Understanding Medical Causes of Unexpected Weight Fluctuations and When to Seek Help
This detailed article explains common medical reasons behind unexpected weight changes, such as thyroid issues, depression, diabetes, and fluid retention. It emphasizes the importance of recognizing symptoms and seeking medical guidance for proper diagnosis and management. Early intervention can improve health outcomes and prevent more serious conditions. The article provides practical advice and highlights lifestyle factors essential for maintaining a healthy weight. Perfect for individuals noticing unexplained fluctuations and seeking to understand when to consult healthcare professionals for effective treatment.

Understanding Medical Causes of Unexpected Weight Fluctuations and When to Seek Help
Achieving and maintaining a consistent body weight can often be difficult for many individuals. Fluctuations in weight are common, but sudden or unexplained changes can lead to concern and raise questions about underlying health issues. These unexpected shifts in weight might be caused by various factors, including lifestyle choices such as diet and physical activity, or they can be symptoms of more serious medical conditions. Recognizing the difference between normal fluctuations and signs of potential health problems is essential for early intervention and effective management.
While minor weight variations are typically harmless, persistent or significant changes should prompt a consultation with healthcare professionals. Unexplained weight variations can sometimes be the body's response to underlying health conditions that require medical attention. Understanding the common medical causes behind these fluctuations can help individuals recognize when it's time to seek professional advice. Here, we explore some of the most prevalent medical reasons for unexpected changes in body weight, along with advice on when to seek help and how to manage these issues effectively.
Depression and Mental Health Disorders
Depression is a mental health condition that can profoundly impact physical health and daily functioning. It often influences eating habits, either causing a significant decrease or increase in appetite. Some individuals may experience emotional eating, leading to weight gain, while others lose interest in food altogether, resulting in weight loss. Depression can also reduce physical activity levels, further influencing weight. Recognizing these signs and seeking treatment is critical because addressing mental health can significantly improve physical health outcomes.
Hypothyroidism
This condition results from an underactive thyroid gland, which produces insufficient hormones necessary for regulating metabolism. When metabolism slows down, individuals often experience weight gain despite no change in diet or activity levels. Symptoms may also include fatigue, cold intolerance, dry skin, and constipation. Hypothyroidism is especially common in women over 50 but can occur at any age. Proper diagnosis and hormone replacement therapy can help manage symptoms and stabilize weight.
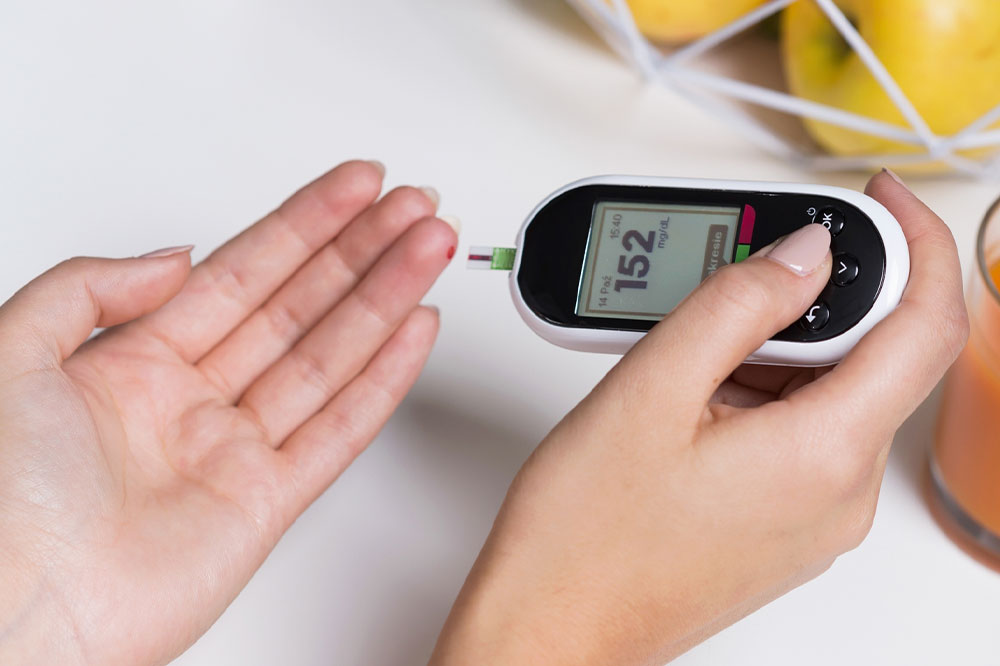
Diabetes and Blood Sugar Imbalances
Diabetes mellitus, particularly type 2 diabetes, can cause rapid and unexplained weight changes. In early stages, individuals might notice weight loss despite increased appetite, alongside symptoms like frequent urination, excessive thirst, and fatigue. High blood sugar levels lead to the body expelling glucose through urine, resulting in calorie depletion and weight loss. Conversely, some individuals may experience weight gain over time, especially if blood sugar levels are poorly controlled. Managing blood glucose through medication, diet, and lifestyle changes is vital for preventing further health complications.
Fluid Retention (Edema)
Fluid accumulation in tissues, known as edema, can cause noticeable weight gain and swelling, especially in the legs, ankles, and abdomen. This condition often indicates underlying health issues such as heart failure, kidney disease, or liver problems. It might also be associated with certain medications or hormonal imbalances. Persistent edema requires medical evaluation to identify and treat the root cause. Managing fluid retention typically involves lifestyle modifications, medication adjustments, and addressing the primary health condition.
Cancer and Related Conditions
While less common, certain types of cancer can influence body weight. Tumors located in the stomach or intestines may interfere with normal food absorption, causing weight loss. Additionally, cancers can trigger inflammation or systemic effects that alter metabolism. Weight loss associated with cancer is often progressive and unintentional, and it may be accompanied by other symptoms such as fatigue, pain, or changes in appetite. Early detection and treatment are crucial for better health outcomes.
Some weight fluctuations are simply part of aging or temporary lifestyle changes, but persistent, unexplained changes should not be ignored. It’s essential for individuals to monitor these shifts and consult healthcare providers for comprehensive evaluation. Besides identifying medical causes, maintaining a healthy lifestyle — including balanced nutrition, regular physical activity, sleep hygiene, and stress management — remains key to long-term weight management and overall wellness. Healthcare professionals can develop personalized strategies to address individual needs, ensuring a safe and effective approach to maintaining a healthy weight.