Comprehensive Guide to Creating Effective Meal Plans for Managing Diabetes
Discover comprehensive strategies for creating meal plans tailored for diabetes management. This detailed guide covers nutrient balance, food choices, and practical tips to maintain stable blood sugar levels and promote overall health. Learn how to include diverse food groups, manage portions, and adopt healthy habits that empower individuals with diabetes to lead healthier, more energetic lives. Effective meal planning is essential for long-term health, and this article provides the tools and insights necessary to succeed.

Essential Strategies for Designing Diabetes-Friendly Nutrition Plans
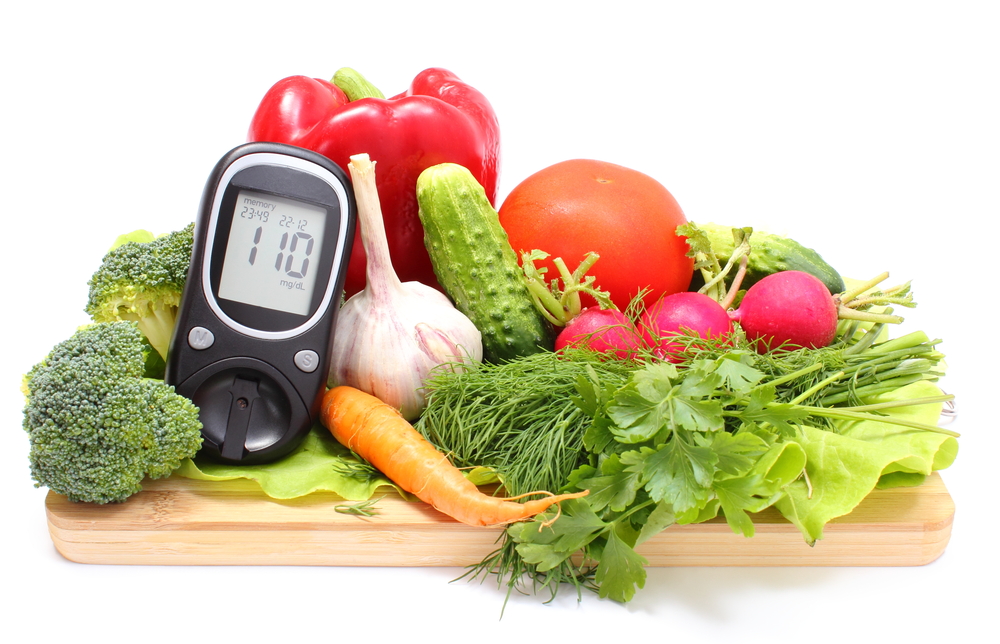
Maintaining optimal health through proper nutrition is a cornerstone for individuals managing diabetes. Your daily dietary choices profoundly impact your overall well-being, influencing blood sugar levels, cholesterol management, blood pressure, and body weight. Diabetes remains one of the most common chronic conditions worldwide, and effective dietary management is key to controlling the disease and improving quality of life. Unfortunately, many individuals fall into the trap of consuming processed or unhealthy foods, which can lead to complications and deteriorate health.
Developing a well-balanced, nutritious meal plan specifically tailored for diabetics is not only essential for blood glucose regulation but also promotes general health. In this comprehensive guide, we explore practical strategies for creating meal plans that empower individuals with diabetes to make healthier choices, enjoy diverse foods, and maintain an active, fulfilling lifestyle. The goal is to help you understand the importance of balanced nutrition, identify foods that support blood sugar stability, and adopt habits that simplify managing your condition effectively.
Understanding Carbohydrates and Their Role
Carbohydrates are fundamental in managing blood glucose levels because they directly influence insulin needs. Careful carbohydrate management is vital for diabetics, especially when planning meals. Choosing the right types of carbs can make a significant difference. Healthy sources include fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes. These foods provide essential nutrients, fiber, and sustained energy release, which help regulate blood sugar levels more effectively.
Avoid foods high in refined sugars, syrups, and processed carbs that cause rapid blood sugar spikes. Reading nutrition labels is crucial to identify hidden sugars and understanding portion sizes helps maintain steady blood glucose. Incorporating complex carbs rather than simple sugars into your diet ensures better overall control and provides lasting energy.
Incorporating Proteins for Satiety and Stability
Proteins are indispensable for preserving muscle mass, supporting immune health, and providing a feeling of fullness without causing blood sugar spikes. They are an excellent component of a diabetes-friendly diet. Sources include lean meats, poultry, fish, eggs, beans, lentils, nuts, and seeds. When planning meals, keep protein portions controlled to avoid excess calorie intake and weight gain.
It's also important to exercise caution with protein supplements and shakes, especially for type 2 diabetics, as they can influence insulin demands. Always consult healthcare professionals before making significant dietary changes.
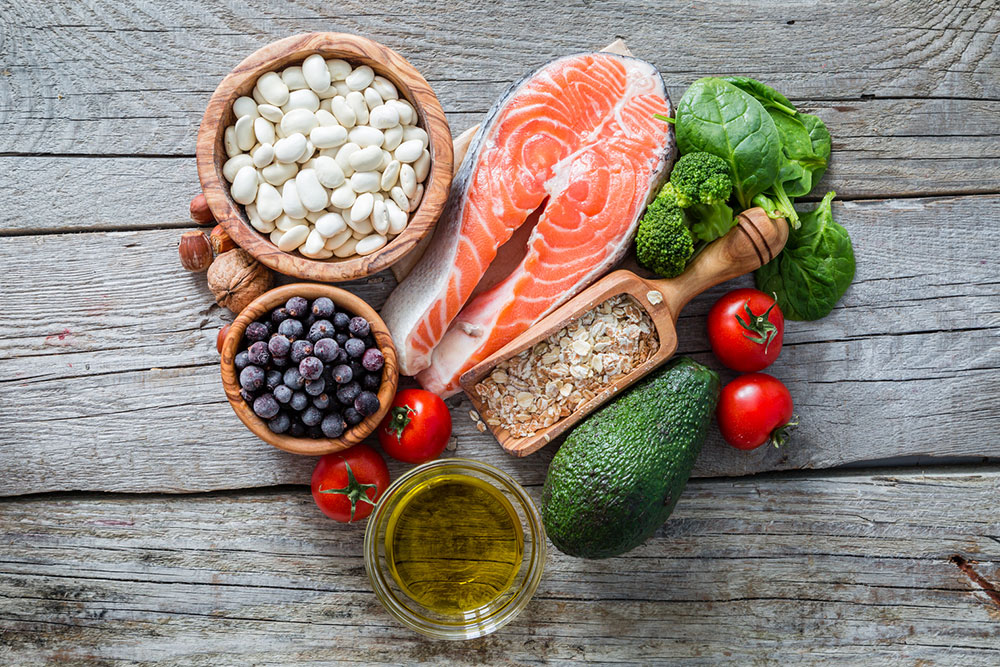
Healthy Fats for Heart and Blood Sugar Health
Healthy fats, such as those found in fatty fish like salmon and mackerel, extra-virgin olive oil, avocados, and nuts, play a critical role in a balanced diet for diabetics. These fats support cardiovascular health, improve blood lipid profiles, and aid in blood sugar regulation. Incorporate these fats into your meals to enhance overall health, always choosing moderation to avoid excessive calorie intake.
The Five Essential Food Groups in a Diabetes-Friendly Diet
Contrary to some beliefs, diabetics do not have to give up tasty or satisfying foods. Instead, the focus should be on balanced consumption from all five food groups to ensure nutrient adequacy and variety:
Fruits — Preferably fresh, seasonal, and consumed in moderation due to natural sugars.
Vegetables — Non-starchy types are especially beneficial for blood sugar management.
Meat and Plant-Based Proteins — Lean meats, poultry, fish, beans, lentils, and plant-based options.
Milk and Dairy Alternatives — Choose low-fat or unsweetened versions to limit saturated fats and sugar intake.
Whole Grains and Starchy Foods — Such as brown rice, quinoa, oats, and sweet potatoes, providing fiber and essential nutrients.
Guidelines for Healthy Eating Habits
Adopting consistent mealtime routines and making informed food choices makes managing diabetes much easier. Here are practical tips to help you customize your diet:
Work with a registered dietitian or diabetes educator to develop personalized meal plans that meet your individual needs.
Focus on nutrient-dense foods—high in vitamins, minerals, and fiber, yet low in unhealthy fats, sugars, and salt.
Prioritize seasonal fruits and fresh vegetables, which often contain more nutrients and flavor.
Maintain consistent meal times—ideally every 4-6 hours—to prevent blood sugar fluctuations and avoid overeating.
Incorporate high-fiber foods such as legumes, whole grains, fruits, and vegetables to slow glucose absorption.
Limit intake of added sugars by reading labels carefully and choosing natural sweeteners or sugar substitutes when necessary.
Stay well-hydrated with calorie-free beverages like water, herbal teas, or black coffee, avoiding sugary drinks that cause insulin spikes.
Foods and Substances to Limit or Avoid
To optimize health and blood sugar control, certain foods should be consumed sparingly or avoided altogether:
Skipping Meals — can cause dramatic blood sugar dips or spikes later on.
Foods high in unhealthy fats and heavy, fried, or greasy options.
Salt-rich snacks like chips and processed foods, which can lead to hypertension.
Foods with added sugars, including candies, jams, honey, and sweetened beverages like sodas.
Refined carbs present in white bread, pastries, and many processed foods.
Saturated and trans fats found in butter, palm oil, coconut oil, and some baked goods.
Key Takeaways for Effective Meal Planning
Preparing your meals ahead of time with a focus on variety ensures that your diet remains balanced and your blood sugar levels stay stable. Meal planning reduces impulsive eating and helps you stick to your dietary goals, making managing diabetes less stressful and more sustainable.
Final Thoughts and Benefits of Structured Meal Plans
Implementing a thoughtfully designed, structured diabetic meal plan can lead to significant improvements in blood sugar control, energy levels, and overall health. While the initial adjustments may require effort, the long-term benefits—like fewer health complications, better weight management, and improved wellbeing—are well worth the investment. Follow these guidelines to develop a sustainable eating routine that supports your health and empowers you to live actively and confidently with diabetes.