Comprehensive Guide to Effectively Managing a Popliteal Cyst (Baker's Cyst)
A Baker's cyst, or popliteal cyst, is a fluid-filled swelling behind the knee caused by excess synovial fluid often linked to arthritis or injury. While many cysts resolve naturally, persistent cases require management. Treatment options include fluid drainage, physical therapy, medications, and surgery. Conservative methods help reduce swelling and pain, while surgical procedures are reserved for severe cases. Proper diagnosis and personalized treatment by healthcare professionals are vital to restoring knee function and preventing recurrence. This comprehensive guide covers effective strategies for managing a popliteal cyst and improving quality of life.
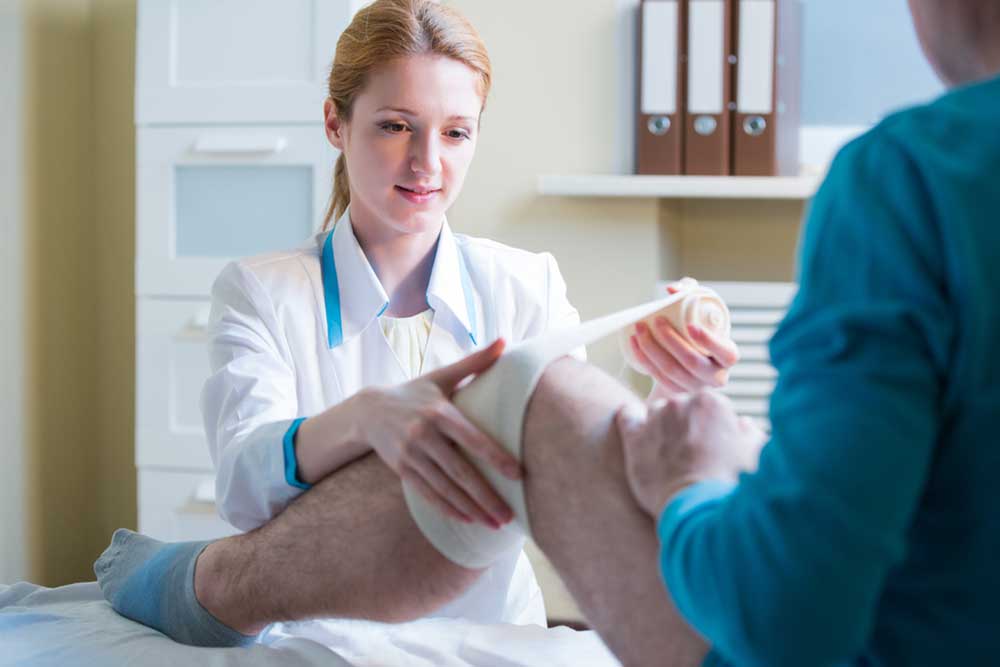
Effective Strategies for Managing a Popliteal Cyst
A popliteal cyst, commonly referred to as a Baker's cyst, is a swelling filled with synovial fluid that forms behind the knee joint. This condition often leads to discomfort, swelling, and mobility issues, impacting daily activities and quality of life. While many cases resolve naturally, understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options is crucial for effective management and recovery.
What Causes a Popliteal Cyst?
A Baker's cyst typically develops due to excess production of synovial fluid within the knee joint. This increased fluid puts pressure on the joint capsule, causing an outpouching or swelling behind the knee. Several underlying conditions can trigger or worsen this process, including osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, joint inflammation, cartilage tears, or other injuries affecting the knee's stability. These conditions often lead to chronic swelling and fluid accumulation, resulting in the formation of the cyst.
How to Effectively Manage a Popliteal Cyst
Although many Baker’s cysts resolve on their own without severe complications, persistent or large cysts, severe pain, or restricted movement may require medical intervention. Proper management involves a combination of conservative treatments, lifestyle modifications, and, in some cases, surgical procedures. Below are of the most common and effective strategies for managing a popliteal cyst:
Fluid Drainage and Aspiration
In cases where the cyst causes significant discomfort or swelling, a healthcare professional can perform percutaneous aspiration, which involves inserting a needle into the cyst guided by ultrasound to remove excess fluid. This minimally invasive procedure offers immediate relief; however, recurrence can happen if the underlying cause remains unaddressed.
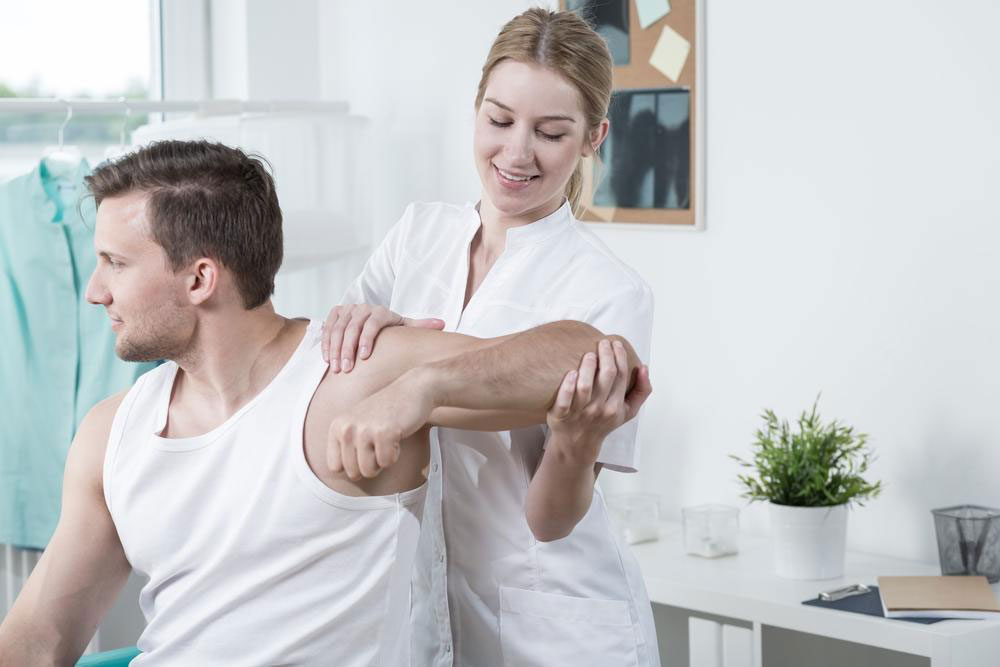
Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation
Engaging in targeted physical exercises helps strengthen the muscles surrounding the knee, improving support and stability. Gentle activities such as walking, swimming, or specialized physical therapy routines can also enhance joint flexibility. Applying cold therapy, like ice packs for 15-20 minutes, helps reduce swelling and inflammation, while compression bandages support the knee and alleviate fluid buildup.
Medications and Injections
To manage pain and inflammation, doctors may administer corticosteroid injections directly into the knee joint. These injections can provide rapid relief and decrease inflammation, making movement easier. Over-the-counter NSAIDs, such as ibuprofen or naproxen, are also recommended to reduce symptoms, but they do not treat the underlying causes of cyst formation. For some patients, combining medications with physical therapy offers the best results.
Surgical Procedures
When conservative treatments fail or in cases of recurrent cysts causing significant pain or joint dysfunction, surgical intervention might be necessary. Arthroscopic surgery allows for the removal of the cyst and repair of associated joint structures. In more severe cases, open surgery may be performed to excise the cyst or address any underlying joint damage. Surgery aims to restore normal knee function and prevent future cyst formation.
It’s important to note that choosing the appropriate treatment depends on several factors, including the size of the cyst, underlying conditions, and the severity of symptoms. Consulting a healthcare professional experienced in musculoskeletal disorders is essential to develop a personalized treatment plan.