Comprehensive Guide to Type 2 Diabetes: Understanding Causes, Symptoms, and Effective Management Strategies
This comprehensive guide explores type 2 diabetes, focusing on its causes, early symptoms, risk factors, potential complications, and effective management strategies. By understanding these aspects, individuals can take proactive measures to prevent or control the disease, reducing serious health risks. The article emphasizes lifestyle changes, medication options, and the importance of early diagnosis, offering valuable insights for patients and caregivers alike to maintain long-term health and quality of life.

Comprehensive Guide to Type 2 Diabetes: Understanding Causes, Symptoms, and Effective Management Strategies
Type 2 diabetes mellitus is a prevalent and chronic metabolic disorder that affects millions of individuals globally. It poses significant health challenges due to its complex nature involving multiple factors that impair the body's ability to regulate blood sugar effectively. Unlike type 1 diabetes, which is often diagnosed during childhood and results from autoimmune destruction of insulin-producing cells, type 2 diabetes typically develops gradually over years, predominantly affecting adults, though increasing rates among children and adolescents have been observed in recent years. Recognizing the underlying causes, early symptoms, potential complications, and management options is vital for long-term health preservation and quality of life.
Understanding the pathophysiology of type 2 diabetes reveals that it is characterized by insulin resistance—a condition where the body's cells do not respond properly to insulin—and eventual insulin deficiency. As a result, glucose accumulates in the bloodstream, leading to hyperglycemia. This interplay is influenced by genetic predisposition, lifestyle choices, and environmental factors. Despite the absence of a definitive cure, proper management through medication, lifestyle modifications, and regular monitoring can significantly reduce the risk of developing severe complications such as cardiovascular disease, nerve damage, kidney failure, and vision loss.
Early identification and intervention are crucial. Recognizing subtle symptoms such as blurred vision, persistent fatigue, unexplained weight loss, and increased thirst can prompt timely medical evaluation. Many individuals remain asymptomatic in the early stages, which underscores the importance of routine screening, especially for those with high-risk factors.
Signs and Symptoms of Type 2 Diabetes
Individuals with early or unmanaged type 2 diabetes may exhibit a variety of symptoms, often subtle and easy to overlook. These symptoms include:
Blurred or fluctuating vision due to changes in blood sugar levels and fluid balance within the eyes
Persistent fatigue and low energy levels impacting daily activities
Significant mood swings, irritability, or feelings of depression
Unexpected weight loss despite increased appetite
Increased hunger sensations, often accompanied by a desire to eat more
Frequent urination, especially during the night, indicating the kidneys' attempt to eliminate excess glucose
Excessive thirst and dry mouth resulting from dehydration caused by urination
Worsening eyesight or sudden difficulty seeing clearly
Understanding these symptoms and acting promptly can prevent escalation and assist in effective management.
When to Seek Medical Advice
If you experience any of the above symptoms, especially in combination, it is essential to seek medical attention promptly. Early diagnosis not only facilitates better control of blood glucose levels but also reduces the risk of developing irreversible complications. Regular health check-ups, blood sugar monitoring, and consultation with healthcare providers are recommended for individuals with risk factors.
Timely medical consultation enables personalized treatment plans that may include lifestyle interventions, medications, or combination approaches tailored to individual needs.
Risk Factors Increasing the Likelihood of Developing Type 2 Diabetes
Several factors contribute to an individual's susceptibility to type 2 diabetes. These include:
Family History: Having close relatives with diabetes significantly increases risk, indicating genetic predisposition.
Genetic Factors: Certain gene variants are linked to insulin resistance and impaired glucose metabolism.
Geographical and Ethnic Variations: The prevalence is higher among certain populations, particularly those originating from South Asia, Africa, the Middle East, and Native American communities. Additionally, living farther from the equator has been correlated with increased risk, potentially tied to vitamin D deficiency and environmental influences.
Obesity and Sedentary Lifestyle: Excess body weight, especially abdominal fat, impairs insulin sensitivity. Lack of physical activity exacerbates the risk.
Unhealthy Diet: Diets high in processed sugars, saturated fats, and low in fiber contribute to obesity and insulin resistance.
Other Factors: Age (especially over 45), high blood pressure, and abnormal cholesterol levels further elevate risk.
Potential Long-Term Complications of Uncontrolled Diabetes
If left unmanaged or poorly controlled, type 2 diabetes can cause a multitude of health issues, impacting almost every organ and system of the body. The chronic hyperglycemia damages blood vessels and nerves, leading to:
Cardiovascular diseases such as coronary artery disease, heart attacks, and strokes
Paresthesia, numbness, and pain due to peripheral nerve damage
Progressive kidney impairment, potentially resulting in chronic kidney disease or failure
Retinopathy, which can cause vision loss or blindness
Foot ulcers, infections, and risk of amputations due to poor wound healing and nerve damage
Skin infections and slow healing processes
Oral health issues like gum disease and periodontal infections
Complications during pregnancy, including gestational diabetes and increased risk of birth complications
Management and Treatment Strategies
Although type 2 diabetes is chronic, effective management can help maintain blood glucose levels within target ranges and prevent complications. The primary pillars of treatment include lifestyle modifications, medications, and regular health monitoring.
Medication Options
Depending on individual needs, healthcare providers may prescribe several types of medications:
Oral Hypoglycemics: Drugs like metformin, sulfonylureas, DPP-4 inhibitors, and SGLT2 inhibitors help improve insulin sensitivity and reduce glucose production by the liver.
Injectable Medications: These include GLP-1 receptor agonists and insulin therapies for those with significant insulin deficiency or resistance.
Insulin Therapy: Various insulin formulations—including rapid-acting, short-acting, intermediate-acting, and long-acting insulins—are used based on blood sugar patterns and lifestyle needs.
Combination Treatments: Some therapies combine multiple agents to synergistically control blood sugar more effectively.
Lifestyle Modifications
Alongside medications, lifestyle changes are critical for managing type 2 diabetes:
Adopting a balanced, carbohydrate-controlled diet rich in fiber, lean proteins, and healthy fats
Engaging in regular physical activity, such as brisk walking, swimming, or cycling
Maintaining a healthy weight through diet and exercise
Practicing stress reduction techniques and ensuring adequate sleep
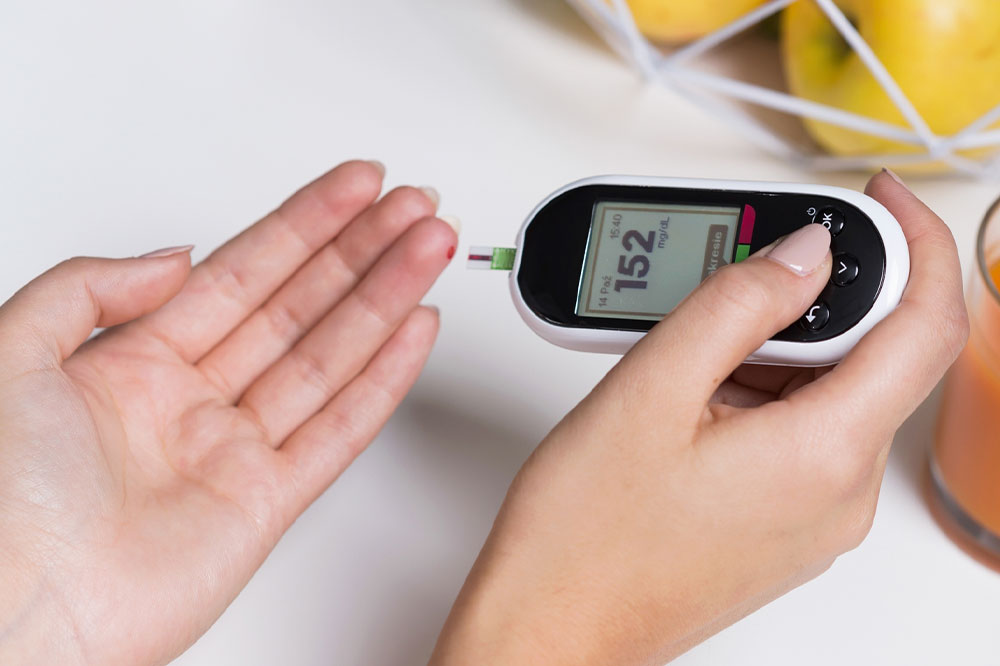
Monitoring blood glucose levels routinely to assess control
Preventive Measures and Regular Screening
Preventive strategies are especially important for individuals with risk factors but no symptoms. Regular screening tests such as fasting blood glucose, HbA1c, and oral glucose tolerance tests can detect prediabetes and early-stage diabetes, enabling prompt intervention.
The Future of Managing Type 2 Diabetes
Advancements in medical research, including continuous glucose monitoring devices, artificial pancreas systems, and personalized medicine, are promising for improving disease management. Education and early intervention remain key components of reducing the global burden of type 2 diabetes.
Ultimately, understanding the multifaceted nature of type 2 diabetes empowers individuals to take proactive steps towards health optimization. Through comprehensive management strategies and lifestyle modifications, many can lead healthy, fulfilling lives despite the challenges posed by this condition.