Comprehensive Non-Surgical Approaches to Alleviate Joint Pain and Improve Mobility
Explore a detailed guide on effective non-surgical strategies to alleviate joint pain and improve mobility. These methods include exercise, medications, support devices, lifestyle changes, and other therapies aimed at managing joint discomfort safely and efficiently. Learn how personalized treatment plans can help you maintain an active lifestyle without resorting to surgery.

Comprehensive Non-Surgical Approaches to Alleviate Joint Pain and Improve Mobility
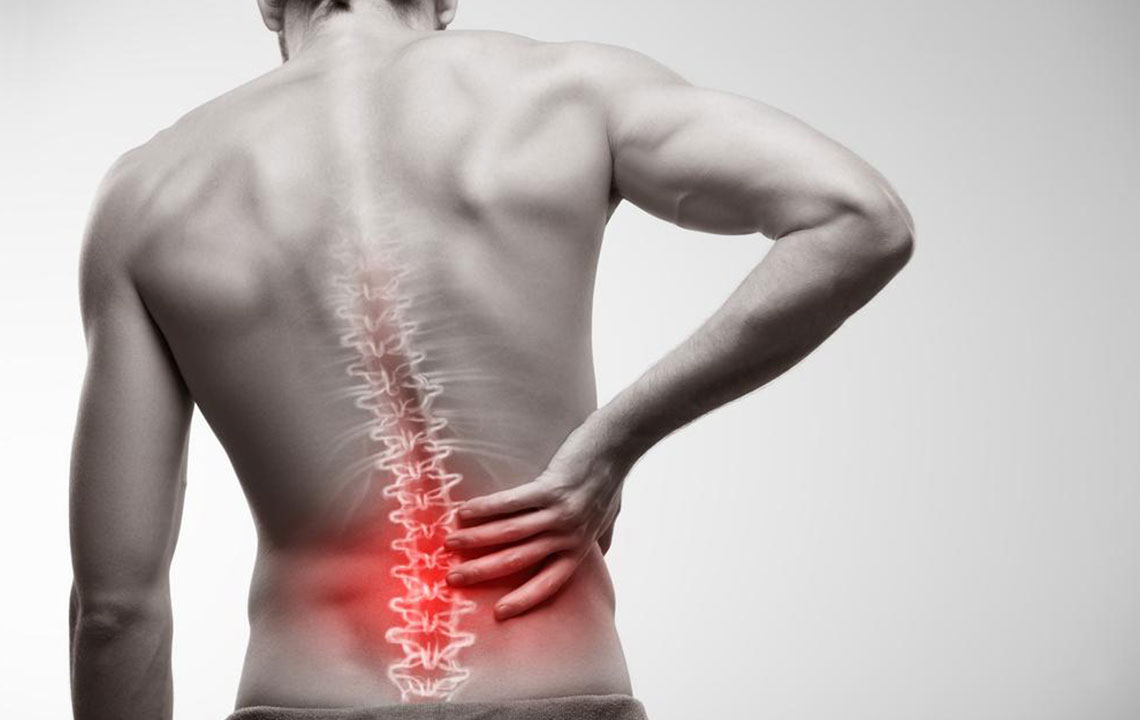
Joint pain and discomfort are common issues affecting people of all ages, often caused by conditions such as osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, sports injuries, ligament strains, or deterioration of cartilage over time. While surgical interventions are sometimes necessary, the majority of patients prefer to explore conservative, non-invasive treatment options first. These methods aim to manage symptoms effectively, reduce pain, and restore joint function, allowing individuals to maintain an active and healthy lifestyle without the risks associated with surgery. Understanding the wide array of available non-surgical strategies can help patients and healthcare providers develop personalized treatment plans that address the specific nature of their joint issues.
Exercise and Physical Therapy
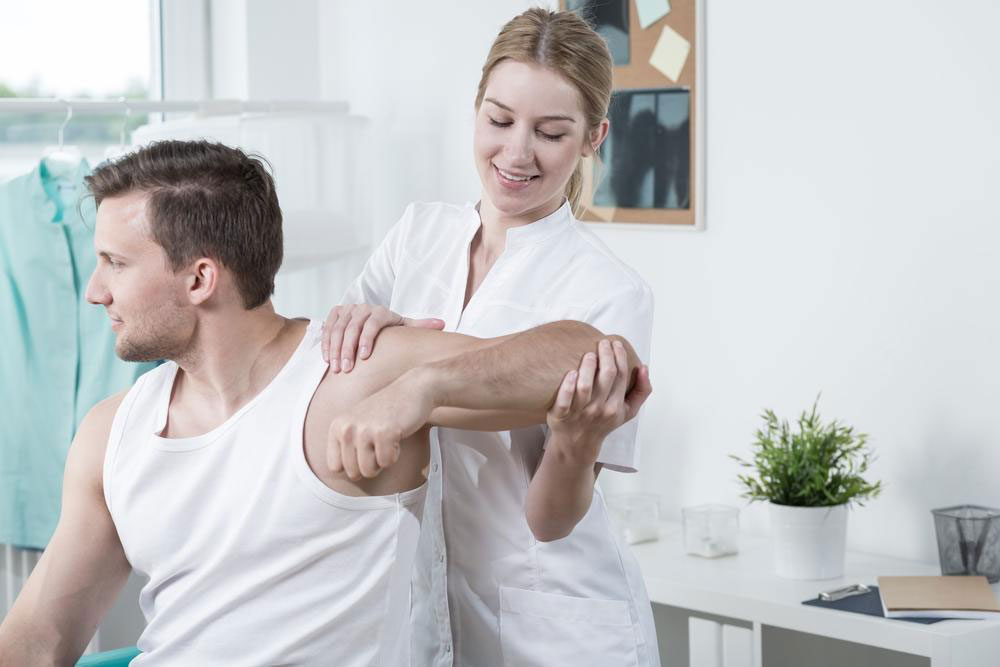
Regular physical activity is a cornerstone of managing joint discomfort, especially in cases of mild to moderate pain. Engaging in low-impact exercises such as walking, swimming, cycling, or tailored physiotherapy routines can strengthen the muscles surrounding the joint, providing better support and stability. Maintaining muscle strength is crucial for reducing joint stress and preventing further damage. Additionally, physical therapy sessions often include targeted stretching, strengthening exercises, nerve stimulation, and manual therapy techniques to enhance flexibility, improve joint mobility, and decrease pain levels. Incorporating heat or cold therapy can also modulate inflammation and alleviate discomfort. Personalized exercise plans designed by physical therapists ensure safety and maximal benefit, empowering patients to proactively manage their joint health.
Medications for Pain and Inflammation Control
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen, naproxen, and aspirin are commonly used to reduce joint pain and mild inflammation. Acetaminophen may also be employed to manage pain without significant anti-inflammatory effects. While these medications can offer quick relief, they should only be used under medical supervision to avoid potential side effects like gastrointestinal irritation, kidney issues, or cardiovascular risks. For some patients, topical NSAIDs or other pain-relief creams may be beneficial as they deliver localized effects with fewer systemic risks.
Support and Stabilization Devices
Support devices such as braces, splints, and orthotic inserts can help stabilize painful joints, correct alignment issues, reduce pressure on affected areas, and improve overall function. These devices are customized according to the specific joint involved and the condition being treated. Proper support can significantly alleviate discomfort during daily activities, prevent further injury, and prolong the lifespan of the joint.
Corticosteroid Injections
For localized inflammation and persistent pain, corticosteroid injections directly into the joint space can provide rapid and often long-lasting relief. These injections, including options like prednisone or methylprednisolone, help diminish inflammation and swelling swiftly. However, repeated use over time should be carefully monitored due to possible adverse effects, such as tissue thinning, joint infection, or systemic impacts like elevated blood sugar levels. These injections are typically part of a broader pain management strategy and should be administered by experienced healthcare professionals.
Weight Management and Lifestyle Modifications
Maintaining a healthy body weight plays a vital role in reducing joint stress, particularly in weight-bearing joints like the knees, hips, and lower back. Excess body weight can accelerate cartilage deterioration and exacerbate pain symptoms. Implementing dietary changes, increasing physical activity, and adopting healthy lifestyle habits can lead to significant improvements in joint health. Besides weight management, other lifestyle adjustments such as avoiding repetitive motions, practicing proper ergonomics, and using assistive devices can help prevent further joint damage and enhance overall quality of life.
Additional complementary therapies including acupuncture, nutritional supplements like glucosamine and chondroitin, and stress reduction techniques such as mindfulness and yoga are also gaining popularity for managing joint discomfort non-surgically. Each individual's condition is unique, so consultation with healthcare professionals is essential to develop a comprehensive, tailored treatment plan that prioritizes safety and efficacy.