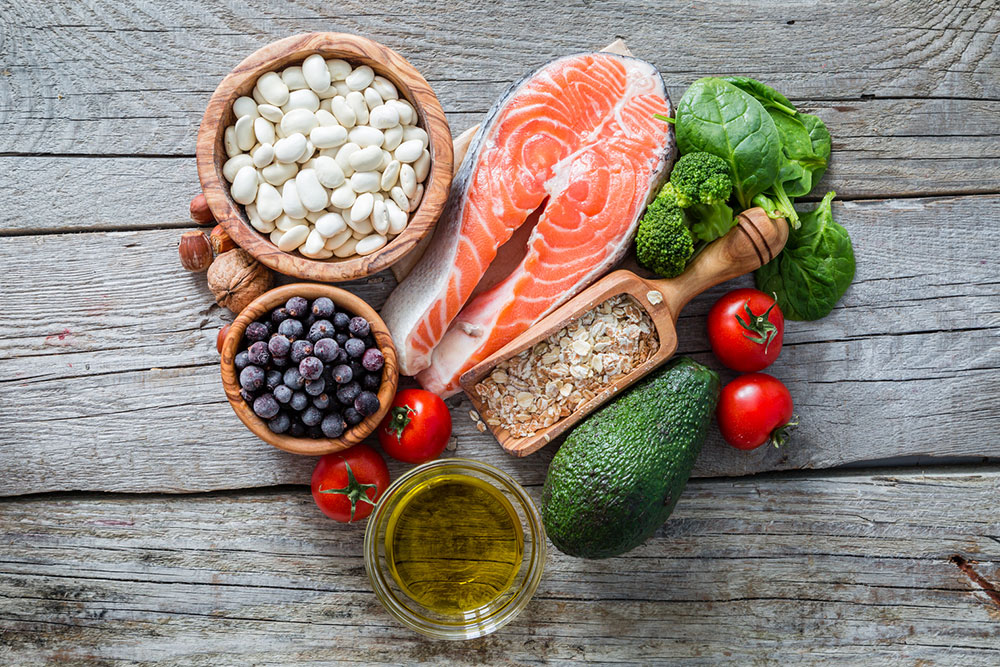
Protein intake should focus on lean sources to support muscle maintenance and overall health without adversely affecting blood sugar. The American Diabetes Association suggests prioritizing fish, poultry such as turkey, and plant-based proteins like beans, lentils, and nuts. Regular consumption of fatty fish like salmon provides omega-3 fatty acids, which contribute to cardiovascular health, a common concern for diabetics. Portion control is crucial for plant proteins due to their calorie density. Limit red and processed meats that are high in saturated fats and sodium, as they elevate health risks.
Fruits and Vegetables
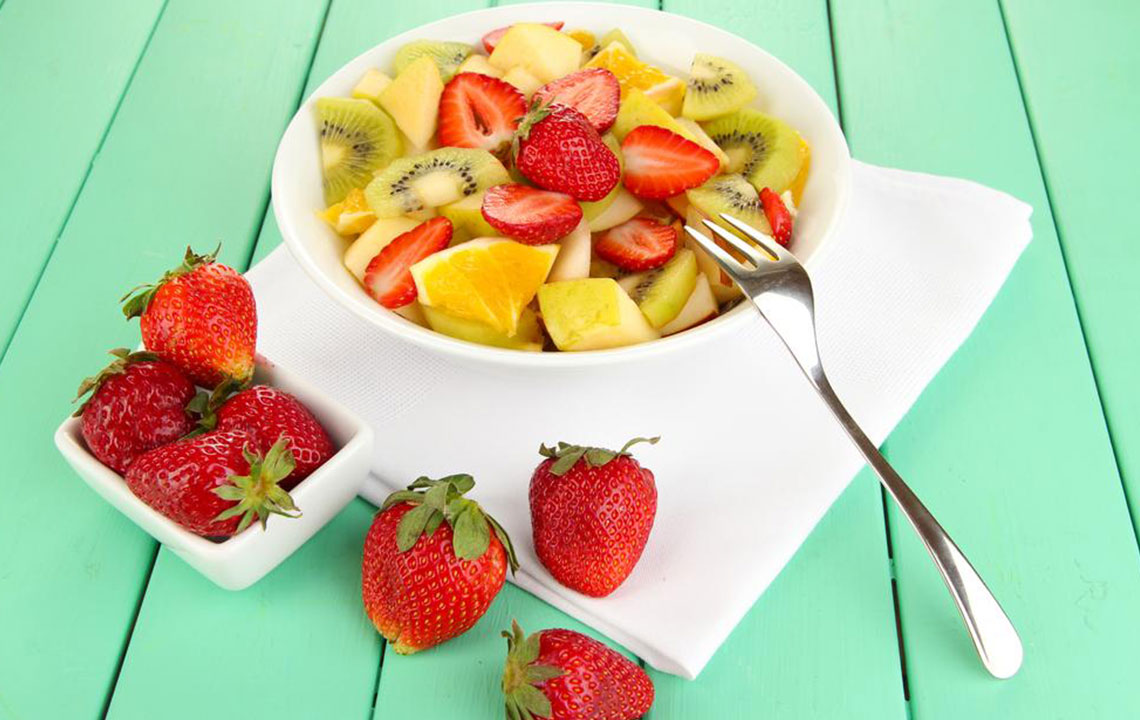
Incorporate a variety of colorful vegetables, especially leafy greens like spinach, kale, and mustard greens, along with cruciferous vegetables such as broccoli, cabbage, and cauliflower. These are low in carbohydrates and high in fiber, vitamins, and antioxidants. Limit starchy vegetables such as potatoes and corn, which can cause blood sugar spikes if consumed in excess. For satisfying sweet cravings, opt for berries like blueberries, strawberries, and raspberries due to their antioxidant and fiber content. Dried fruits like dates or raisins should be avoided or consumed sparingly because of their high sugar content.
Healthy Fats
Consumption of healthy fats plays a vital role in managing diabetes and supporting heart health. Focus on monounsaturated fats found in avocados, nuts like almonds and pecans, and oils such as olive oil and sunflower oil. These fats help improve cholesterol levels and reduce inflammation. Polyunsaturated fats from sources like walnuts and flaxseed are also beneficial. Limit saturated fats present in dairy products like cheese and butter, as well as processed snacks, to prevent cardiovascular risks associated with diabetes. A balanced intake of healthy fats supports overall metabolic health.
Effectively controlling type 2 diabetes demands a comprehensive approach that combines disciplined dietary habits with a healthy lifestyle. Consistent nutrition management helps minimize complications, boosts energy, and contributes to a sustained improved quality of life for diabetics.