Effective Strategies for Managing Type 2 Diabetes: A Comprehensive Guide
This comprehensive guide offers in-depth strategies for managing Type 2 diabetes effectively. It covers the basics of the condition, recognizing symptoms, and practical lifestyle changes including diet, exercise, and medication adherence. Empower yourself with knowledge and tools to control blood sugar levels and improve overall health, ensuring a better quality of life despite the challenges posed by diabetes.

In-Depth Approaches to Managing and Living with Type 2 Diabetes
Are you recently diagnosed with Type 2 diabetes or caring for someone who is? Navigating this condition can bring many questions and concerns about health, lifestyle, and treatment options. While your healthcare professional provides personalized advice, understanding the basics of diabetes, how it affects your body, and the latest management strategies can empower you to take control of your health. This comprehensive guide explores what diabetes entails, its effects on the human body, and effective, modern treatment methods supported by cutting-edge research.
What Exactly is Diabetes?
Diabetes mellitus is a chronic metabolic disorder characterized by the body's inability to regulate blood glucose levels effectively. It exists in several forms, with Type 2 diabetes being the most prevalent, accounting for approximately 90-95% of all cases worldwide. This condition occurs when the body's cells become resistant to insulin or when the pancreas does not produce enough insulin to meet the body's needs. In essence, it results in elevated glucose levels in the blood — a state known as hyperglycemia — which, if left unmanaged, can lead to serious health complications like cardiovascular disease, kidney failure, nerve damage, and vision impairment.
Contrary to common misconceptions, consuming sugar itself isn't inherently harmful; rather, it's the quantity and sources that matter. Healthy sugars derived from naturally occurring sources like fruits and vegetables are essential for maintaining energy and supporting cellular functions. Your brain predominantly relies on glucose— a simple sugar — to fuel cognitive processes. Therefore, cutting out all sugars isn't advisable or necessary; moderation is key. Opting for natural, unprocessed sugars and maintaining a balanced diet helps manage blood sugar levels effectively.
Recognizing the Signs and Symptoms of Diabetes
If you've been diagnosed or suspect you might have diabetes, understanding its symptoms is crucial for early intervention. According to 2014 statistics from the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, nearly 29.1 million Americans are affected by diabetes, underscoring its widespread prevalence. The condition manifests differently in individuals depending on how their body handles insulin and glucose. The core issue lies in insulin — a hormone produced by the pancreas that facilitates the entry of glucose into cells for energy production. When insulin production or efficacy is compromised, blood sugar levels rise, giving rise to the characteristic symptoms:
Excessive thirst and dry mouth
Frequent urination, especially at night
Persistent hunger despite eating
Unusual fatigue and tiredness
Irritability or mood swings
Blurred or impaired vision
Slow wound healing and frequent infections
Being aware of these signs can prompt earlier screening and management, helping prevent severe complications.
Key Approaches to Managing and Living with Type 2 Diabetes
The foundation of managing Type 2 diabetes lies in lifestyle modification and proper medical intervention. Emphasizing healthy habits can significantly influence disease progression and quality of life. Here are the most effective strategies:
1. Dietary Adjustments and Nutrition
Eating a balanced diet tailored to your individual needs is vital. Focus on nutrient-dense foods such as fresh fruits, vegetables, legumes, lean proteins, and whole grains. These foods provide essential vitamins, minerals, fiber, and antioxidants that support overall health and help control blood sugar. Reducing intake of processed foods, sugary snacks, sweetened beverages, and refined grains limits blood glucose spikes and prevents weight gain.
A registered dietitian can help craft a personalized meal plan that accommodates your preferences, lifestyle, and metabolic requirements. Emphasize portion control and mindful eating to avoid overeating, which can destabilize blood sugar levels. Incorporating healthy fats like olive oil, nuts, and seeds further benefits heart health and insulin sensitivity.
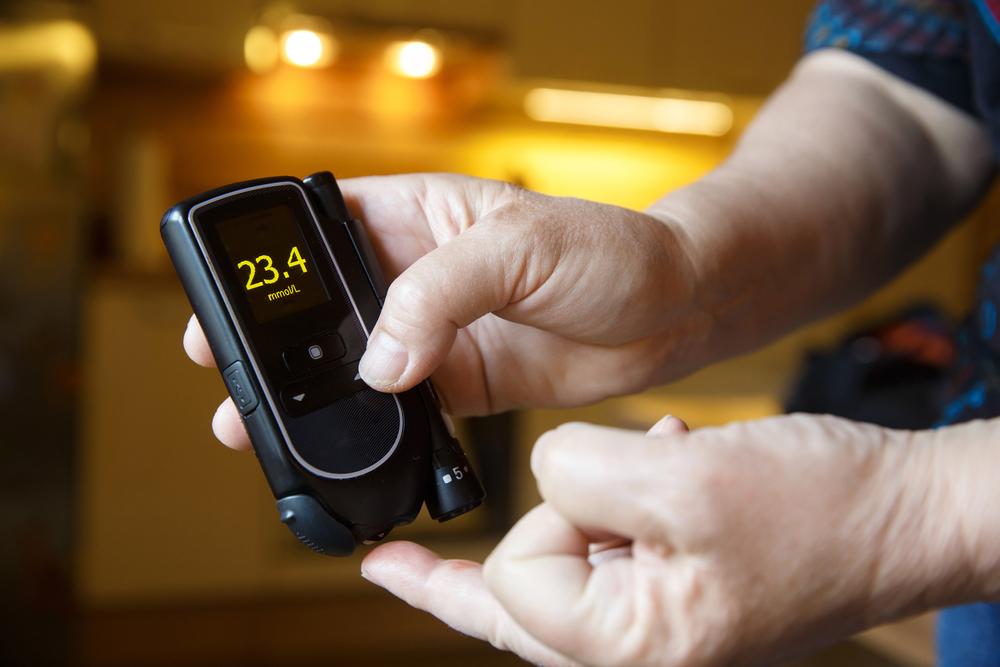
2. Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels
Consistent monitoring of blood glucose is critical in managing diabetes effectively. Using glucometers or continuous glucose monitoring devices enables you to track fluctuations in blood sugar throughout the day. Monitoring helps identify patterns, evaluate the impact of diet and activity, and adjust your management plan accordingly.
If prescribed, medications such as oral hypoglycemics or insulin injections can assist in maintaining target blood sugar ranges. Regular consultation with your healthcare team ensures your treatment remains optimal, especially if adjustments are needed based on your blood glucose readings and overall health status.
3. Physical Activity and Exercise
Engaging in regular physical activity is one of the most effective ways to improve blood sugar regulation, support weight management, and enhance cardiovascular health. Even moderate exercises like brisk walking, cycling, swimming, or yoga for 30 minutes a day can significantly reduce insulin resistance and the risk of developing Type 2 diabetes.
Exercise stimulates muscle cells to absorb glucose independently of insulin, lowering blood sugar levels. Additionally, physical activity boosts mood, increases energy, and helps maintain a healthy weight—all factors that contribute to better disease management.
Creating a consistent exercise routine and gradually increasing intensity are recommended. Always consult your healthcare provider before starting any new physical activity, especially if you have other health conditions.
4. Weight Management
Maintaining a healthy weight is a powerful factor in preventing and controlling Type 2 diabetes. Excess weight, particularly around the abdomen, increases insulin resistance. Losing even a modest amount of weight — 5-10% of your body weight — can lead to significant improvements in blood sugar levels and reduce the need for medications.
Combined with diet and exercise, weight management strategies should be tailored to individual needs. Approaches like behavioral therapy, nutritional counseling, and, in some cases, medical interventions can support sustained weight loss and better glycemic control.
5. Medication and Medical Interventions
While lifestyle changes form the cornerstone of management, some individuals might require medications to keep blood sugar within target ranges. Various classes of drugs, such as metformin, sulfonylureas, or newer agents like SGLT2 inhibitors, work through different mechanisms to improve insulin sensitivity or increase insulin production.
In some cases, insulin therapy may be necessary, especially if oral medications are insufficient. Your healthcare team will determine the best treatment plan based on your blood sugar levels, overall health, presence of complications, and lifestyle considerations. Adherence to prescribed medications, regular check-ups, and continuous education are vital components of effective management.
Conclusion: Empowering Yourself to Manage Diabetes
Living with Type 2 diabetes requires a proactive approach that combines lifestyle modification, regular monitoring, and, when necessary, medical treatment. By adopting a balanced diet, staying physically active, maintaining a healthy weight, and adhering to medical advice, you can effectively control blood sugar, reduce risks, and enjoy a high quality of life. Advances in diabetes research continue to provide new tools and therapies, empowering many to lead healthier, more active lives despite the diagnosis.
Remember, managing diabetes is a lifelong journey. Support from healthcare professionals, family, and community resources plays a crucial role in achieving optimal health outcomes. Stay informed, stay active, and take charge of your well-being every day.