Comprehensive Guide to Managing Type 2 Diabetes Effectively
This comprehensive guide provides detailed strategies for managing Type 2 diabetes effectively. Covering blood sugar monitoring, diet, exercise, medication, and lifestyle changes, it offers valuable insights for those seeking to improve their health. Emphasizing a holistic approach, it helps individuals prevent complications and maintain vitality through informed choices and consistent management.
Comprehensive Strategies for Effective Management of Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes mellitus is a chronic metabolic disorder characterized by high blood sugar levels resulting from the body's ineffective use of insulin. Unlike Type 1 diabetes, where the body's immune system destroys insulin-producing cells, Type 2 diabetes primarily involves insulin resistance and gradual pancreatic beta-cell dysfunction. As one of the most prevalent forms of diabetes worldwide, managing Type 2 diabetes requires a multifaceted approach that includes lifestyle modifications, medication adherence, and regular monitoring to prevent complications and maintain a high quality of life.
Understanding the nature of Type 2 diabetes is crucial for effective management. This condition affects people across all age groups, including children and adolescents, although it is more common in adults, especially those with factors such as obesity, sedentary lifestyles, and genetic predisposition. Recognizing early symptoms and addressing risk factors can significantly improve health outcomes and reduce the risk of severe complications such as cardiovascular disease, neuropathy, nephropathy, and retinopathy.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the various aspects of Type 2 diabetes management, including the underlying causes, symptoms, preventive strategies, and effective treatment plans designed to help individuals lead healthier lives.
Understanding Types of Diabetes
Diabetes mellitus encompasses different types, but the focus here is primarily on Type 2 diabetes due to its high prevalence and unique management needs.
Type 1 Diabetes: In this autoimmune condition, the body's immune system attacks insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas, resulting in little to no insulin production. It generally develops in childhood or adolescence and necessitates lifelong insulin therapy for survival. Managing Type 1 diabetes involves daily insulin injections, continuous blood glucose monitoring, and strict lifestyle management.
Type 2 Diabetes: As the most common form, Type 2 diabetes is characterized by the body's resistance to insulin and a relative insulin deficiency. It can develop at any age but is most often diagnosed in adults. Factors such as obesity, poor diet, physical inactivity, and genetic predisposition significantly increase the risk. Effective management involves a combination of lifestyle changes and medications.
Key signs of Type 2 diabetes include:
Persistent hunger and fatigue
Blurry vision or visual disturbances
Slow-healing cuts or wounds
Frequent urination and infections
Excessive thirst and dry mouth
Over time, unmanaged Type 2 diabetes can lead to serious health issues such as cardiovascular disease, nerve damage, kidney failure, and eye problems. Early diagnosis and consistent management are vital in preventing these complications.
Effective Management Strategies for Type 2 Diabetes
Managing Type 2 diabetes successfully requires an integrated approach involving multiple lifestyle and medical interventions designed to normalize blood sugar levels and improve overall health outcomes.
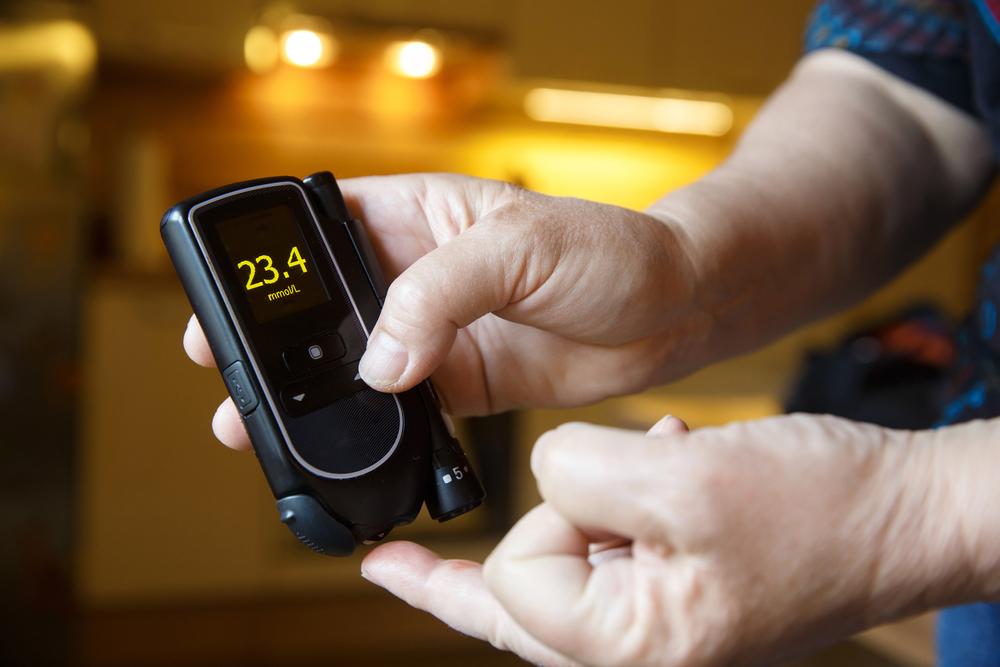
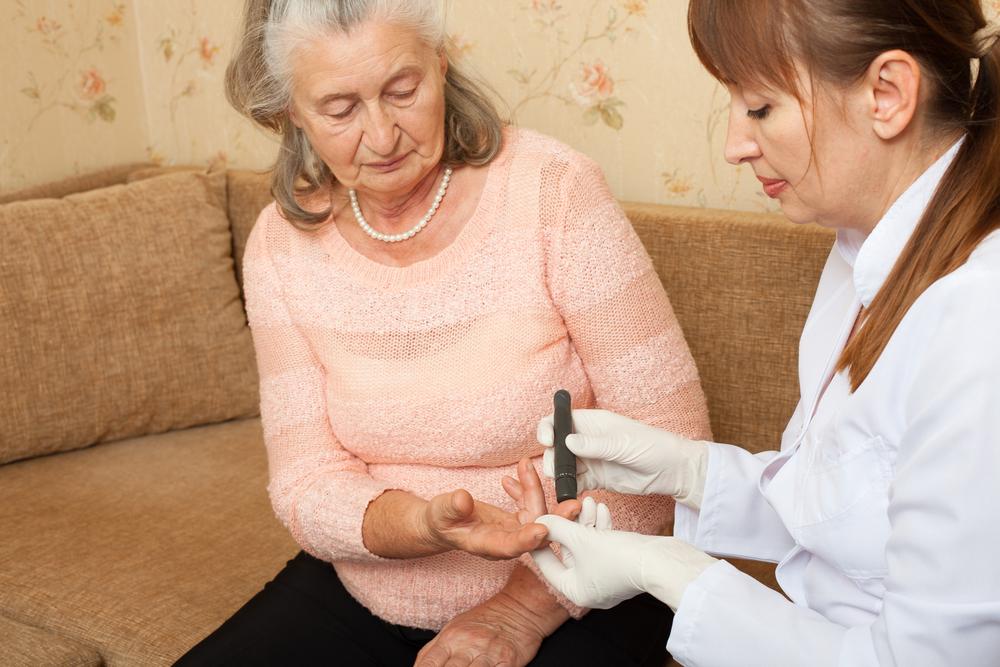
1. Regular Blood Sugar Monitoring
One of the foundational practices in diabetes management is frequent blood glucose testing. Monitoring blood sugar levels helps individuals understand how their body responds to different foods, activities, and medications. It also allows healthcare providers to tailor treatment plans effectively. Using glucometers or continuous glucose monitoring systems (CGMS) provides real-time data that is invaluable for making daily adjustments and preventing hyperglycemia or hypoglycemia.
2. Adopting a Healthy and Balanced Diet
Dietary management plays a crucial role in controlling blood glucose. Emphasizing whole grains, fiber-rich vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats helps stabilize blood sugar levels. Limiting refined sugars, processed foods, and high-carbohydrate snacks prevents unnecessary spikes in blood glucose. Consulting with a registered dietitian can assist in creating personalized meal plans that meet individual health needs and preferences.
3. Engaging in Regular Physical Activity
Exercise is a cornerstone of effective diabetes management. Activities such as brisk walking, swimming, cycling, and strength training improve insulin sensitivity and assist in weight management. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise each week, combined with muscle-strengthening activities on two or more days. Physical activity not only helps control blood sugar but also reduces the risk of cardiovascular diseases and improves mental well-being.
4. Maintaining a Healthy Weight
Weight loss has been shown to significantly improve blood glucose control and reduce the need for medication in many individuals with Type 2 diabetes. Even modest weight reduction through diet and exercise can produce meaningful health benefits. Focused weight management goals should be established in consultation with healthcare professionals to ensure safe and sustainable progress.
5. Medication Adherence and Medical Management
Depending on the severity, healthcare providers may prescribe oral hypoglycemic agents such as metformin, sulfonylureas, or newer classes of medications like SGLT2 inhibitors and GLP-1 receptor agonists. In some cases, insulin therapy may be necessary. It is essential to take medications as prescribed and attend regular check-ups to monitor progress, adjust dosages, and prevent adverse effects.
6. Preventive Care and Lifestyle Changes
Beyond blood sugar control, managing associated risks involves regular screening and preventive measures. This includes managing blood pressure and cholesterol levels, quitting smoking, reducing alcohol intake, and managing stress effectively. Keeping up with eye exams, foot check-ups, and kidney function tests helps catch complications early and maintain long-term health.
Additional Tips for Effective Diabetes Management
Building a supportive environment and adopting sustainable habits are essential for long-term success. Strategies include setting realistic goals, seeking support from family and healthcare teams, and staying educated about diabetes management innovations. Use technology such as mobile apps and online resources to track progress and stay motivated.
In conclusion, managing Type 2 diabetes is a lifelong commitment that benefits greatly from education, lifestyle adjustments, and medical cooperation. By understanding the disease and employing comprehensive management strategies, individuals can lead vibrant, healthy lives while minimizing the risk of complications.