Comprehensive Dietary Strategies for Eczema Management: Foods to Eat and Avoid
This comprehensive guide explores essential dietary strategies for eczema sufferers, highlighting beneficial foods and those to avoid. Incorporating anti-inflammatory, nutrient-rich foods like leafy greens, fatty fish, and nuts can help reduce skin inflammation and promote healing. Conversely, limiting or avoiding common triggers such as dairy, eggs, gluten, and processed sugar is crucial for managing flare-ups. Tailoring your diet through allergy testing and consultation with healthcare professionals can enhance skin health and improve quality of life. Proper nutrition supports immune function, reduces inflammation, and promotes healthier skin from within.

Optimizing Eczema Management through Diet: Essential Foods to Incorporate and Avoid
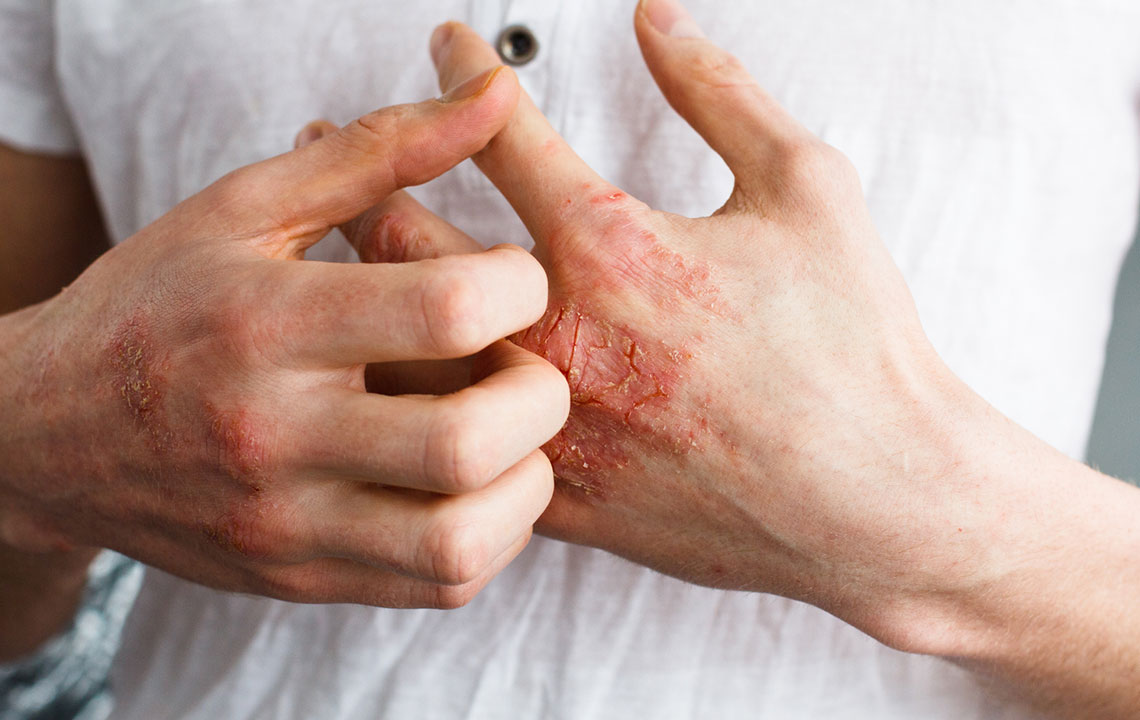
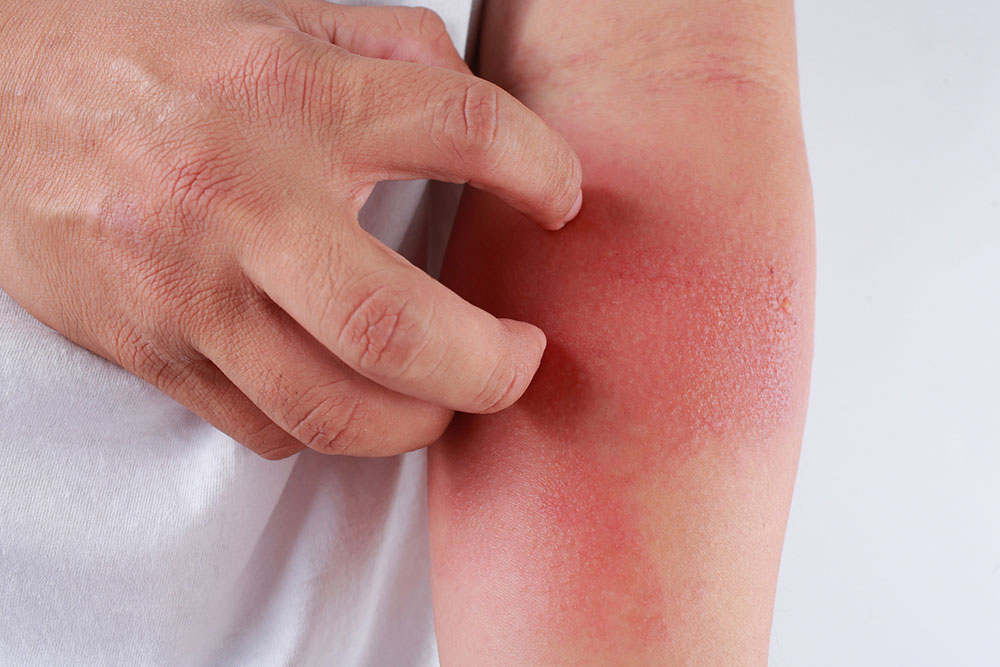
Eczema, medically known as atopic dermatitis, is a prevalent skin condition that manifests through inflamed, intensely itchy, cracked, and sometimes blistered skin. The affected skin often becomes rough, sensitive, and prone to irritation. According to epidemiological studies, approximately 30% of the American population experiences eczema at some point in their lives, making it a common concern among individuals of various ages. While eczema can be a chronic and persistent condition, many sufferers find relief and even achieve remission through a combination of lifestyle modifications, medication, and dietary adjustments. Since inflammation plays a central role in eczema's pathology, paying close attention to dietary choices can be a powerful tool in alleviating symptoms and improving overall skin health.
This comprehensive guide delves into foods that can soothe eczema symptoms and those that are best avoided or limited to prevent flare-ups. Proper nutrition, combined with medical advice, can significantly enhance quality of life for those living with eczema.
Foods to Embrace for Eczema Relief
Vegetables: Incorporate an abundance of nutrient-rich green leafy vegetables such as spinach, kale, and Swiss chard. These vegetables provide antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals essential for supporting skin integrity and reducing oxidative stress, which can exacerbate inflammation.
Whole grains: Opt for unrefined, fiber-dense grains like oats, brown rice, and quinoa. These foods help lower inflammatory responses compared to refined carbohydrates found in white bread and processed cereals, promoting a healthier immune system and skin barrier function.
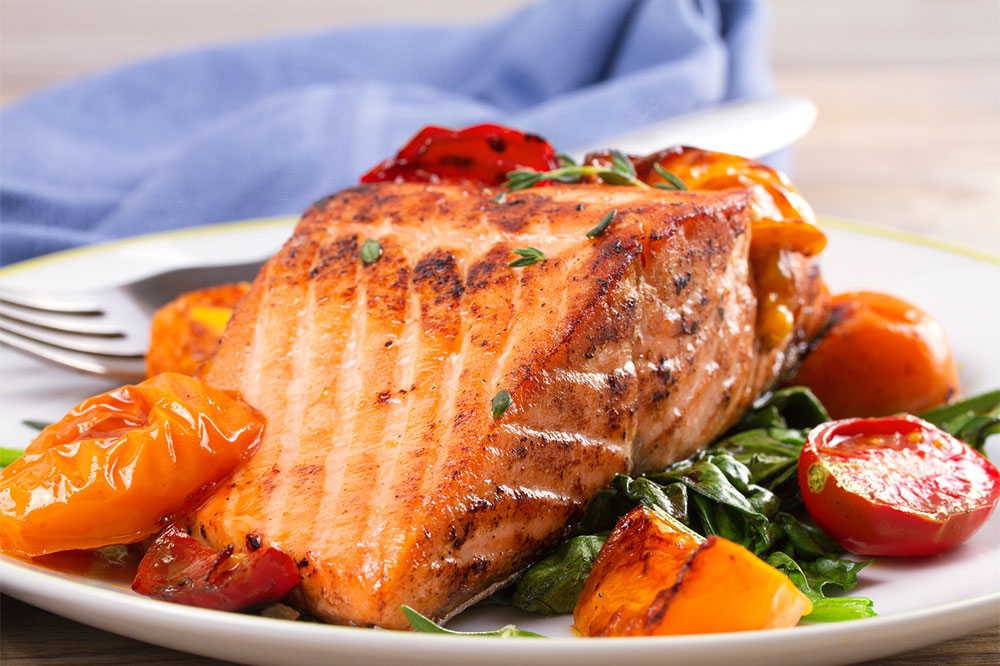
Seafood rich in omega-3 fatty acids: Including fatty fish such as salmon, mackerel, sardines, and tuna in your diet supplies high levels of omega-3 fatty acids. These nutrients are well-known for their anti-inflammatory properties, which can reduce skin inflammation and decrease the severity of eczema symptoms.
Nuts and seeds: Almonds, walnuts, flaxseeds, and chia seeds are excellent sources of healthy fats, antioxidants, and micronutrients that support immune health and combat inflammatory processes.
Vitamins and minerals: Ensure your diet contains a variety of nutrient-dense foods rich in vitamins A, C, E, and D, as well as flavonoids and essential minerals like zinc and magnesium. These nutrients are critical for skin repair, immune support, and reduction of inflammation. Incorporate foods like carrots, bell peppers, citrus fruits, and pumpkin seeds into your meals.
Furthermore, foods high in potassium, such as bananas, sweet potatoes, and avocados, can help balance electrolytes and reduce inflammation. Fiber-rich foods like oats and legumes support gut health, which is increasingly recognized for its role in immune function and skin health. Emerging research also suggests that probiotic-rich foods like yogurt, kefir, and fermented vegetables may assist in managing eczema by promoting a healthy gut microbiome and modulating immune responses.
Foods to Limit or Steer Clear of for Eczema Control
Eggs: Some individuals with eczema report worsening symptoms after consuming eggs, possibly due to sensitivities or allergies.
Milk and dairy products: Dairy can trigger inflammation or allergic reactions in susceptible individuals, leading to flare-ups.
Soy-based foods: Soy products have been linked to allergic responses that may exacerbate eczema symptoms in certain people.
Wheat and gluten: Gluten-containing grains might trigger eczema flare-ups in individuals with gluten sensitivities or celiac disease.
Refined sugars and processed foods: Excessive consumption of refined sugars and heavily processed snacks can promote systemic inflammation. Opt for natural sweeteners like honey when needed.
Citrus fruits and acidic foods: Oranges, grapefruits, grapes, and tomatoes may irritate sensitive skin or trigger flare-ups in some individuals.
Cruciferous vegetables: Vegetables like broccoli, cabbage, and cauliflower might irritate some eczema sufferers, though this varies depending on individual sensitivities.
Since certain foods have the potential to trigger or worsen eczema symptoms, seeking allergy testing or consultation with a healthcare professional is highly recommended. Tailoring your diet based on personal sensitivities can lead to significant improvement. Maintaining a diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods, ensuring proper hydration, and integrating medical treatments as prescribed can collectively make a profound difference in managing eczema. Prioritizing nutrient-dense, skin-friendly foods not only helps control symptoms but also promotes healthier skin and overall well-being.