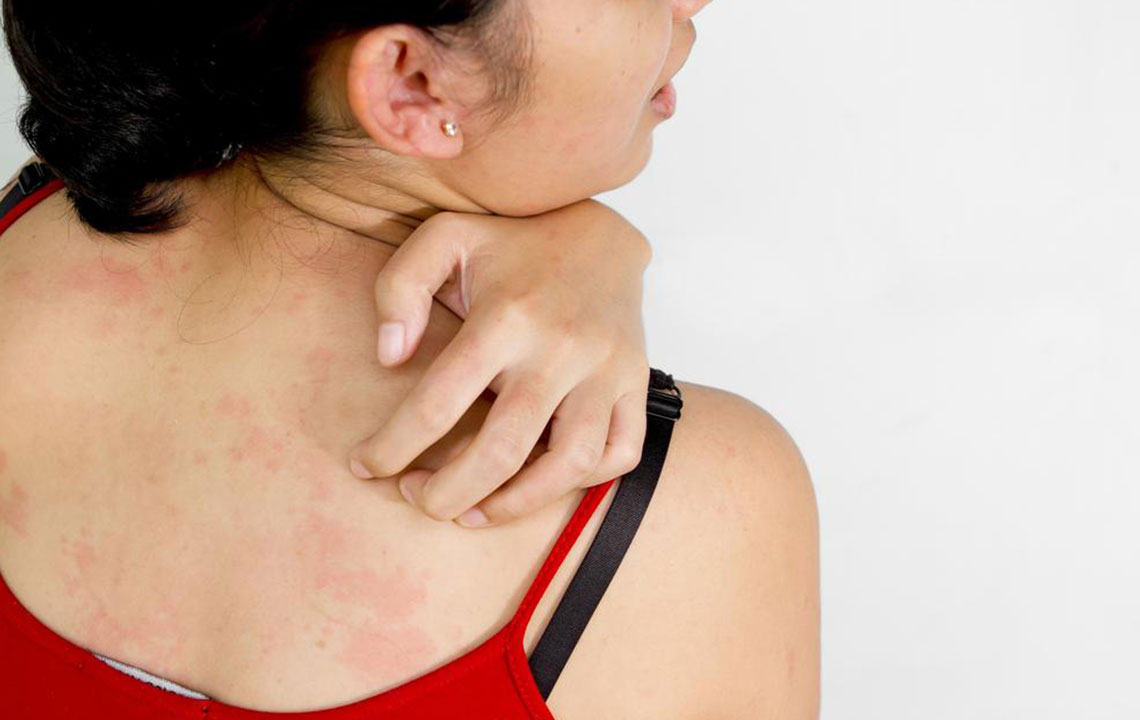
Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Diagnosing Persistent Itchy Skin
Persistent itchy skin, or Pruritus, can stem from skin conditions, internal health issues, infections, allergies, or psychological factors. This comprehensive guide details causes, diagnostic procedures, and treatment options, emphasizing the importance of timely medical intervention to manage discomfort and underlying health problems effectively. Recognizing symptoms early and seeking professional help can lead to successful treatment outcomes and improved skin health.
Chronic itchy skin, medically known as Pruritus, is a common concern that can significantly impact an individual's quality of life. The persistent urge to scratch not only causes discomfort but can also lead to further skin damage, infections, and emotional distress. Recognizing the underlying causes of itchy skin is crucial for effective treatment and management. This comprehensive guide explores the various causes, diagnostic methods, and treatment options for itchy skin, helping individuals understand when to seek medical advice and how to achieve relief.
Persistent skin itching can manifest in different ways, from mild irritation to severe, relentless discomfort. Itching can be localized, affecting specific areas, or generalized across large parts of the body. Often, patients worry that their symptoms may be indicative of a serious health problem; therefore, understanding the root causes is essential for proper care.
Common Causes of Itchy Skin
There are numerous reasons why someone might experience persistent itching. These causes can be broadly categorized into skin-related conditions, systemic health issues, infections, allergic reactions, and psychological factors.
Skin Conditions
Various dermatological issues can result in itching. Dry skin (xerosis) is one of the most common culprits, especially during cold weather or in low humidity environments. Eczema (atopic dermatitis) and psoriasis are chronic skin conditions that often cause intense itching accompanied by redness, scaling, and inflammation. Contact dermatitis results from exposure to irritants or allergens, leading to localized itching, swelling, and redness.
Infections
Skin infections caused by fungi, bacteria, or parasites can trigger itchy sensations. For example, fungal infections like athlete’s foot, scabies caused by mites, and bacterial skin infections often present with itching as a primary symptom. Proper diagnosis of these infections is necessary for effective treatment, which may involve topical or systemic medications.
Internal Health Disorders
Chronic itching can be a symptom of underlying systemic conditions. Kidney disease, particularly in its advanced stages, causes waste build-up in the body that can result in generalized itching. Liver diseases such as hepatitis or cirrhosis may also present with itchy skin. Thyroid imbalances, especially hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism, can influence skin health and cause dryness and itching. Additionally, blood disorders like anemia and certain cancers have been associated with persistent pruritus.
Allergic Reactions and Environmental Factors
Allergies to soaps, detergents, fragrances, or certain fabrics can lead to contact dermatitis and itching. Environmental irritants such as pollution, pollen, or pet dander may also contribute. Exposure to harsh chemicals or allergens triggers immune responses that manifest as skin irritation and itching.
Psychological Factors
Stress, anxiety, and mental health conditions can exacerbate the perception of itching. Psychogenic pruritus is a recognized condition where psychological stress influences skin sensations, often leading to compulsive scratching and further skin damage.
How Is Itchy Skin Diagnosed?
Diagnosis of the root cause of itchy skin involves a detailed medical history, physical examination, and targeted tests. Healthcare professionals will ask about the duration, distribution, intensity of itching, associated skin changes, and any recent exposures or health changes.
Laboratory tests are essential for pinpointing underlying issues. These include:
Blood Tests: Complete blood count (CBC) to check for anemia or infections, liver and kidney function tests to evaluate organ health, and thyroid function tests.
Skin Allergy Tests: Patch tests or skin prick tests to identify allergic triggers.
Skin Biopsy: In cases where skin cancer, infection, or rare skin conditions are suspected, a biopsy may be performed for microscopic examination.
Treatment Options for Itchy Skin
The treatment approach depends on the underlying cause. Effective management may involve topical therapies, systemic medications, lifestyle modifications, and addressing psychological factors.
Topical Treatments
Moisturizers and emollients are vital for managing dry skin. Corticosteroid creams help reduce inflammation and itching in cases of dermatitis, eczema, or psoriasis. Antihistamine creams or oral medications may alleviate allergic reactions. Calming skin with gentle cleansers and avoiding irritants is also recommended.
Systemic Medications
For cases caused by systemic conditions, medications like antihistamines, antibiotics, antifungals, or treatments for liver or kidney diseases may be necessary. Management of the underlying health condition often alleviates the associated pruritus.
Lifestyle and Environmental Changes
Adopting gentle skin care routines, avoiding harsh soaps, and using humidifiers can improve skin hydration. Avoiding known allergens and irritants reduces flare-ups. Stress management techniques such as meditation or counseling can mitigate psychogenic pruritus.
When to Seek Medical Attention
If itching persists for more than two weeks, worsens, or is accompanied by other symptoms such as skin ulcerations, sores, fever, weight loss, or changes in skin color, consulting a healthcare provider is crucial. Early diagnosis of underlying health issues can prevent complications and provide relief.
In conclusion, persistent itchy skin is a multifaceted condition that requires careful evaluation to uncover its causes. With appropriate diagnosis and treatment, individuals can find relief and improve their quality of life. Do not ignore ongoing itching—seek professional medical advice promptly for optimal care and management.