Comprehensive Guide to 7 Nutritional Strategies for Blood Sugar Reduction and Diabetes Management
Discover effective nutritional strategies with this comprehensive guide highlighting 7 key foods that help reduce blood sugar levels and manage diabetes. Learn how nutrient-rich foods like avocados, pumpkin seeds, cinnamon, seafood, tomatoes, broccoli, and legumes can support blood glucose control, improve insulin sensitivity, and promote overall health. This detailed review offers practical dietary tips, the importance of avoiding sugary foods, and lifestyle recommendations to help those with or at risk of diabetes maintain optimal blood sugar levels for a healthier life.

Comprehensive Guide to 7 Nutritional Strategies for Blood Sugar Reduction and Diabetes Management
Diabetes mellitus, a chronic metabolic disorder, fundamentally results from the body's inability to produce sufficient insulin or effectively utilize the insulin that is available. Insulin is an essential hormone that facilitates the transformation of glucose—sugar—in the bloodstream into usable energy for cells. When the body fails to regulate blood insulin levels properly, glucose accumulates in the blood, leading to persistent hyperglycemia. Over time, sustained high blood sugar levels can cause serious complications like cardiovascular disease, nerve damage, kidney failure, and vision problems. Therefore, maintaining blood sugar within healthy ranges is crucial for preventing these adverse outcomes and ensuring overall health.
Understanding the Role of Nutrition in Managing Diabetes
While factors such as stress levels and physical activity significantly influence blood glucose control, dietary management remains a cornerstone of diabetes care. A well-balanced, nutrient-rich diet can enhance insulin sensitivity, promote glucose stability, and reduce the risk of complications associated with diabetes. Proper nutrition not only supports immediate blood sugar regulation but also plays a vital role in long-term health, weight management, and metabolic health.
It is critical to avoid foods that cause rapid spikes in blood glucose. Items like candies, sugary desserts, sweetened beverages, and processed foods with high refined carbohydrate content can destabilize blood sugar levels dangerously. Instead, focus on nutrient-dense foods that support stable glucose levels, provide essential vitamins and minerals, and promote overall well-being. Consulting nutritional charts and glycemic indexes can help identify foods that are beneficial or should be limited. Prioritizing whole foods and minimizing processed ingredients are effective steps toward controlling blood sugar effectively.
Choosing the right foods is one of the most effective strategies to quickly lower blood glucose levels and manage diabetes comprehensively. For individuals newly diagnosed with diabetes or those seeking to improve their dietary habits, understanding which foods to include and avoid can be overwhelming. Education and awareness are essential for making sustained dietary choices that support diabetes control and overall health.
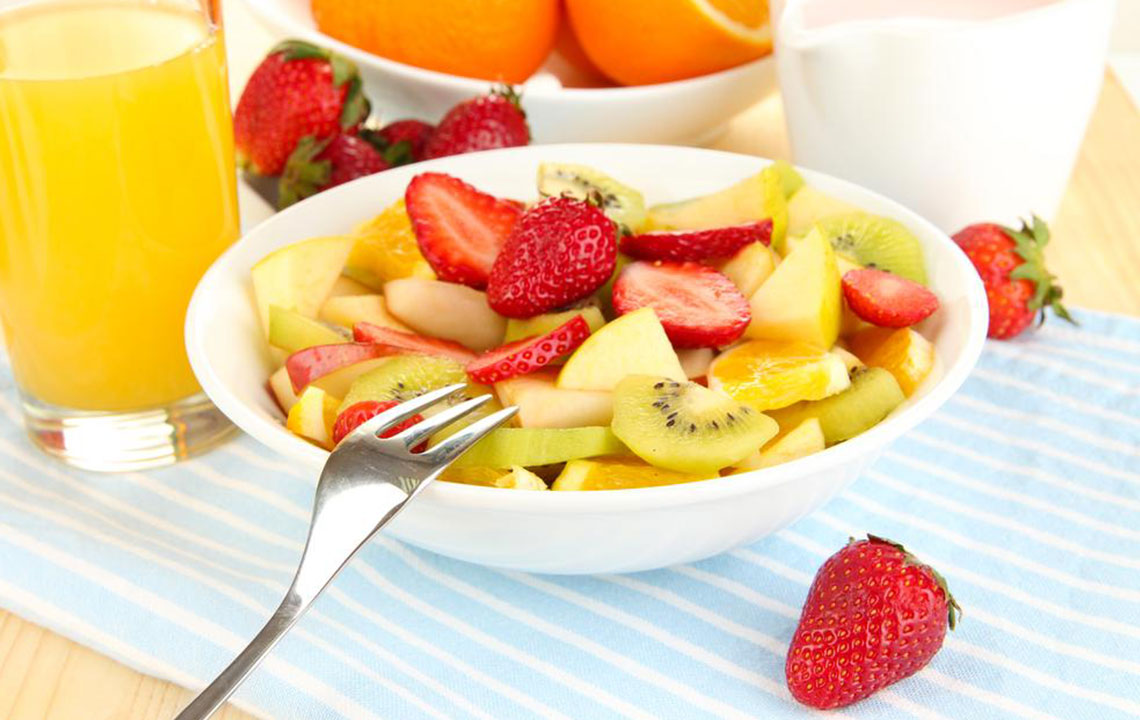
Below are some of the most recommended foods known to help lower blood sugar naturally, improve insulin sensitivity, and support a healthier, more balanced lifestyle:
Avocados – Rich in healthy monounsaturated fats, dietary fiber, potassium, magnesium, and vitamins A and C, avocados are an excellent addition to a diabetic-friendly diet. Their low glycemic index ensures that they do not cause significant blood sugar spikes. The high fiber content in avocados—approximately seven grams per half—slows digestion and helps stabilize blood glucose levels. Additionally, the healthy fats promote satiety and improve lipid profiles, which are often compromised in diabetics. Incorporating avocados into salads, spreads, or smoothies can be both delicious and health-promoting.
Pumpkin Seeds – These nutrient-dense seeds have traditionally been used in various cultures to assist in managing blood sugar levels. Pumpkin seeds are high in dietary fiber, antioxidants, magnesium, and zinc, all of which contribute to better blood sugar regulation. Magnesium plays a critical role in carbohydrate metabolism and insulin action; low magnesium levels are commonly observed in diabetic patients. Regular consumption of pumpkin seeds, whether as a snack or added to meals, can support metabolic health and improve insulin sensitivity.
Cinnamon – This aromatic spice is not only flavorful but also has demonstrated benefits in managing blood glucose levels. Studies indicate that cinnamon can improve insulin sensitivity and slow carbohydrate absorption. Adding cinnamon to meals such as sweet potato dishes, roasted vegetables like carrots, or brewing it into teas and warm milk can help regulate post-meal blood sugar spikes. Cinnamon is low in calories and carbs, making it a valuable addition to a diabetic diet, especially when used to replace sweeter flavorings.
Searfood (Salmon, Shellfish, and Similar Varieties) – Seafood provides a wealth of nutrients including omega-3 fatty acids, high-quality protein, antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals. Salmon, shellfish, tilapia, and sardines are excellent choices for maintaining stable blood sugar levels. Fatty fish such as salmon are carb-free and rich in omega-3s, which help reduce inflammation and improve insulin function. Seafood consumption has been linked to improved lipid profiles and cardiovascular health—critical aspects for diabetics who are at increased risk of heart disease.
Tomatoes – With a naturally low glycemic index, tomatoes release glucose gradually into the bloodstream, preventing rapid spikes. Rich in fiber, vitamins C and K, potassium, and antioxidants like lycopene, tomatoes support immune health and vascular function. The fiber content promotes fullness and better blood sugar regulation. Additionally, tomatoes help lower blood pressure and reduce inflammation, which are common concerns among diabetics at risk for cardiovascular disease.
Broccoli – A cruciferous vegetable loaded with dietary fiber, vitamins C and K, and antioxidants such as sulforaphane, broccoli has multiple benefits for diabetics. Sulforaphane has been shown to reduce blood sugar levels, oxidative stress, and improve insulin sensitivity. Regular consumption of broccoli or other cruciferous vegetables can contribute to lower inflammation, better glucose control, and enhanced overall metabolic health.
Lentils and Beans – These legumes are rich in resistant starch and soluble fiber, which slow down digestion and glycemic response. Lentils, kidney beans, chickpeas, and pinto beans are staples for managing blood sugar. Their high fiber content helps prevent sudden glucose surges post-meals and maintains stable blood glucose levels. Additionally, their high protein content supports satiety and weight management, both important factors in diabetes control.
Achieving effective blood sugar reduction requires a disciplined approach encompassing dietary modifications, physical activity, medication adherence, and regular blood glucose monitoring. Educating oneself on the nutritional content of foods and their glycemic impacts is essential. Coupling dietary strategies with consistent exercise can enhance insulin sensitivity and overall metabolic health. Long-term commitment to lifestyle changes is vital for optimal diabetes management and reducing the risk of related complications.