Comprehensive Guide to Causes and Effective Treatments for Itchy Skin
This comprehensive guide explores the various causes of itchy skin, from dry skin to internal health issues, and provides detailed treatment strategies. Learn how to identify triggers, manage symptoms effectively, and when to seek medical help. Proper skincare, lifestyle changes, and emerging treatments can help alleviate pruritus and improve skin health for lasting relief.

Comprehensive Guide to Causes and Effective Treatments for Itchy Skin
Itchy skin, clinically referred to as pruritus, is a common yet often distressing dermatological symptom that can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life. This sensation compels scratching, which in turn can worsen skin conditions and lead to secondary infections if not properly managed. Understanding the underlying causes of itchy skin is essential for effective treatment and relief. This comprehensive guide explores the various reasons behind pruritus, from common factors like dry skin to more complex internal health conditions, and provides detailed strategies for managing and alleviating this discomfort.
What Is Itchy Skin and Why Does It Occur?
Itchy skin is a sensation that triggers an urge to scratch, resulting from a variety of physiological and environmental factors. Medically termed pruritus, this condition can be localized to specific areas or widespread across the entire body. While occasional itching can be normal, persistent or severe pruritus warrants attention as it may signal underlying health issues.
Common Causes of Itchy Skin
Dry Skin (Xerosis): The most prevalent cause, especially among older adults, dry skin occurs when the skin’s moisture content drops. Factors such as cold weather, low humidity, frequent washing with harsh soaps, and aging reduce skin hydration, leading to itching.
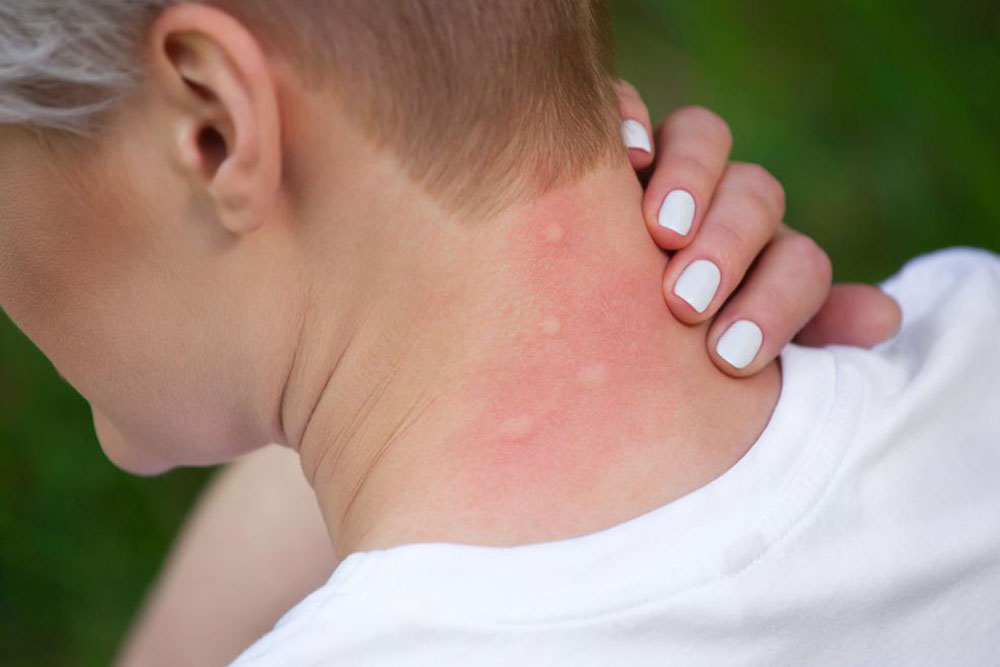
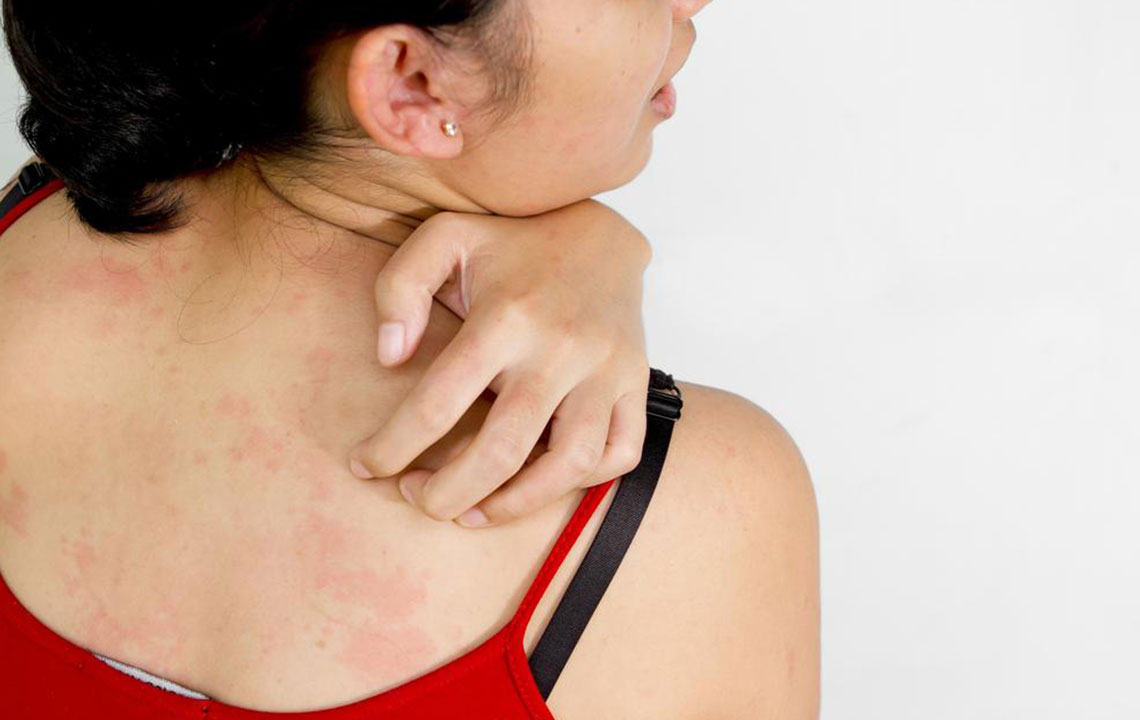
Skin Infections and Conditions: Fungal infections like athlete’s foot, bacterial infections, eczema, and psoriasis can cause localized itching. Skin inflammation and damage expose nerve endings, intensifying the itch sensation.
Allergic Reactions: Contact with allergens such as certain cosmetics, detergents, plants (like poison ivy), or food allergens can trigger allergic dermatitis, resulting in itchy, inflamed skin.
Internal Medical Conditions: Diseases including liver disease, kidney failure, thyroid disorders, and blood disorders can manifest as generalized itching due to metabolic imbalances or toxin buildup.
Nerve-Related Issues: Neuropathic pruritus occurs when nerve damage or irritation affects itch sensation pathways, often associated with conditions like shingles, multiple sclerosis, or nerve injury.
Pregnancy and Hormonal Changes: Hormonal fluctuations during pregnancy can lead to dry, itchy skin, especially on the abdomen, thighs, and hands.
Medications: Certain drugs, including antibiotics, opioids, and antihistamines, may cause allergic reactions or dry skin as side effects, leading to pruritus.
Why Does Itching Worsen at Night?
Many individuals notice that their itching sensations become more intense at night. This phenomenon may be attributed to several factors including body temperature fluctuations, decreased cortisol levels (which have anti-inflammatory properties), and reduced distractions, making you more aware of the itch sensation. Additionally, skin tends to become drier overnight, compounding the discomfort.
Effective Strategies for Managing and Relieving Itchy Skin
Relief from pruritus often involves both lifestyle modifications and targeted treatments. Here are some proven strategies:
Moisturize Regularly: Using rich, fragrance-free emollients helps restore the skin’s barrier, locking in moisture and reducing dryness. Apply moisturizers immediately after bathing to maximize hydration.
Avoid Irritants and Allergens: Switch to gentle, fragrance-free soaps and detergents. Avoid known allergens and irritants that trigger itching.
Maintain Proper Skin Hygiene: Keep the skin clean and dry. Use lukewarm water instead of hot water to prevent skin drying.
Cooling Compresses and Oatmeal Baths: Applying cool, damp cloths or taking oatmeal baths can soothe inflamed skin and reduce itching intensity.
Use Over-the-Counter Medications: Antihistamines can help alleviate allergic-related itching. Topical corticosteroids are effective for inflammatory skin conditions but should be used under medical supervision.
Manage Underlying Health Conditions: Treating the primary cause, such as liver disease or kidney issues, often alleviates secondary skin symptoms.
Improve Air Quality and Humidity: Using humidifiers in dry environments can prevent skin from becoming excessively dry.
When to Seek Medical Assistance
If symptoms persist for more than a few weeks, worsen, or if you notice additional signs like swelling, blistering, infection, or systemic symptoms such as fever or fatigue, consult a healthcare professional promptly. A dermatologist can evaluate for underlying conditions, perform necessary tests, and recommend appropriate treatments tailored to your specific needs.
Innovations and Future Perspectives in Pruritus Management
Research continues to advance in understanding the mechanisms behind itch sensation and developing targeted therapies. Emerging treatments include biologics for severe inflammatory conditions, nerve-modulating drugs for neuropathic pruritus, and novel topical agents that improve skin barrier function. Additionally, wearable devices monitoring skin condition and emerging telemedicine platforms facilitate early detection and management.
In conclusion, itchy skin is a multifaceted symptom with diverse causes, ranging from simple dry skin to complex internal diseases. Recognizing the root cause is crucial for effective treatment. With proper skincare routines, lifestyle adjustments, and medical interventions, most individuals can find relief from pruritus, improving their comfort and quality of life.