Essential Foods for Naturally Managing Blood Glucose Levels: A Comprehensive Guide
Discover the top foods that naturally help regulate blood glucose levels. This comprehensive guide highlights nutrient-dense vegetables, fruits, healthy fats, and lean proteins that support diabetes management and metabolic health. Incorporate these foods into your daily diet along with lifestyle changes for optimal blood sugar control and improved overall wellness.

Essential Foods for Naturally Managing Blood Glucose Levels: A Comprehensive Guide
Maintaining optimal blood sugar levels is crucial for individuals dealing with diabetes and those seeking to prevent blood sugar spikes. Adopting a nutritious, balanced diet that emphasizes specific foods can significantly influence your body's ability to regulate glucose effectively. Proper nutrition, coupled with lifestyle modifications such as regular exercise, stress management, and proper hydration, forms the cornerstone of blood sugar control.
This detailed guide explores the top eight foods that are renowned for their ability to help manage blood glucose levels naturally. These foods are easy to incorporate into everyday meals, are widely available, and have scientifically supported benefits for blood sugar regulation. By understanding these dietary choices, you can design a meal plan that promotes better metabolic health, supports weight loss where necessary, and enhances overall well-being.
1. Low-Carbohydrate Vegetables Are Essential for Blood Sugar Stability
Vegetables should form a core component of any blood sugar management plan due to their rich nutrient profile and low glycemic index. Focus on a variety of non-starchy vegetables like mushrooms, cherry tomatoes, sprouts, onions, and leafy greens. These vegetables are low in carbohydrates but high in fiber, vitamins, and minerals, which help slow down glucose absorption and prevent sudden spikes.
Cooking methods matter—prefer steaming, roasting, or sautéing with minimal oil to preserve nutrients. Incorporating herbs and spices such as turmeric, garlic, or cumin can add flavor and may offer anti-inflammatory benefits, further aiding metabolic health.
2. Broccoli: A Superfood for Heart and Blood Glucose Health
Broccoli is packed with nutrients like vitamin C, vitamin K, chromium, and beta-carotene. Its antioxidant properties are compelling for preventing oxidative stress, which is linked to insulin resistance. Regular consumption of broccoli—either steamed, roasted, or blended into soups—can support cardiovascular health and enhance blood sugar control. Additionally, its fiber content promotes satiety, reducing overeating and aiding weight management.
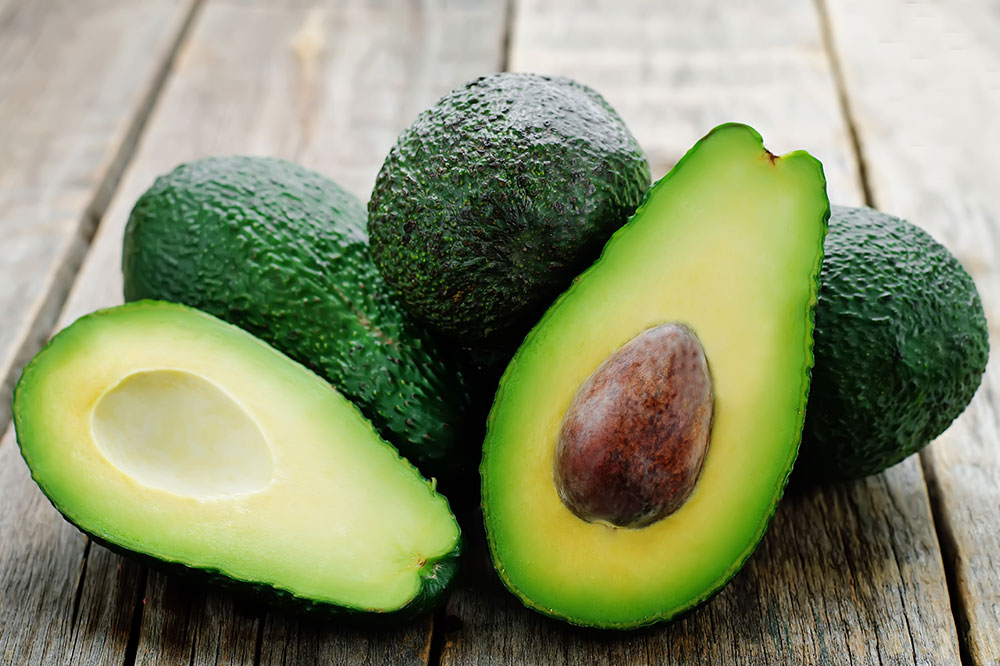
3. Avocado: A Fat-Healthy Food Enhancing Insulin Function
Avocados are a rich source of monounsaturated fats, which play a vital role in heart health. These healthy fats are also linked to improved insulin sensitivity, making them an excellent choice for managing blood glucose levels. Whether added to salads, smashed onto toast, or blended into smoothies, avocados provide a creamy texture coupled with numerous health benefits, including lowering bad cholesterol and reducing inflammation.
4. Asparagus: A Low-Calorie, Diabetic-Friendly Vegetable
Asparagus contains just about 5 grams of carbohydrates per serving, making it ideal for blood sugar regulation. Its high fiber and water content help stabilize glucose levels while supporting digestion. Asparagus also contains nutrients like vitamins A, C, E, and K, along with folate, contributing to overall metabolic health. Enjoy it grilled, steamed, or incorporated into stir-fries for a healthy, insulin-supportive meal.
5. Beans: A Rich Source of Dietary Fiber
Beans—including black beans, lentils, chickpeas, and kidney beans—are excellent sources of soluble fiber, which slows carbohydrate digestion and absorption, leading to steadier blood sugar levels. They are also high in protein, making them a filling and nutritious addition to various dishes. Opt for low-sodium canned beans or cook dried beans without added salt to maximize health benefits. Incorporate beans into salads, soups, or as side dishes to enhance satiety and support glucose regulation.
6. Blueberries: Nature’s Antioxidants for Blood Sugar Control
Blueberries contain flavonoids, particularly anthocyanins, known for their antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. These compounds help reduce the risk of heightened blood sugar levels after meals, and ongoing research suggests they can improve insulin sensitivity. Regular inclusion of blueberries in your diet—whether fresh, frozen, or added to cereals and smoothies—may also provide neuroprotective benefits, supporting overall metabolic health.
7. Lean Fish: A Source of Heart-Healthy Protein
Fish such as salmon, sardines, trout, and herring are rich in omega-3 fatty acids. These fats are beneficial for reducing inflammation and improving lipid profiles in the blood, which are crucial for those managing diabetes. Lean fish are low in saturated fat and provide high-quality protein, essential for muscle maintenance and metabolic regulation. Incorporate fish into your diet at least twice a week by grilling, baking, or steaming for optimal health benefits.
8. Leafy Greens: Foundation for Blood Sugar Balance
Dark leafy greens like kale, spinach, arugula, and chard are nutrient-dense and low in calories and carbohydrates. They contain magnesium, which enhances insulin sensitivity, and fiber that promotes satiety. Include these greens in salads, wraps, or sautéed as side dishes. Pairing leafy greens with healthy fats and proteins enhances nutrient absorption and supports stable blood sugar levels.
In addition to dietary choices, regular physical activity, stress reduction, quality sleep, and hydration are essential components of a comprehensive blood sugar management plan. Some individuals may also consider natural supplements like Glucocil, which aids in reducing excess glucose and improving cellular glucose utilization, complementing dietary efforts.
Remember, individual needs vary, and consulting with healthcare professionals or registered dietitians can help tailor an effective, personalized plan for blood sugar regulation. By making informed food choices and adopting supportive lifestyle practices, you can significantly improve your health outcomes and overall quality of life.