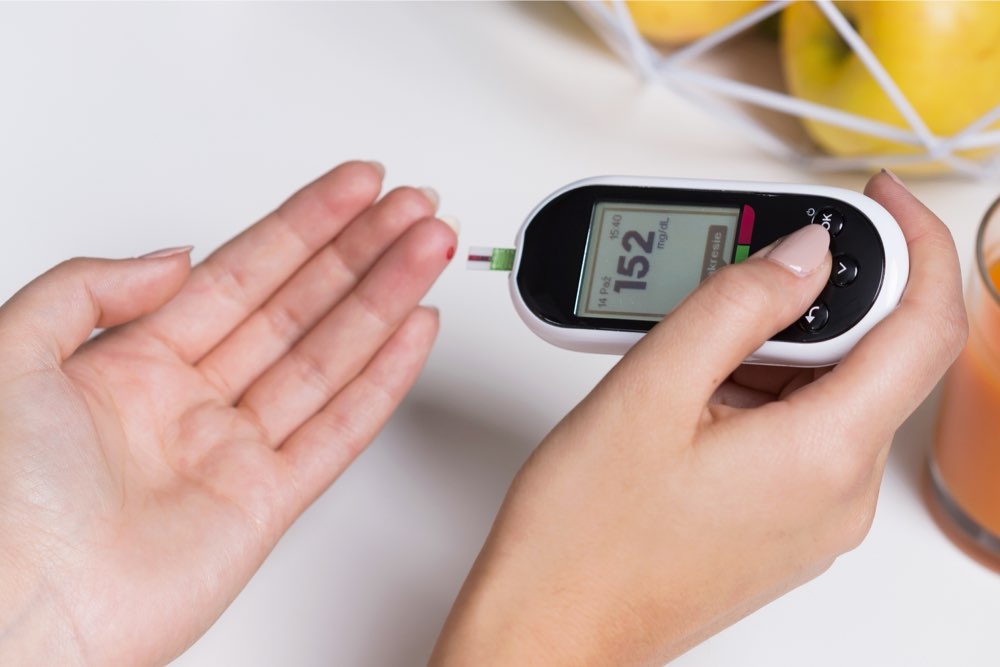
Comprehensive Guide to Maintaining Optimal Blood Sugar Levels for Better Health
This comprehensive guide offers essential strategies for maintaining healthy blood sugar levels through lifestyle modifications, including diet, exercise, weight management, and sleep hygiene. Implementing these habits can prevent complications related to diabetes, improve insulin sensitivity, and promote overall health and vitality. Learn how to regulate your glucose levels effectively and lead a healthier, more active life with practical tips and expert advice.

Comprehensive Strategies for Maintaining Optimal Blood Sugar Levels
In recent years, the prevalence of blood sugar imbalance and conditions such as diabetes has surged globally. This increase can be attributed to various factors, including unhealthy eating habits, sedentary lifestyles, elevated stress levels, and genetic predispositions. Understanding how to maintain healthy blood glucose levels is paramount for individuals aiming to prevent chronic diseases and promote overall health. While genetics provide a baseline risk, lifestyle choices play a critical role in either exacerbating or mitigating this risk. Therefore, adopting targeted habits can make a significant difference in managing blood sugar effectively.
Persistent high blood sugar, if unmanaged, can lead to serious health complications, including cardiovascular issues, nerve damage, kidney disease, and vision problems. As diabetes remains a chronic condition without a definitive cure, focus must be on controlling blood glucose levels and preventing complications through consistent and informed lifestyle modifications.
Achieving stable blood sugar levels requires a multifaceted approach encompassing dietary adjustments, physical activity, weight management, and behavioral changes. Integrating these habits into daily routines can significantly improve insulin sensitivity, reduce risk factors, and enhance overall well-being.
Achieve and Maintain a Healthy Body Weight
One of the foundational steps in blood sugar management is maintaining an appropriate weight. Excess body weight, particularly around the abdomen, can lead to insulin resistance, where cells become less responsive to insulin's effects. This resistance causes glucose to accumulate in the bloodstream rather than being absorbed by cells for energy processing. Losing as little as 5-10% of your body weight has been shown to markedly improve insulin sensitivity and glucose regulation. To achieve sustainable weight loss, it is advisable to work with healthcare professionals or nutritionists who can craft personalized, calorie-controlled, and nutritionally balanced meal plans.
Adopt a Nutrient-Dense, Balanced Diet Centered on Complex Carbohydrates
Diet plays a crucial role in blood sugar control. Foods rich in simple sugars and refined carbs cause rapid spikes in blood glucose levels, leading to energy crashes and increased hunger. Conversely, a diet emphasizing complex carbohydrates, such as whole grains, legumes, vegetables, and fruits, provides a steady release of glucose, aiding in sustained energy levels. Limiting intake of processed foods, sugary snacks, and fried items is essential. Incorporating dietary fiber from plant-based sources can slow digestion and absorption, preventing sharp blood sugar rises.
Engage in Regular Physical Activity
Physical activity enhances insulin sensitivity and promotes more effective glucose utilization by cells. It also aids in weight management and improves cardiovascular health. Activities such as brisk walking, cycling, swimming, or strength training for at least 150 minutes per week have been shown to effectively control blood sugar levels. Including movement into daily routines—for example, taking stairs instead of elevators or short walks during breaks—further contributes to metabolic health. Regular exercise not only stabilizes blood glucose but also promotes mental well-being and reduces stress levels.
Limit Gluten Intake, Especially from Wheat
Emerging research suggests that gluten, particularly from wheat-containing products, may influence blood sugar levels and insulin response. Some individuals experience better glycemic control when reducing or eliminating gluten from their diets. While gluten sensitivity varies among individuals, removing wheat and processed gluten-rich foods can aid in maintaining a balanced glucose level by reducing inflammation and processing similarities to sugar in the body. Consulting with healthcare providers before making significant dietary changes is recommended.
Start the Day with Protein-Rich Breakfasts
Consuming high-protein foods like eggs, dairy, or lean meats at breakfast helps stabilize blood sugar by slowing carbohydrate absorption. Including protein in the morning provides sustained energy throughout the day and supports satiety, reducing overeating and cravings. This habit is particularly beneficial for individuals aiming to lose weight or manage diabetes.
Incorporate Resistant Starch for Improved Glucose Control
Resistant starches are types of carbohydrates that resist digestion in the small intestine and ferment in the large intestine, promoting gut health. Foods such as legumes, green bananas, cooled cooked potatoes, and unripe plantains are rich sources. These foods help moderate post-meal blood sugar spikes, improve insulin sensitivity, and support digestive health. Regular inclusion of resistant starches in your diet can assist in better metabolic regulation and weight management.
Consume Nuts in Moderation
Nuts like almonds, walnuts, pistachios, and cashews provide healthy fats, fiber, and protein, which are essential for blood sugar balance. Incorporating a small handful of nuts daily can help suppress hunger, improve cholesterol levels, and stabilize post-meal blood glucose responses. However, due to their high-calorie content, portion control is vital to avoid unintended weight gain.
Prioritize Consistent and Restful Sleep
Sleep quality significantly influences hormonal balance, appetite regulation, and blood sugar levels. Chronic sleep deprivation or irregular sleep patterns increase the risk of insulin resistance and metabolic disturbances. Striving for at least 7-8 hours of uninterrupted sleep per night, maintaining a regular sleep schedule, and creating a restful sleeping environment can enhance glucose metabolism and overall health.
In summary, controlling blood sugar levels requires a comprehensive lifestyle management approach. By adopting healthy habits related to diet, physical activity, weight maintenance, and sleep hygiene, individuals can effectively prevent or manage diabetes and enhance their overall health. Consistency and mindful choices are crucial for long-term success in blood sugar regulation and overall well-being.