Comprehensive Guide to Relieving Back Muscle Pain and Discomfort
Discover comprehensive strategies to effectively relieve back muscle discomfort. Learn about medical options, physical therapies, ergonomic tips, and lifestyle changes to prevent and manage back pain. This detailed guide emphasizes proactive care for lasting back health and improved quality of life.

Comprehensive Strategies for Alleviating Back Muscle Pain and Discomfort
Experiencing sudden or persistent back muscle pain is a common concern affecting individuals across various age groups. Whether it's a sharp ache after a long day at work, a lingering discomfort from improper posture, or pain resulting from injury, back muscle discomfort can significantly interfere with daily activities and overall quality of life. Understanding the underlying causes of this pain and exploring effective management and prevention strategies are crucial for maintaining back health and enhancing well-being.
In today's modern society, factors such as prolonged sitting at desks, frequent heavy lifting, accidents, poor ergonomics, and stress can contribute to back muscle issues. The repercussions of ignoring these symptoms can lead to chronic pain, limited mobility, and in some cases, more serious health complications. Therefore, it is essential to adopt a comprehensive approach to pain relief that includes medical treatments, lifestyle adjustments, and preventative measures.
Over-the-counter non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): Medications like ibuprofen (commonly known by brand names such as Advil or Motrin) are frequently used to mitigate inflammation and provide quick relief from acute or chronic back pain. These drugs are accessible and effective but should be used cautiously, always adhering to recommended doses and consulting healthcare professionals to avoid adverse effects.
Muscle relaxants: When back muscles spasm intensely, doctors may prescribe muscle relaxants to alleviate stiffness and reduce spasms. These medications can enhance comfort and mobility but commonly cause drowsiness and dizziness, so caution should be exercised, especially when driving or operating machinery.
Topical pain relief treatments: Creams, gels, balms, and patches applied directly to the skin are popular for providing localized relief. They work by numbing affected areas and reducing pain temporarily. While they are quick and convenient, they mainly manage symptoms rather than addressing the root cause of the discomfort.
Prescription opioids: In severe cases, especially when other therapies are ineffective, healthcare providers may consider prescribing opioids like Hydrocodone or Codeine. Due to the risk of dependency and other side effects, such medications are used under strict medical supervision and typically for short durations.
Antidepressants and other medications: Certain low-dose antidepressants, including amitriptyline, have shown efficacy in managing chronic back pain, particularly when it is linked with nerve issues or nerve-related pain.
Injections for pain and inflammation: Corticosteroid injections can provide targeted relief by reducing inflammation and numbness in affected areas, especially when pain radiates down the legs (sciatica). These injections are generally part of a broader treatment plan and offer temporary relief.
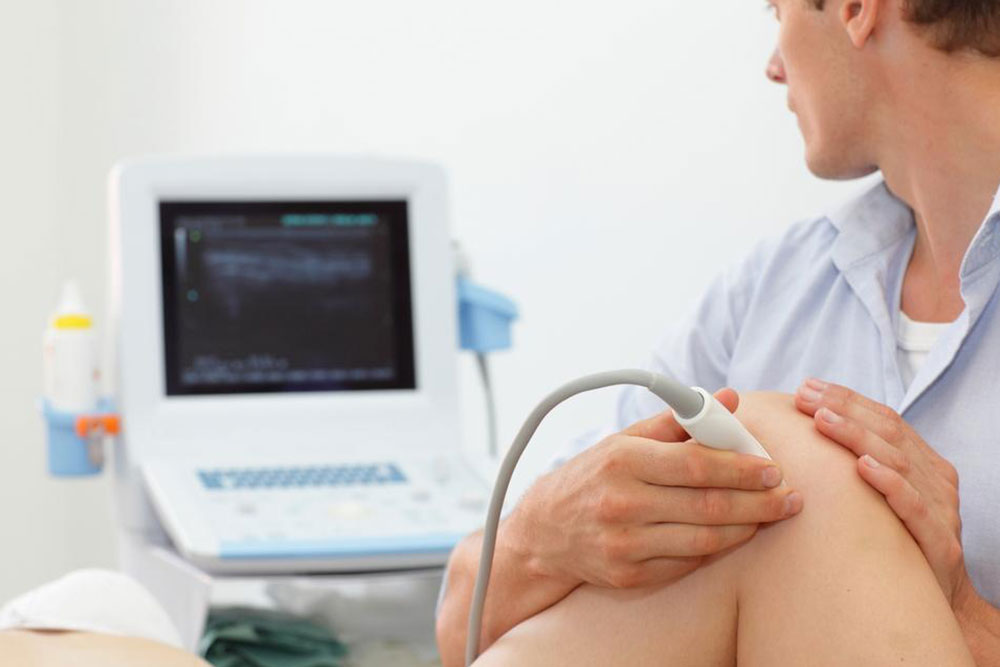
Physical therapy and rehabilitative techniques: Engaging with physical therapists can be highly effective. These professionals employ methods such as ultrasound therapy, heat or cold applications, electrical muscle stimulation, and manual therapy techniques to relieve muscle tension, promote healing, and teach patients exercises to strengthen back muscles and improve posture.
Surgical options: While rarely necessary, surgery may be recommended in cases where severe back pain persists despite conservative treatments or when structural issues, such as herniated discs or spinal stenosis, are identified. Surgical interventions vary depending on the specific condition but are typically considered a last resort.
Preventing back muscle discomfort is equally important. Adopting healthy lifestyle habits can significantly reduce the risk. Maintaining a healthy weight alleviates stress on the spine and muscles, while regular exercise enhances muscle strength and flexibility. Activities like brisk walking, swimming, or specific back-strengthening exercises performed at least 30 minutes daily can improve posture, increase resilience, and prevent injuries.
Practicing proper ergonomics at work and home—such as using ergonomic chairs, adjusting your workstation height, and avoiding prolonged periods of immobility—can prevent strain. Learning correct lifting techniques and avoiding heavy lifting when possible also help protect back muscles from injury.
Additionally, incorporating stretches and core strengthening routines into your daily schedule can optimize back support. Adequate sleep with a supportive mattress and pillow can also influence back health positively.
Ultimately, being proactive about back health involves awareness, timely medical consultation, and lifestyle adjustments. Maintaining an active, healthy life is the most effective way to prevent and manage back muscle discomfort. Remember, early intervention and consistent preventive measures are key to avoiding chronic pain and ensuring mobility and comfort in daily life.
In conclusion, managing back muscle pain requires a multifaceted approach that combines medical treatment, physical activity, ergonomic practices, and lifestyle choices. By understanding the causes and effective strategies for relief, individuals can lead healthier, pain-free lives. Prioritize your back health today—your body will thank you for it!