Understanding Key Endocrine Disorders: Essential Knowledge for Maintaining Hormonal Health
This comprehensive guide explores key endocrine disorders, their symptoms, causes, and treatments. It emphasizes the importance of early detection and lifestyle changes for better hormonal health. Understanding these conditions helps in effective management and improves quality of life, making it essential knowledge for maintaining overall health.

The endocrine system is one of the body's most intricate and vital networks, consisting of various glands responsible for producing and secreting hormones that regulate a wide array of physiological processes. These processes include growth and development, metabolism regulation, mood stabilization, reproductive functions, and the body's ability to heal itself. When the endocrine system functions optimally, it keeps the body's internal environment balanced, supporting overall health and vitality. However, disruptions or malfunctions within this system can lead to a range of health issues that may significantly impact an individual's quality of life.
Understanding the common endocrine disorders is crucial for early detection, effective management, and preventing potential complications. These disorders primarily involve glands such as the pituitary, thyroid, pancreas, adrenal glands, and gonads. Each of these glands plays a specific role in hormone production, and any imbalance can manifest with distinct symptoms, making awareness and recognition essential.
Major Endocrine Glands and Their Functions
Pituitary Gland: Often referred to as the 'master gland,' it controls other endocrine glands and regulates growth, blood pressure, and reproduction.
Thyroid Gland: Produces hormones that regulate metabolism, energy generation, and overall growth.
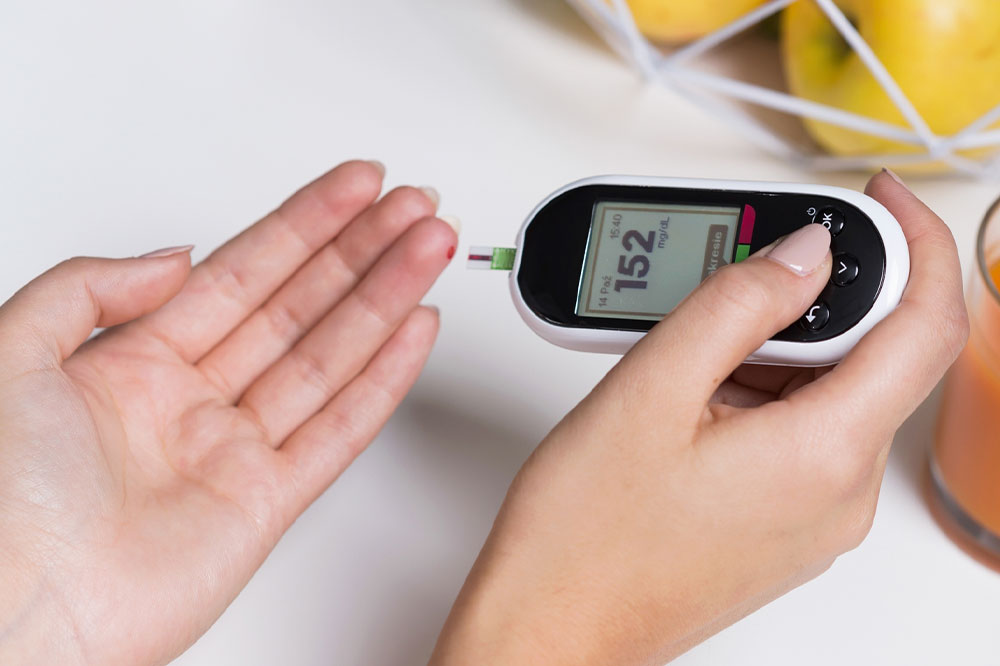
Pancreas: Produces insulin and glucagon to manage blood sugar levels.
Adrenal Glands: Secrete hormones like cortisol and adrenaline that help respond to stress and regulate blood pressure.
Gonads (Ovaries and Testes): Responsible for reproductive hormones such as estrogen, progesterone, and testosterone.
Common Endocrine Disorders and Their Symptoms
1. Hypothyroidism
This condition occurs when the thyroid gland is underactive, resulting in low production of thyroid hormones. Symptoms include fatigue, weight gain, cold intolerance, depression, and slowed heart rate. It often develops gradually and can be mistaken for other health issues.
2. Hyperthyroidism
Conversely, an overactive thyroid produces excessive hormones, leading to weight loss, rapid heartbeat, tremors, anxiety, and heat intolerance. Graves' disease is a common cause of hyperthyroidism.
3. Diabetes Mellitus
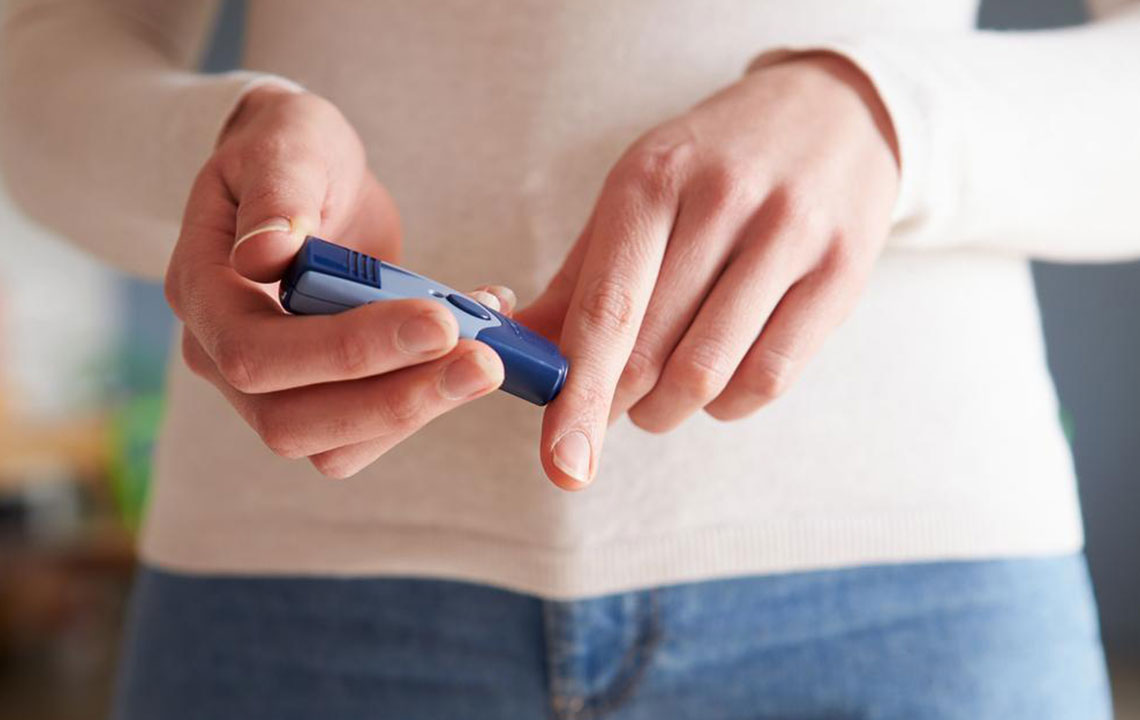
This metabolic disorder stems from insufficient insulin production or ineffective insulin use, resulting in high blood sugar levels. Symptoms include frequent urination, excessive thirst, fatigue, blurred vision, and slow healing of wounds. Diabetes type 1 and type 2 are the most prevalent forms.
4. Adrenal Insufficiency (Addison’s Disease)
Characteristic of insufficient cortisol production, this disorder can cause fatigue, muscle weakness, weight loss, low blood pressure, and skin darkening.
5. Hormonal Imbalances in Reproductive Glands
Disorders such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) in women or low testosterone in men can lead to fertility issues, abnormal menstrual cycles, or other reproductive challenges.
Factors Contributing to Endocrine Disorders
Genetics: Family history can predispose individuals to certain disorders.
Autoimmune Responses: Conditions where the immune system attacks endocrine glands, such as Hashimoto’s thyroiditis.
Lifestyle Habits: Poor diet, lack of exercise, stress, and exposure to toxins can disrupt hormone balance.
Environmental Exposures: Chemicals like pesticides, plastics, and pollutants can interfere with endocrine function.
Tumors and Growths: Benign or malignant tumors in endocrine glands can alter hormone production.
Diagnosing Endocrine Disorders
Early detection is vital for effective treatment. Diagnostic methods include blood tests to measure hormone levels, imaging studies like ultrasounds or MRIs to identify tumors, and sometimes biopsies. Regular health check-ups and paying attention to unusual symptoms help in catching these disorders early.
Management and Treatment Options
Treatment varies based on the specific disorder and its severity. Hormone replacement therapy is common for conditions like hypothyroidism or adrenal insufficiency. Medications such as antithyroid drugs for hyperthyroidism, insulin for diabetes, and contraceptives or fertility treatments for reproductive issues are used. Lifestyle modifications—balanced diet, regular exercise, stress management—are integral to managing these conditions. In some cases, surgery might be necessary, especially when tumors are involved.
Preventive Measures and Lifestyle Tips
Maintain a balanced diet rich in essential nutrients.
Engage in regular physical activity to support metabolic health.
Avoid exposure to environmental toxins and chemicals known to disrupt endocrine function.
Manage stress through mindfulness, meditation, or yoga.
Attend routine health screenings and hormone level assessments as recommended.
In conclusion, understanding the critical functions of the endocrine system and recognizing the signs of common endocrine disorders are essential steps toward maintaining hormonal health. Early intervention and lifestyle modifications can significantly improve outcomes and quality of life. As science advances, ongoing research continues to improve diagnostic techniques and treatment options, offering hope to those affected by these health conditions.