Comprehensive Guide to Effectively Managing Blood Sugar Levels for Better Health
This comprehensive guide provides in-depth insights into managing blood sugar levels effectively. It covers normal ranges, lifestyle strategies, dietary recommendations, and when to seek medical advice, helping individuals maintain metabolic health and prevent diabetes-related complications.

Comprehensive Guide to Effectively Managing Blood Sugar Levels for Better Health
Maintaining optimal blood sugar levels is crucial for overall health and well-being. Fluctuations in blood glucose are natural throughout the day, influenced by various factors such as diet, physical activity, stress levels, and underlying health conditions. Understanding how to monitor and regulate these levels can prevent serious health complications and lead to a healthier lifestyle. This extensive guide provides detailed insights into managing blood sugar effectively, encompassing practical strategies, dietary recommendations, and important medical considerations.
Blood sugar, or blood glucose, is the primary source of energy for the body's cells. It originates mainly from carbohydrates in the foods we eat, and maintaining it within a healthy range is essential for energy balance and metabolic health. Healthy blood glucose regulation helps prevent conditions such as diabetes mellitus, hypoglycemia, and other metabolic disorders.
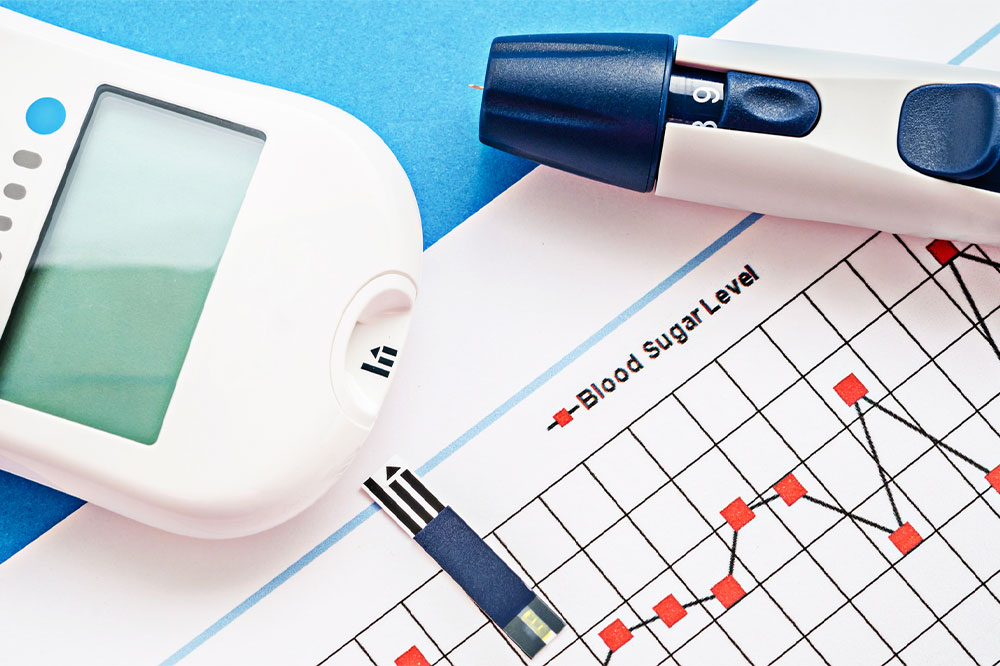
One of the most effective ways to keep blood sugar within optimal ranges is through regular monitoring. Using a standard blood sugar chart, individuals can track their levels at different times of the day—fasting, post-meal, and before bedtime—to understand their body’s responses to food and activity. Knowing these patterns allows for personalized lifestyle adjustments and early detection of potential issues.
Understanding Normal Blood Sugar Levels
For individuals without diabetes or other health issues, typical blood sugar levels follow a predictable pattern. During fasting, which involves abstaining from food for at least 8 hours, normal blood sugar levels should remain between 70 and 99 mg/dL. This fasting range indicates that the body is efficiently managing glucose without excess accumulation.
After eating, especially within the first two hours, blood glucose levels usually stay below 140 mg/dL. This post-meal range signifies healthy glucose metabolism, where the body effectively processes the carbohydrate intake. Persistent readings above or below these levels can signal underlying health concerns that warrant medical attention.
The Importance of Lifestyle and Diet in Blood Sugar Control
Achieving and maintaining stable blood sugar levels requires a holistic approach involving lifestyle choices, dietary habits, and physical activity. Here are essential strategies to incorporate into daily routines:
Adopt a nutrient-dense diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats such as omega-3 fatty acids. These foods support insulin sensitivity and help regulate blood sugar fluctuations.
Choose foods with naturally moderate glucose impact rather than processed, high-sugar options. Incorporate complex carbohydrates that digest slowly, providing sustained energy and preventing spikes in blood sugar.
Limit intake of refined sugars and highly processed foods, which can cause rapid increases in blood glucose followed by crashes that lead to hunger and overeating.
Practice portion control to avoid overeating, which can overload the body's ability to regulate sugar efficiently.
Incorporate regular physical activity into your routine. Exercise enhances insulin sensitivity, promotes glucose uptake by muscles, and helps maintain a healthy weight.
Prioritize adequate sleep and stress management techniques. Both poor sleep and chronic stress can negatively impact blood sugar regulation by affecting hormonal balance.
Recognizing Symptoms and When to Seek Medical Help
Despite best efforts, sometimes blood sugar levels can stray beyond healthy ranges. Recognizing early warning signs of hyperglycemia (high blood sugar) and hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) is vital for prompt intervention.
Symptoms of high blood sugar include excessive thirst, frequent urination, fatigue, blurred vision, and slow-healing wounds. If these symptoms persist, consulting a healthcare professional is essential for diagnosis and management adjustments.
Conversely, low blood sugar can cause dizziness, confusion, sweating, weakness, and in severe cases, seizures or loss of consciousness. Immediate intake of fast-absorbing carbohydrates can help stabilize levels, but ongoing medical assessment is crucial.
Effective management of blood sugar involves routine medical check-ups, understanding individual responses, and utilizing tools such as blood glucose meters or continuous glucose monitoring devices. This proactive approach can prevent complications like heart disease, kidney damage, nerve damage, and other life-threatening issues associated with unmanaged blood sugar levels.
Conclusion: Building a Sustainable Lifestyle for Blood Sugar Management
Maintaining balanced blood sugar levels is a lifelong commitment that involves consistent effort and informed decision-making. By adopting a wholesome diet, engaging in regular physical activity, practicing stress reduction, and monitoring levels routinely, individuals can significantly improve their metabolic health and quality of life. Consulting healthcare providers for personalized guidance ensures safe and effective blood sugar management tailored to individual health needs.
Empowering yourself with knowledge about blood sugar management is the first step toward preventing disease and fostering a healthier, more energetic life. Remember, small daily changes can lead to substantial long-term benefits—your health depends on it.