Comprehensive Guide to Causes and Signs of Type 2 Diabetes: Prevention and Management
This comprehensive article explores the main causes and symptoms of type 2 diabetes, emphasizing the importance of early detection and lifestyle modifications. It discusses genetic, lifestyle, and environmental factors contributing to insulin resistance. The piece highlights key signs like thirst, fatigue, hunger, vision changes, and poor wound healing, guiding readers on when to seek medical advice. By understanding these aspects, individuals can better prevent or manage type 2 diabetes, reducing the risk of long-term health issues through proactive health strategies and treatments.

In-Depth Exploration of the Causes and Symptoms of Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is a prevalent chronic health condition characterized by the body's ineffective use of insulin, leading to elevated blood glucose levels. Unlike type 1 diabetes, which is typically diagnosed in childhood, type 2 usually develops in adults but is increasingly seen in younger populations due to lifestyle factors. Managing this condition effectively is crucial to preventing long-term health complications such as cardiovascular disease, kidney failure, nerve damage, and vision loss.
This illness does not have a definitive cure at present, but with proper management—including lifestyle modifications and medication—individuals can achieve good control over their blood sugar levels and lead healthy lives. Early diagnosis and intervention are essential to mitigate the severity of the disease and prevent irreversible damage.
The Root Causes of Type 2 Diabetes: The development of type 2 diabetes is multifactorial. Central to its pathogenesis are insulin resistance—where the body's cells become less responsive to insulin—and a progressive decline in insulin production by the pancreas. While these core mechanisms are well established, the triggers and contributing factors are still being studied. Nonetheless, several key elements significantly influence the risk of developing the disease:
Genetics: Family history plays an important role. If close relatives have diabetes, the likelihood of inheriting genetic predispositions increases.
Obesity: Excessive body fat, especially stored around the abdomen, contributes to increased insulin resistance.
Physical Inactivity: Sedentary lifestyles reduce muscle activity that aids in glucose utilization, raising blood sugar levels over time.
Unhealthy Diet: Diets high in refined sugars, saturated fats, and processed foods exacerbate insulin resistance.
Other Factors: Age, certain ethnicities, and conditions like hypertension and high cholesterol also elevate risk.
Understanding these causes underscores the importance of lifestyle adjustments and early screening to prevent or delay the onset of diabetes.
Proactive management of risk factors can significantly delay or even prevent the progression of type 2 diabetes. Interventions such as maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in regular physical activity, and adopting a balanced diet are foundational in this effort.
Identifying the Symptoms of Type 2 Diabetes: Since symptoms often develop gradually, many individuals remain unaware during the early stages of the disease. Recognizing these signs is vital for prompt diagnosis and treatment to prevent complications.
Persistent Thirst and Frequent Urination: Elevated blood sugar causes kidneys to work harder to filter and absorb excess glucose, leading to dehydration and increased urination.
Chronic Fatigue: Without effective glucose uptake by cells, energy levels decline, resulting in constant tiredness.
Increased Hunger and Possible Weight Loss: Cells deprived of glucose signal the body to seek energy sources, leading to heightened appetite. Concurrently, weight loss may occur as the body begins burning fat stores.
Blurred Vision: High blood glucose levels cause fluid to seep into the eyes' lenses, distorting vision.
Impaired Healing and Increased Infections: Elevated blood sugar hampers immune function and delays wound healing, increasing susceptibility to infections.
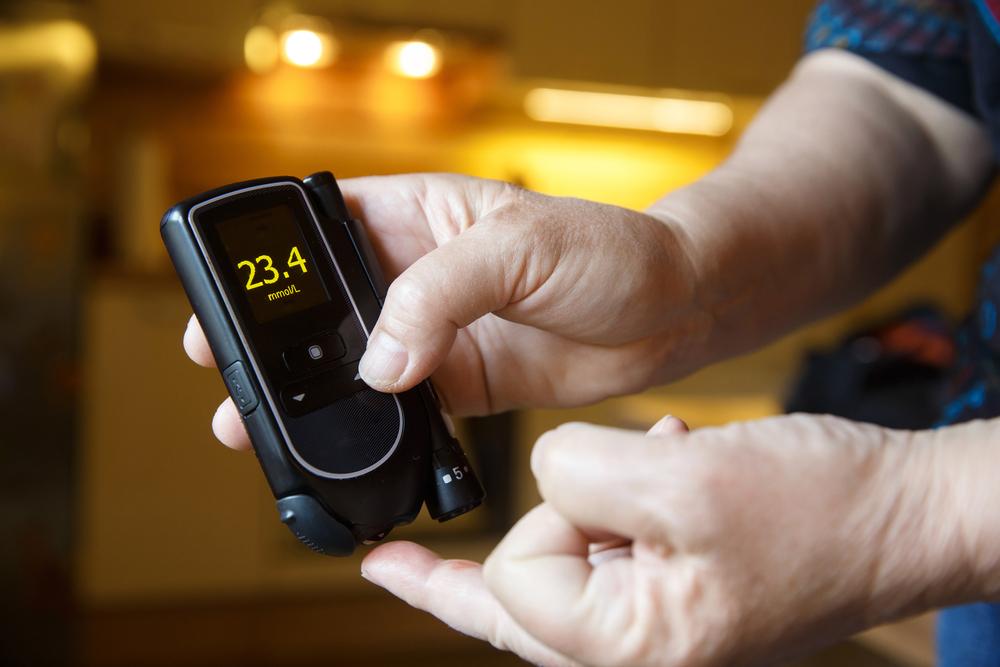
If you notice any two or more of these symptoms, it is strongly advised to consult a healthcare professional for evaluation. The diagnosis typically involves blood tests such as fasting blood sugar, HbA1c, and oral glucose tolerance tests.
Effective management of type 2 diabetes hinges on a combination of medication—such as oral hypoglycemics or insulin therapy—and lifestyle modifications. Emphasizing a nutritious diet, regular physical activity, weight management, and routine monitoring can help maintain blood sugar within a target range and prevent the onset of severe complications.