Comprehensive Guide to Top 8 Nutritional Strategies for Effective Blood Sugar Management
This comprehensive guide explores the top 8 foods essential for controlling blood sugar effectively. From vegetables and fruits to proteins and healthy fats, learn how incorporating these nutrient-rich options into your daily diet can help manage diabetes, improve heart health, and foster overall well-being. Practical tips and versatile meal ideas make healthy living achievable for everyone seeking stable blood glucose levels.

Essential Foods for Maintaining Stable Blood Glucose Levels
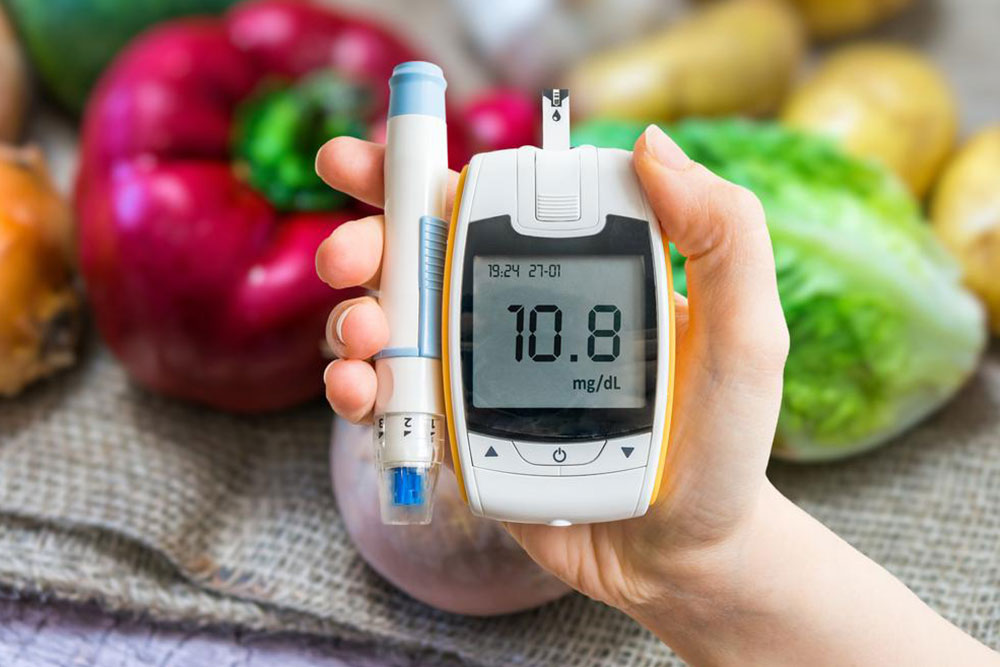
Maintaining healthy blood sugar levels is a vital aspect of managing diabetes and promoting overall well-being. Nutrition plays a pivotal role in controlling blood glucose, preventing fluctuations, and supporting metabolic health. A well-balanced diet that emphasizes specific nutrient-rich foods can significantly help individuals with diabetes or those aiming to prevent it. Many overlook the impact of dietary choices, but integrating the right foods into your daily intake can have transformative effects.
If you're managing diabetes or concerned about your blood sugar, understanding which foods to prioritize is essential. Incorporating these eight highly nutritious, accessible options into your meal planning can make a substantial difference. Here's an expanded overview of each of these top foods, how they work, and practical ways to include them in your diet.
Eating Vegetables as a Foundation for Blood Sugar Regulation
Vegetables are the cornerstone of any healthy diet, especially for blood sugar management. They are low in calories and carbohydrates but rich in fiber, vitamins, and minerals—all of which contribute to stabilized blood glucose levels. Incorporating a variety of vegetables ensures you receive a broad spectrum of nutrients necessary for overall health.
Focusing on vegetables like mushrooms, tomatoes, bean sprouts, onions, and leafy greens allows for effective blood sugar control. These vegetables are low in carbs and have a low glycemic index, meaning they won't cause rapid spikes in blood sugar. Use fresh herbs and spices to flavor your vegetable dishes without added sugars or unhealthy fats, making your meals both tasty and healthful.
Broccoli: An Excellent Choice for Heart and Blood Sugar Health
Broccoli is often recommended by healthcare professionals for individuals with elevated blood sugar levels due to its potent health benefits. This cruciferous vegetable is packed with vitamin C—providing more than oranges—and high levels of beta-carotene, which aids in vitamin A production. Its antioxidant properties help combat oxidative stress, a common issue related to diabetes and cardiovascular diseases.
Research suggests that regularly consuming broccoli can lower the risk of heart disease, a common complication in diabetes. It can be enjoyed steamed as a side, roasted with olive oil, or blended into nutrient-rich soups. The versatility of broccoli makes it easy to include in various meals, thereby enhancing your overall health profile.
Avocados: Enhancing Insulin Sensitivity and Metabolic Health
Known for their heart-healthy monounsaturated fats, avocados are a powerhouse for metabolic health. They have been shown to boost insulin efficiency, helping your body utilize blood sugar more effectively. Including avocados in your diet not only supports blood sugar control but also reduces the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
Enjoy sliced avocados on toast, add them to salads, or blend into smoothies. Their creamy texture and mild flavor make them a versatile addition to many dishes. Regular consumption can promote better metabolic function and contribute to weight management, essential factors in diabetes control.
Asparagus: A Low-Carb, Diabetic-Friendly Vegetable
An excellent choice for those monitoring blood sugar, asparagus contains only about 5 grams of carbs per serving. It is rich in nutrients that support insulin production and overall glucose regulation. Its natural diuretic properties also help reduce bloating and improve metabolic health.
Incorporate asparagus into your meals by grilling, steaming, or adding it to stir-fries and salads. The vegetable's delicate flavor and nutritional profile make it a valuable addition to any diabetic-friendly diet.
Beans: High in Dietary Fiber for Blood Sugar Stability
Beans such as black beans, lentils, chickpeas, and kidney beans are excellent sources of dietary fiber, which plays a crucial role in slowing carbohydrate absorption and preventing blood sugar spikes. Their high protein content makes them a nourishing option for main courses or side dishes.
Low in sodium and versatile in preparation, beans can be added to salads, stews, or made into dips. Their fiber aids digestion, enhances satiety, and supports sustained energy levels throughout the day.
Blueberries: Rich in Flavonoids for Blood Sugar Control
Blueberries are a delicious and nutritious fruit rich in flavonoids and antioxidants such as anthocyanins. These compounds help lower inflammation and improve insulin sensitivity, making blueberries beneficial for preventing and managing elevated blood sugar levels.
Regular intake of blueberries has been associated with a reduced risk of developing type 2 diabetes and improved glycemic control in those already diagnosed. Enjoy them fresh, add to cereals, or blend into smoothies for a flavorful health boost.
Fish: Lean Protein and Omega-3s for Glucose Regulation
Fish, especially varieties like salmon, sardines, mackerel, and herring, is an excellent source of lean protein and omega-3 fatty acids. These nutrients are crucial for improving insulin sensitivity, reducing inflammation, and supporting cardiovascular health—common concerns for individuals with elevated blood sugar.
Including fish in your diet at least twice a week can contribute to better blood glucose management. Prepare grilled, baked, or steamed fish to retain its nutritional integrity and maximize health benefits.
Leafy Greens: Nutrient-Dense Vegetables for Daily Use
Vegetables like kale, spinach, Swiss chard, and collard greens are rich in fiber, magnesium, and antioxidants—all of which support blood sugar regulation. Their low carbohydrate content makes them ideal for daily consumption.
These greens can be roasted, sautéed, or added raw to salads and wraps. Their high nutrient density enhances overall health and complements other protein sources for a balanced, blood-sugar-friendly meal.
To optimize blood sugar control, combine these foods with whole grains, consistent physical activity, and proper hydration. Creating flavorful, nutrient-dense meals will empower you on your health journey to maintain balanced blood glucose levels and reduce the risk of complications related to high blood sugar.