Essential Nutrients and Dietary Strategies to Alleviate Eczema Symptoms
Discover the top nutrients and dietary tips to reduce eczema symptoms naturally. Learn how omega-3s, probiotics, vitamins, and anti-inflammatory foods can help soothe irritated skin, decrease inflammation, and improve overall skin health. This comprehensive guide provides practical dietary strategies to manage eczema effectively and enhance your quality of life.

Essential Nutrients and Dietary Strategies to Alleviate Eczema Symptoms
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a persistent and often bothersome inflammatory skin condition that mainly manifests through dryness, redness, itching, and irritation. For millions worldwide, managing eczema involves a comprehensive approach that includes skincare routines, lifestyle adjustments, and crucially, dietary modifications. Understanding the impact of specific foods and nutrients on eczema can be transformative in controlling flare-ups and improving overall skin health.
This detailed guide explores the vital nutrients that aid in reducing inflammation, soothing irritated skin, and supporting immune health — particularly focusing on foods that are beneficial and potential dietary triggers to avoid. By incorporating these nutrients into your daily diet, you can significantly diminish the frequency and severity of eczema symptoms, leading to a more comfortable and healthier life.
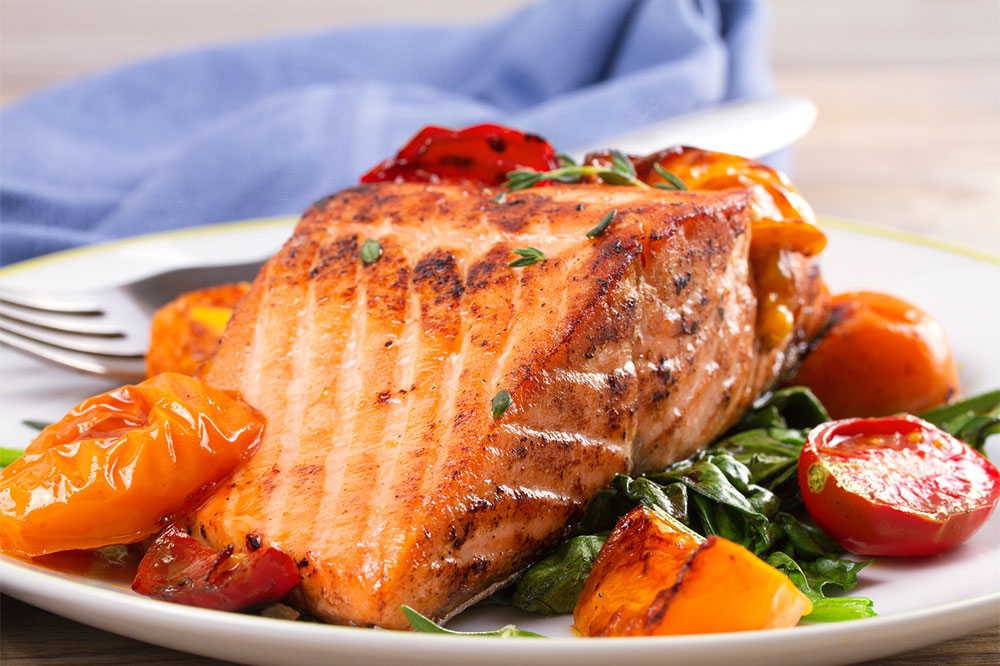
Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, such as oily fish—salmon, mackerel, sardines—as well as plant-based sources like chia seeds and flaxseeds, have been extensively studied for their anti-inflammatory properties. These healthy fats contribute to reducing skin dryness and inflammation during eczema flare-ups. For many, supplementing with fish oil capsules can be an effective way to boost omega-3 intake, especially if dietary sources are limited or insufficient.
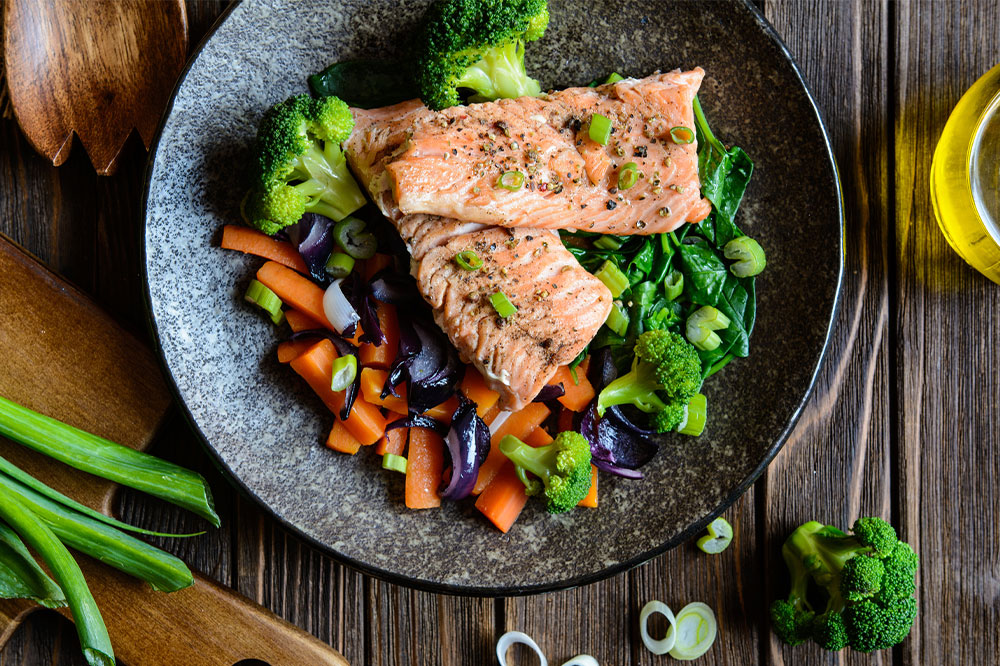
Anti-inflammatory Foods
Managing inflammation is central to controlling eczema symptoms. Dietary choices play a pivotal role; foods rich in antioxidants help neutralize free radicals that can exacerbate skin inflammation. Emphasize vegetables like spinach, kale, and broccoli; lean proteins such as chicken and turkey; and whole grains like brown rice and oats. Limiting intake of dairy products and red meats, which may trigger allergic reactions or inflammation in some individuals, can further support skin health. Incorporating fatty fish, flaxseeds, and nuts into meals provides essential nutrients that promote skin repair and resilience.
Probiotics
The balance of gut bacteria significantly influences immune function and allergic response. Consuming probiotic-rich foods such as yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, and kimchi can enhance gut health and strengthen immune defenses. These beneficial microbes help reduce allergic sensitivities and inflammatory responses, which are often linked to eczema flare-ups. Probiotic supplements are also available and may offer additional support for those with compromised gut flora.
Essential Vitamins
Vitamins A, E, and D are critical for maintaining healthy skin and supporting immune responses. Vitamin A helps repair skin tissue, while Vitamin E combats oxidative stress, and Vitamin D modulates immune activity. Including a variety of colorful fruits and vegetables—carrots, sweet potatoes, spinach, berries—and seeds like sunflower and pumpkin can boost vitamin intake. Healthcare professionals may recommend supplements when dietary sources are inadequate or if deficiency is diagnosed.
Flavonoids
These plant compounds, abundant in berries, apples, onions, and dark chocolate, exhibit anti-inflammatory and antihistamine properties. Flavonoids can help reduce histamine levels, thereby alleviating itching and swelling associated with eczema. Regular consumption of flavonoid-rich foods supports immune regulation and skin barrier function, leading to fewer outbreaks and better overall skin health.
Potassium
Adequate intake of potassium-rich foods like bananas, sweet potatoes, avocados, and spinach can help regulate fluid balance and reduce inflammation. Potassium's role in maintaining cellular health extends to supporting skin repair and reducing eczema discomfort. Prioritizing a diet loaded with colorful vegetables, healthy fats, and whole grains ensures sufficient potassium levels to aid in eczema management.
Gluten-Free Options
Some individuals find that eliminating gluten from their diet reduces eczema severity. Foods made from gluten-free grains such as rice, corn, millet, and quinoa are widely available and safe alternatives. Many meal delivery services now cater to gluten-free diets, making it easier to adhere to this dietary adjustment. For those considering a gluten-free lifestyle, consulting a healthcare provider or a registered dietitian is recommended to ensure nutritional adequacy.
These dietary strategies and nutrients form a foundation for managing eczema effectively. While diet plays a vital role, individual responses vary, and it is essential to tailor nutrition plans to personal needs. Consulting with a healthcare professional, dermatologist, or nutritionist can help develop a personalized plan that considers specific triggers, nutritional requirements, and lifestyle factors, paving the way for healthier skin and improved quality of life.