Comprehensive Safety Guide for Optimizing Ozempic Use in Diabetes Management
This comprehensive guide explores the safe and effective use of Ozempic (Semaglutide) for type 2 diabetes management. It covers essential safety precautions, potential side effects, contraindications, and tips for optimal treatment adherence. With detailed insights into the medication’s mechanism, proper administration, and risk factors, patients and healthcare providers can ensure safe usage, prevent complications, and improve health outcomes. This article emphasizes the importance of personalized care and regular medical monitoring to maximize the benefits of Ozempic in controlling blood glucose levels and supporting overall wellness.
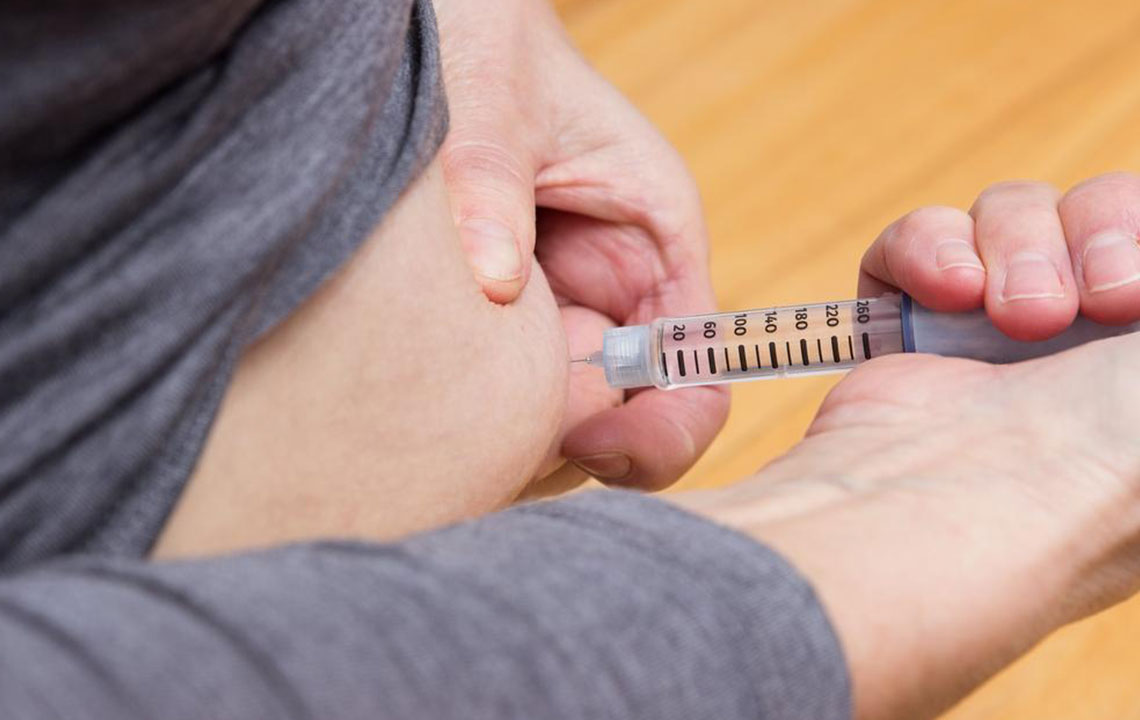
Essential Safety Strategies When Using Ozempic for Diabetes Control
Medical science has made remarkable progress in tackling many life-threatening diseases, dramatically reducing mortality rates and improving patient outcomes. However, chronic conditions such as diabetes mellitus continue to pose significant health challenges worldwide. Managing these long-term illnesses effectively is vital for enhancing quality of life, preventing complications, and maintaining overall health. Among the various treatment options available, medications like Ozempic (Semaglutide) have gained prominence for their role in controlling type 2 diabetes, especially when lifestyle modifications and other medications are insufficient.
Diabetes mellitus is a complex metabolic disorder characterized by elevated blood glucose levels resulting from inadequate insulin production, impaired insulin effectiveness, or both. The condition affects millions globally, with estimates indicating around 100 million individuals in the United States alone living with either diagnosed diabetes or prediabetes. These numbers underscore the importance of effective management strategies that incorporate medication, diet, and lifestyle changes.
Multiple factors contribute to the development of diabetes, including genetics, poor dietary habits, sedentary lifestyles, obesity, and other environmental influences. While traditional treatments like metformin, insulin injections, and sulfonylureas have been mainstays, newer therapeutic agents like Ozempic have revolutionized management approaches. Ozempic, known generically as Semaglutide, is a glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist that enhances the body's own insulin secretion based on blood glucose levels. This medication is particularly suitable for patients with type 2 diabetes who require additional control beyond diet and exercise or who experience difficulty managing blood sugar levels with traditional drugs.
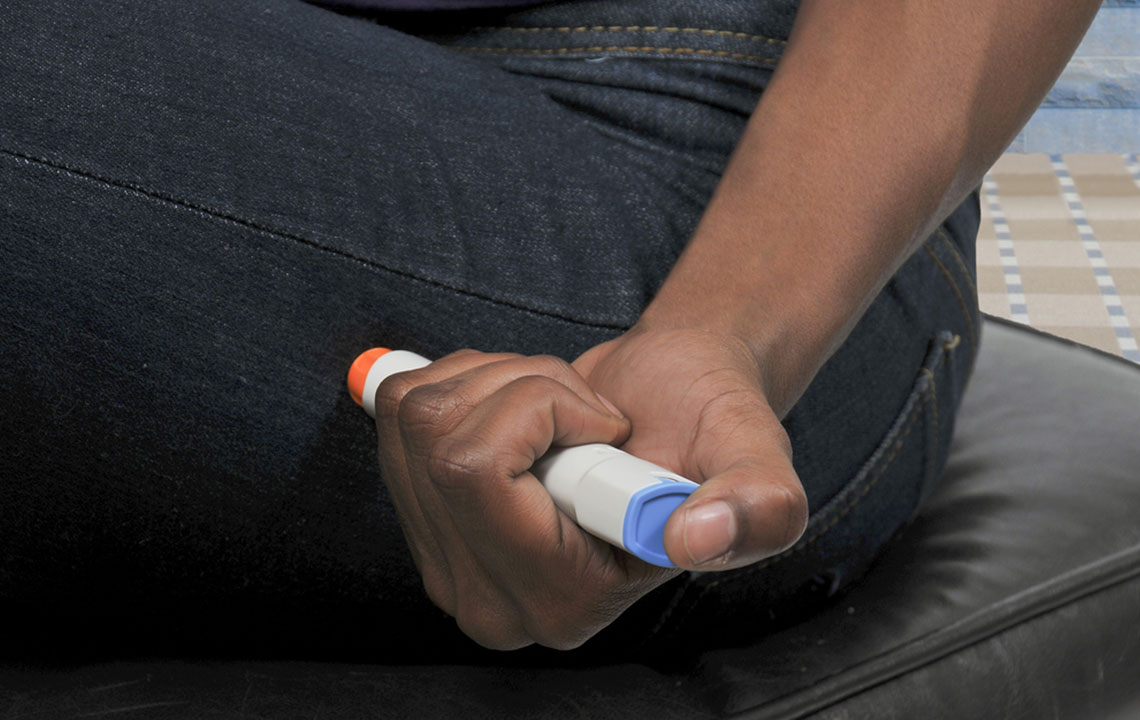
Ozempic is administered subcutaneously via a prefilled pen, typically starting at a dose of 0.25 mg weekly. Over time, the dosage may be adjusted to optimize efficacy based on individual response and tolerability. The mechanism of action involves mimicking the incretin hormones, which stimulate insulin release, suppress glucagon secretion, slow gastric emptying, and promote a feeling of fullness, thereby aiding in weight loss—a beneficial secondary effect for many with type 2 diabetes.
Precautions and Safety Considerations for Ozempic Users
Despite its advantages, Ozempic must be used cautiously, considering potential side effects and contraindications. Patients with existing heart conditions should seek medical advice before starting therapy, as the medication can induce a slight increase in heart rate and may influence cardiac rhythm. Regular monitoring is advisable for individuals with cardiovascular risks to ensure safety.
Another critical safety aspect involves the risk of hypoglycemia. When combined with other antidiabetic medications such as insulin or sulfonylureas, Ozempic can lower blood sugar levels excessively, leading to hypoglycemia. Symptoms include dizziness, sweating, rapid heartbeat, weakness, and in severe cases, loss of consciousness. Patients must be aware of these signs and work closely with their healthcare providers to adjust doses appropriately.
Patients with a personal or family history of medullary thyroid carcinoma or Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia type 2 (MEN 2) should avoid Ozempic. Animal studies have suggested a potential increase in thyroid tumors, though data in humans remains limited. As such, screening and risk assessment are essential before initiating therapy.
Individuals with renal impairments or compromised kidney function should consult their healthcare providers, as Ozempic can influence renal parameters. Proper kidney function assessment is necessary to prevent adverse outcomes. Women who are pregnant or breastfeeding should abstain from using Ozempic unless explicitly prescribed by their doctor. Its safety profile during pregnancy and lactation has not been established, and alternative treatments are usually recommended during these periods.
To maintain safety, never share your Ozempic pen with others, as this can transmit infections and lead to serious health risks. Patients should also adhere strictly to prescribed dosing schedules and avoid skipping injections or adjusting doses without medical approval. Regular follow-up visits are crucial for monitoring effectiveness, side effects, and overall health status.
In summary, Ozempic offers a promising avenue for managing type 2 diabetes but necessitates careful consideration of individual health profiles. Following safety guidelines, being vigilant about side effects, and maintaining ongoing communication with healthcare professionals are key to maximizing benefits while minimizing risks. With responsible use, Ozempic can significantly improve blood sugar control, support weight management, and enhance overall health outcomes for those living with diabetes.