Comprehensive Guide to Itchy Skin: Causes, Treatments, and Relief Strategies
This comprehensive article explores the common causes of itchy skin, including dry skin, allergies, insect bites, and systemic conditions. It offers detailed management strategies such as moisturizing, avoiding triggers, and seeking medical advice. Learn how to effectively relieve persistent itching and maintain healthy skin through expert-recommended treatments and preventive measures. Ideal for anyone experiencing repeated or severe skin irritation, this guide highlights the importance of proper diagnosis, tailored care, and professional consultation to improve skin health and comfort.

Understanding the Most Common Causes of Itchy Skin and How to Effectively Manage Them
What is itchy skin?
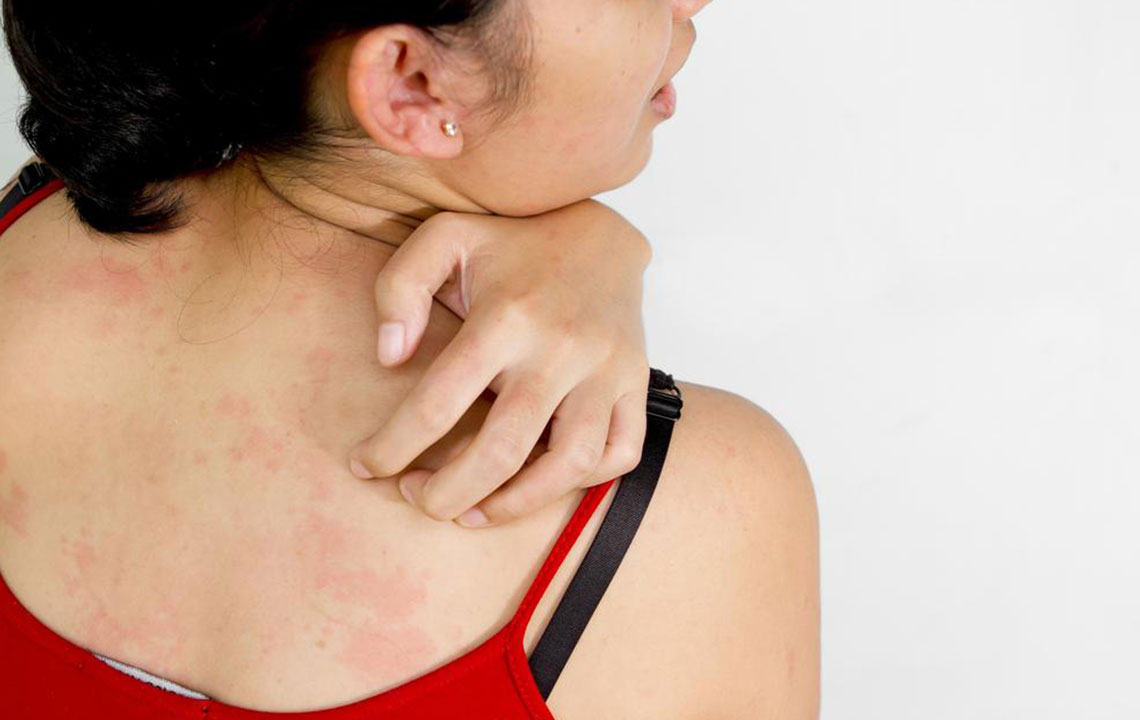
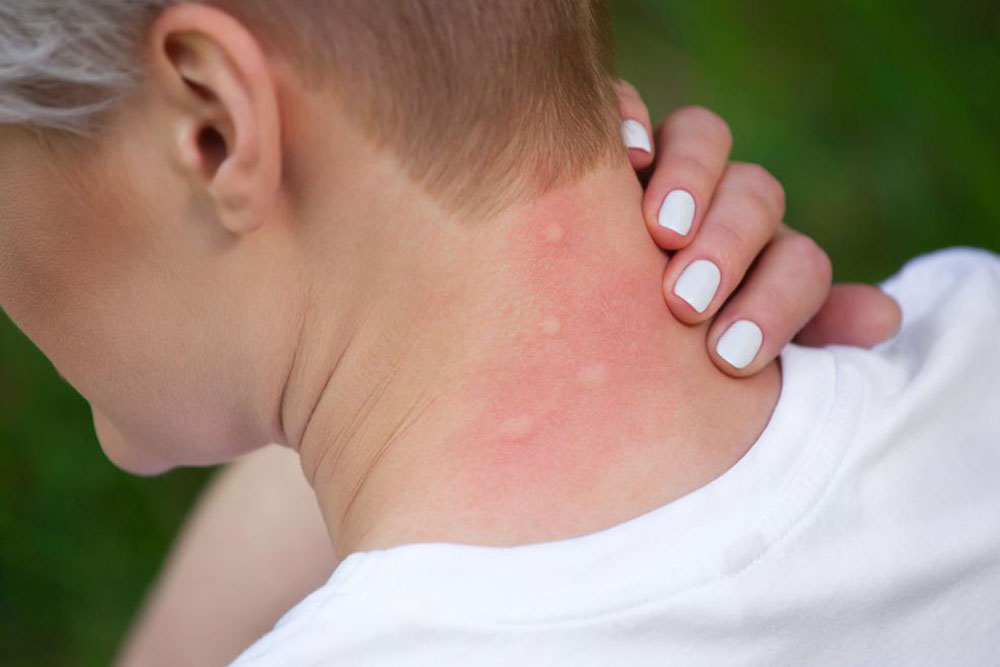
Itchy skin, medically known as pruritus, is a widespread discomfort that prompts an irresistible urge to scratch the affected area. This sensation can develop anywhere on the body—from the scalp to the soles of the feet—and is often accompanied by visible signs such as redness, dryness, peeling, or flakiness of the skin. Although it might seem like a minor issue, persistent or severe itching can lead to more serious skin problems, including infections, ulcers, or permanent scarring. Recognizing the underlying causes of itchiness is crucial for effective treatment and relief. If the symptoms persist beyond two weeks or intensify, seeking professional medical advice from a dermatologist is strongly recommended to diagnose and tailor appropriate treatment plans.
Common Causes of Itchy Skin and Their Management
Understanding what triggers itchy skin helps in selecting the right treatment and alleviation methods. The causes range from benign environmental factors to systemic diseases. Below are the most prevalent reasons behind itchy skin, along with practical tips for relief and management.
Dry Skin (Xerosis): One of the leading causes of itching worldwide, dry skin results from environmental factors such as cold weather, low humidity, or excessive exposure to harsh chemicals. Certain medications, frequent bathing with soap that strips natural oils, or aging-related skin changes also contribute to dehydration and irritation of the skin. The hallmark of dry skin is roughness and flakiness, often accompanied by mild redness and persistent itching.
Managing dry skin effectively involves consistent use of emollient-rich moisturizers such as lotions, creams, or ointments specifically formulated to restore hydration. Choosing products free from fragrances or dyes reduces irritation. Furthermore, using gentle, moisturizing soaps and avoiding long, hot showers helps prevent skin dehydration. Staying well-hydrated by drinking plenty of water throughout the day is also vital to maintain skin moisture levels. For individuals with dry skin without any rashes, these simple skincare habits can significantly reduce itchiness and improve overall skin health.
Food Allergies: Allergic reactions to specific foods like shellfish, dairy products, soy, nuts, or wheat can manifest with skin symptoms including itching, hives, and swelling. The immune system mistakenly identifies these foods as harmful, releasing histamines and other chemicals that cause pruritus and inflammation. Identifying food allergies through proper testing and avoiding trigger foods are essential for symptom relief. In some cases, a nutritionist or allergist may recommend an elimination diet to pinpoint specific allergenic foods.
In addition to food-related causes, insect bites are a common source of localized itching. Bites from mosquitoes, fleas, bedbugs, or other insects inject irritants or proteins that trigger immune responses, resulting in swelling, redness, and intense itching. Over-the-counter antihistamine creams or oral medications, cold compresses, and topical anti-itch ointments can soothe these symptoms. Proper insect avoidance measures, including using repellents and maintaining a clean living environment, help prevent bites altogether.
Other significant causes of itchy skin include:
Varicella (Chickenpox): A contagious viral infection characterized by itchy, fluid-filled blisters that crust over after a few days. The contagious nature of chickenpox makes isolation and prompt treatment necessary to prevent spread.
Kidney Disease: Advanced renal impairment hampers waste elimination, leading to a buildup of toxins that cause pruritus. Itching associated with kidney problems often worsens at night and may be accompanied by dry, flaky skin, rashes, or ulcers. Managing underlying kidney function through dialysis or medication can significantly reduce symptoms.
Gallstone or Liver Issues (Biliary Disorders): Damage or disease affecting the liver or gallbladder can lead to intense itching, often accompanied by jaundice—yellowing of the skin and eyes. The accumulated bile salts in the skin act as irritants, intensifying the itching sensation. Early diagnosis and treatment of liver or gallbladder conditions are vital to prevent further complications and relieve symptoms.
Eczema (Atopic Dermatitis): A chronic inflammatory skin condition that causes redness, dryness, swelling, and intense itching. Eczema often flares in response to irritants, allergens, or stress. Treatment typically involves the use of steroid or moisturizing creams, along with lifestyle adjustments to reduce triggers.
Hives (Urticaria): Allergic reactions from foods, medications, insect stings, or environmental factors result in the sudden appearance of raised, red, and itchy bumps on the skin. Histamine release plays a key role in their development. Managing hives involves antihistamines, avoiding known triggers, and in severe cases, using prescribed medications like corticosteroids.
Understanding these common causes enables individuals to seek appropriate treatment and prevent complications. In cases where symptoms persist, worsen, or are accompanied by other signs such as fever, swelling, or difficulty breathing, prompt medical attention is essential.Overall, managing itchy skin involves identifying the root cause and applying targeted treatments, whether through lifestyle adjustments, skincare routines, or medical interventions. Proper diagnosis and personalized care can significantly improve comfort and skin health. Regular consultations with healthcare professionals are recommended for persistent or severe cases to ensure effective management and prevention of complications.