Comprehensive Guide to Naturally Lower Your A1C Levels and Improve Diabetes Management
This comprehensive guide offers proven strategies to naturally lower your A1C levels, including personalized management plans, dietary tips, physical activity, stress management, and medical guidance. Maintaining optimal A1C levels is crucial for preventing diabetes complications and improving overall health. Learn effective, practical steps to achieve and sustain healthier blood sugar levels for a better quality of life.

Comprehensive Guide to Naturally Lower Your A1C Levels and Improve Diabetes Management
Effective management of diabetes is essential for maintaining overall health, preventing serious complications, and enhancing quality of life. One of the key indicators used by healthcare professionals to evaluate blood sugar control over time is the A1C test. Regular monitoring and understanding of A1C levels provide crucial insights into how well your diabetes is being managed and help you make informed decisions about lifestyle and treatment adjustments. This comprehensive guide explores what A1C is, its significance, normal ranges, and proven strategies to naturally lower A1C levels for better health outcomes.
Understanding the A1C Test and Its Importance in Diabetes Care
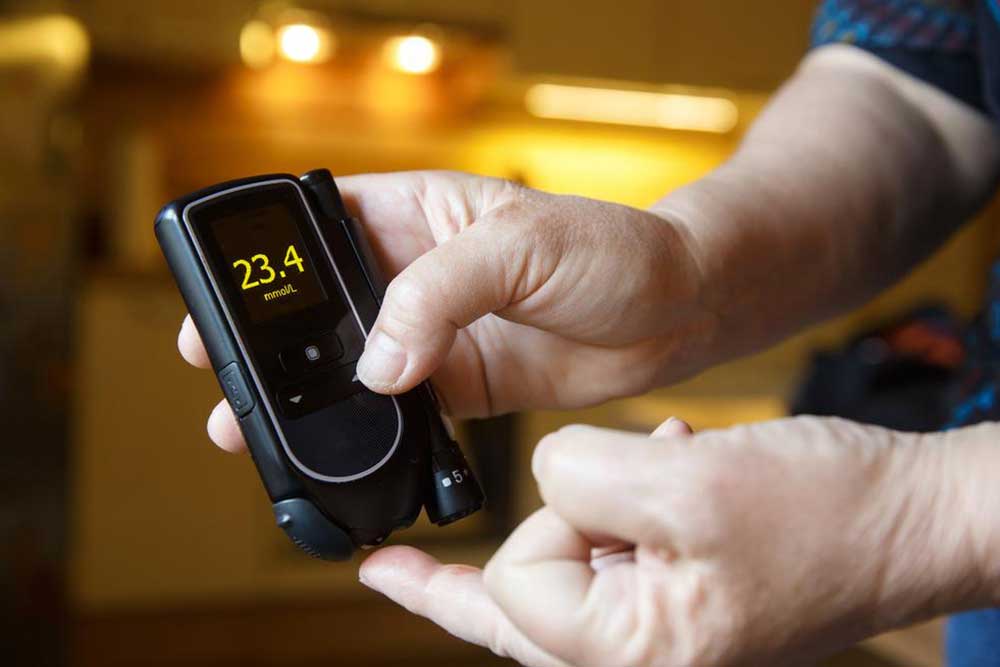
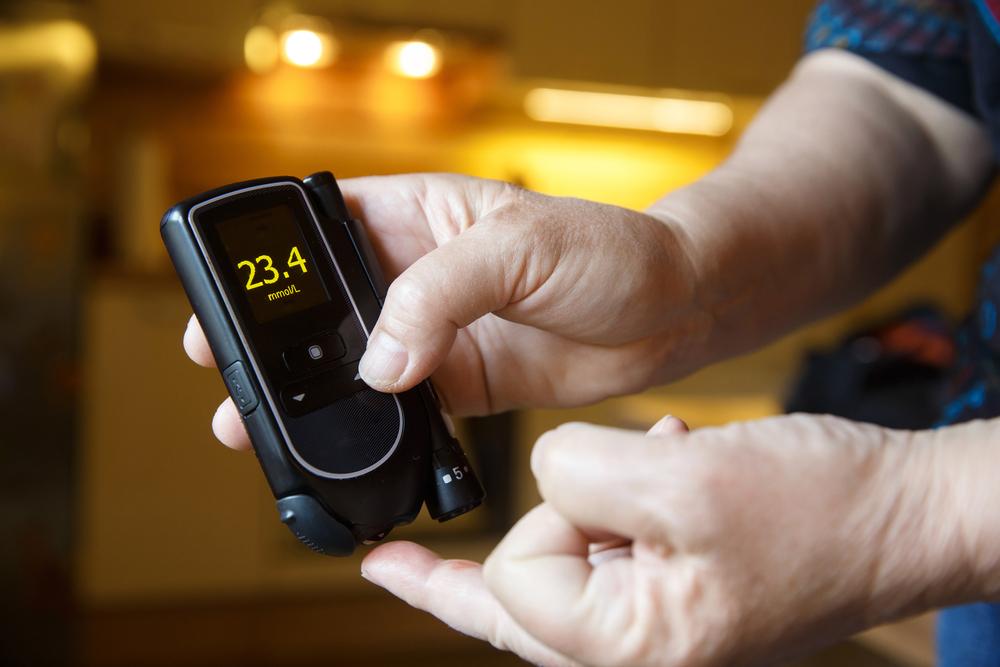
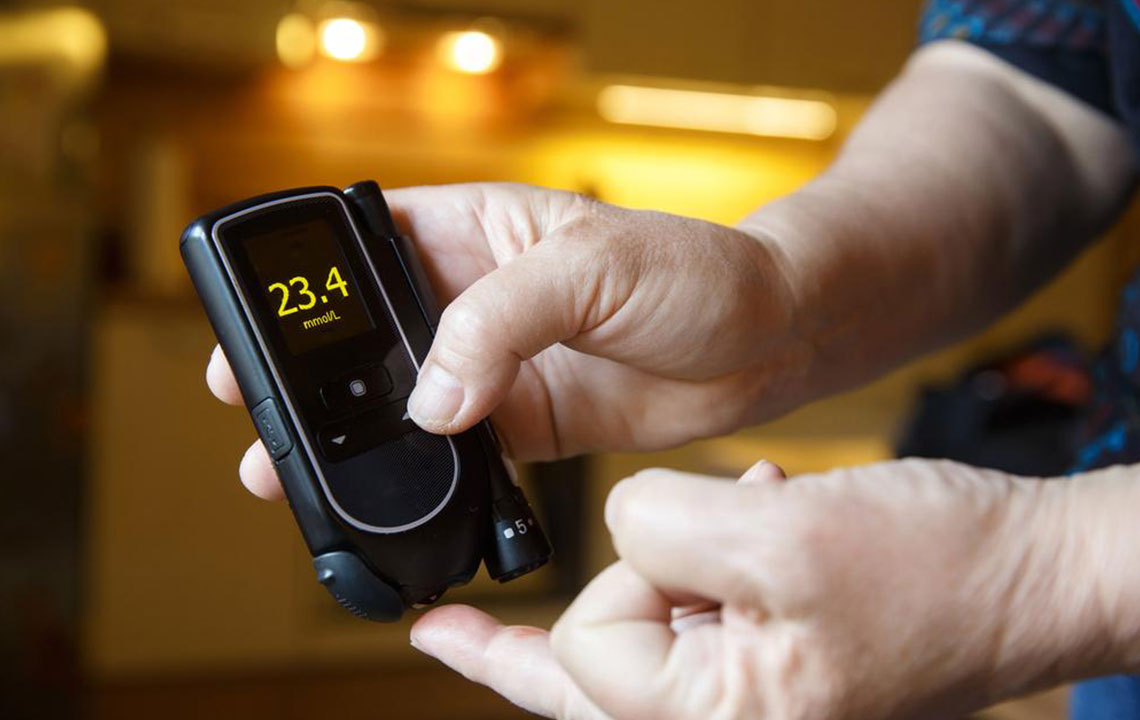
The A1C test, also known as glycated hemoglobin test, measures the percentage of hemoglobin molecules in your blood that have sugar attached to them. Since red blood cells live approximately three months, the A1C provides an average blood glucose level over the past two to three months. This makes it a valuable tool for evaluating long-term blood sugar control rather than just momentary readings. The test results are expressed as a percentage, with higher percentages indicating poorer blood sugar management.
Why Is the A1C Test Essential?
The significance of the A1C test lies in its ability to inform both diagnosis and ongoing management. It helps in detecting prediabetes—a condition where blood sugar levels are elevated but not yet classified as diabetes. Early detection enables timely lifestyle interventions that can halt or delay progression. Moreover, for individuals already diagnosed with diabetes, maintaining target A1C levels reduces the risk of developing complications such as nerve damage, kidney disease, eye problems, and cardiovascular issues.
Interpreting Your A1C Results: What Do the Numbers Mean?
The normal A1C level for individuals without diabetes is below 5.7%. An A1C between 5.7% and 6.4% indicates prediabetes, a warning sign that you're at higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes in the next decade. A measurement of 6.5% or above confirms a diabetes diagnosis. For people managing diabetes, experts generally recommend keeping A1C levels below 7% to minimize the risk of complications. However, individualized targets may vary based on age, health status, and specific conditions, so it's crucial to consult your healthcare provider for personalized goals.
Maintaining optimal A1C levels is a proactive step toward better health, reducing the chance of long-term complications associated with uncontrolled blood glucose.
Practical Strategies to Lower A1C Levels Naturally
If you're looking to improve your blood sugar control and lower your A1C levels, implementing lifestyle changes is a proven and effective approach. Here, we outline comprehensive strategies that can help you achieve healthier A1C levels through natural methods and consistent management practices.
Create a Personalized Diabetes Management Plan
Every individual with diabetes or prediabetes faces unique challenges. Developing a tailored management plan that considers your specific circumstances—such as weight, activity levels, diet preferences, stress levels, and medication regimen—is essential. Collaborate closely with your healthcare team to establish realistic and achievable targets.
Focus on gradual weight loss if overweight or obese, as excess weight significantly impacts blood sugar levels.
Incorporate regular physical activity into your routine, aiming for at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise weekly.
Follow a balanced, nutrient-dense diet rich in vegetables, fruits, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
Implement stress reduction techniques like meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises to prevent stress-induced blood sugar spikes.
Establish a Consistent Routine and Monitor Progress
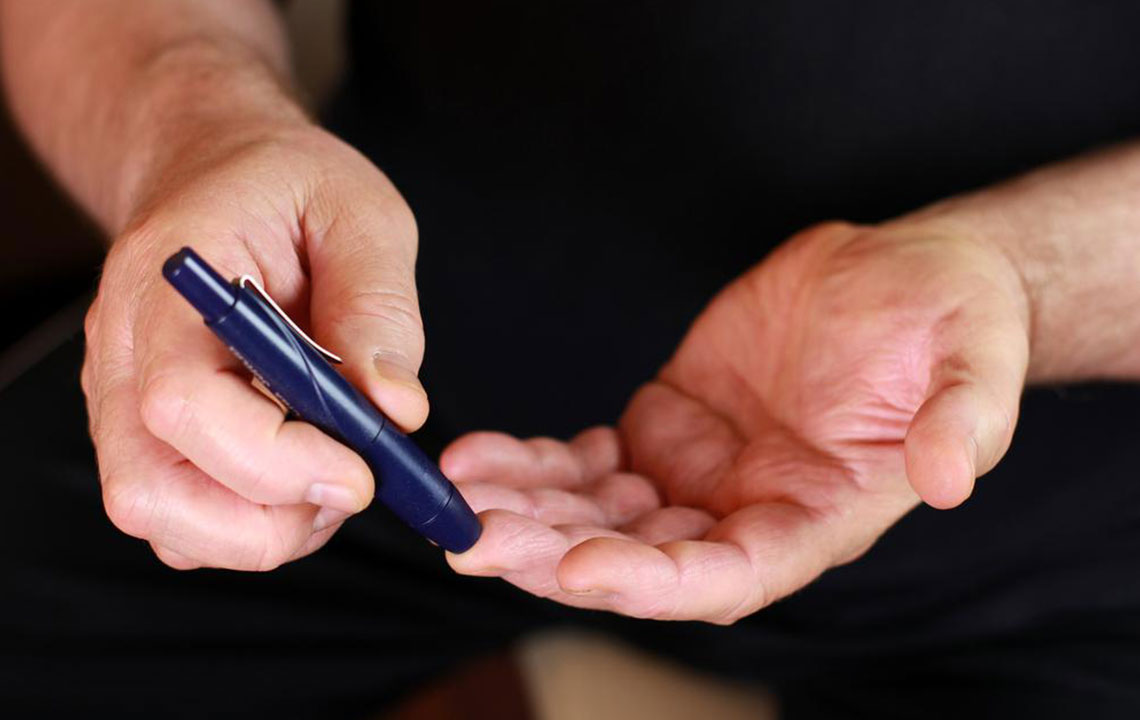
Consistency is key in managing blood sugar levels. Use a glucose monitoring device to track how your body responds to different foods, activities, and stressors. Regular monitoring provides valuable insights and helps you and your healthcare provider adjust your management plan effectively.
Work with your doctor to determine how often to check blood sugar levels and to interpret the results correctly. Keeping a detailed log can help identify patterns and trigger points that influence your A1C.
Adopt a Nutritious Diet with Emphasis on Portion Control
Nutrition plays a vital role in regulating blood sugar. Prioritize non-starchy vegetables such as leafy greens, broccoli, and peppers. Incorporate moderate amounts of fruits, emphasizing berries and apples over high-sugar options. Opt for healthy fats found in nuts, seeds, avocados, and olive oil, which support heart health and promote satiety.
Include quality proteins like fish, poultry, tofu, and legumes. Focus on complex carbohydrates, such as whole grains, brown rice, and sweet potatoes, which release glucose more slowly, preventing sudden spikes. Limit intake of processed foods, sugary drinks, sodas, and refined carbs that contribute to elevated blood sugar levels.
Enhance Physical Activity and Maintain Weight Loss Goals
Regular exercise is one of the most effective ways to improve insulin sensitivity and lower blood sugar. Aim for a mix of aerobic activities—such as brisk walking, cycling, or swimming—and strength training exercises to build muscle mass. Even moderate activity performed consistently can have a lasting impact on A1C levels.
Maintaining a healthy weight through a combination of diet and physical activity significantly enhances your ability to keep blood sugar in check. Consult your healthcare provider for personalized recommendations and to create an exercise plan suitable to your fitness level.
Manage Stress and Prioritize Mental Well-being
Stress triggers the release of hormones like cortisol, which can elevate blood sugar levels. Incorporate relaxation techniques such as mindfulness meditation, yoga, deep breathing, or engaging in hobbies you enjoy. Adequate sleep is also crucial for hormone regulation and blood sugar control.
Limit exposure to stressful situations when possible and develop healthy coping mechanisms to prevent stress-related spikes in blood glucose.
Adjust Medication and Seek Regular Medical Guidance
Medications may be necessary for some individuals to achieve target A1C levels. Always follow your healthcare provider's instructions regarding medication use and timing. Regular check-ups allow your doctor to monitor disease progression and adjust treatment plans accordingly.
Stay informed about new or alternative therapies that could complement your existing regimen. Never alter or stop medications without medical consultation.
In conclusion, lowering your A1C levels naturally involves a combination of lifestyle modifications, consistent monitoring, and medical guidance. Adopting healthy habits, maintaining a balanced diet, staying active, managing stress, and working closely with your healthcare team can significantly improve your blood sugar control and overall health. Remember, proactive management today can prevent serious health issues in the future. Always consult your doctor before making significant lifestyle changes or starting new treatments to ensure your approach is safe and effective.