Comprehensive Guide to Managing Blood Sugar After Excessive Sugar Consumption
This comprehensive guide offers practical strategies for managing blood sugar levels after consuming excessive sugar. It emphasizes hydration, exercise, monitoring, meal planning, and low-GI foods to help reduce spikes and promote overall health. Suitable for individuals with diabetes or those looking to stabilize their blood glucose, this article provides science-backed tips to prevent complications and support metabolic health effectively.

Comprehensive Guide to Managing Blood Sugar After Excessive Sugar Consumption
Indulging in sweet treats like desserts, candies, or sugary beverages during special occasions or even as daily snacks is a common practice for many. While enjoying these foods occasionally is usually harmless for most people, for individuals living with diabetes or those with insulin sensitivity, consuming too much sugar can lead to sudden and significant spikes in blood glucose levels. These spikes can pose health risks, including long-term complications such as nerve damage, kidney issues, and cardiovascular problems. Fortunately, understanding and implementing effective strategies can help mitigate these effects, ensuring better blood sugar management even after a sugar overload. This article explores practical, scientifically supported methods to regain control over blood glucose levels and promote overall health after consuming excess sugar.
Prioritize Hydration to Support Blood Sugar Regulation
When you consume a large amount of sugar, your pancreas responds by increasing insulin production to help cells absorb glucose. This process enhances urination, which can quickly lead to dehydration if you're not drinking enough fluids. Dehydration not only worsens your overall health but also impairs your body’s ability to eliminate excess sugar through urine. Therefore, staying well-hydrated is crucial. Drinking plenty of water helps dilute the concentration of sugar in your bloodstream, making it easier for your kidneys to process and eliminate the excess glucose. Adequate hydration supports kidney function, prevents blood thickening, and maintains optimal metabolic functioning—all vital for stabilizing blood sugar levels after a spike.
Engage in Physical Activity to Boost Metabolism
Physical activity plays a pivotal role in managing post-sugar consumption blood glucose spikes. Moving your body—even light movements like walking or stretching—releases endorphins that elevate mood and increase energy. More importantly, exercise enhances your muscles' ability to absorb and burn glucose more efficiently, reducing blood sugar levels more rapidly. This process not only helps offset the immediate impact of sugar overload but also improves insulin sensitivity over time. Regular activity can prevent the onset of insulin resistance and make it easier to control blood sugar in the long run. After a sugar-rich meal or snack, even a brief walk or gentle workout session can significantly help stabilize glucose levels, reduce symptoms such as fatigue, and prevent feelings of irritability or sluggishness associated with hyperglycemia.
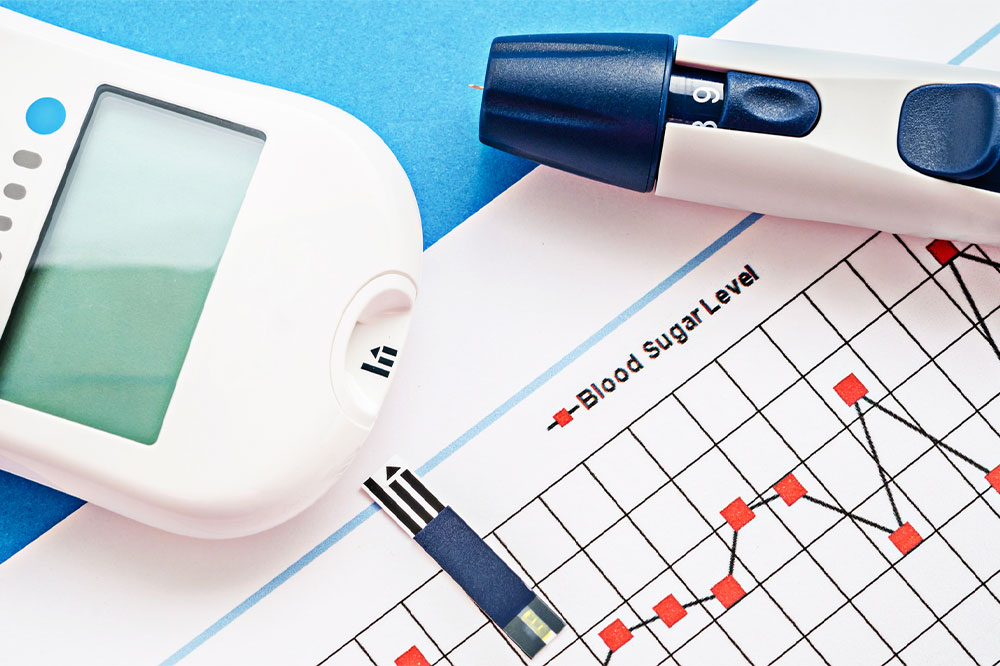
Monitor Blood Sugar Levels Diligently
Keeping a close eye on your blood glucose levels after consuming excess sugar is essential, especially if you have diabetes or prediabetes. Elevated blood sugar can result in hyperglycemia, which manifests through various symptoms including extreme thirst, frequent urination, fatigue, dizziness, and mood swings. Regular monitoring enables you to assess how your body responds to high sugar intake, allowing for timely adjustments in diet or medication. Devices such as glucometers or continuous glucose monitors provide real-time data, helping you make informed decisions. If your blood sugar remains elevated for an extended period or reaches dangerously high levels, consult your healthcare provider immediately. They might recommend adjustments in your medication regimen, insulin therapy, or other interventions to better manage glucose levels.
For severe cases, healthcare professionals may recommend specific insulin dosages or adjustments in other diabetes management medications to promptly bring down high blood glucose levels and prevent complications.
Plan Your Future Meals Strategically
After indulging in sweets or sugary drinks, it’s imperative not to skip subsequent meals. Instead, aim to distribute your carbohydrate intake evenly throughout the day. Consuming large amounts of carbs in one sitting can cause further blood sugar spikes, whereas spacing meals helps your body process carbohydrates more smoothly. Incorporate high-fiber foods and lean proteins into your diet, which can slow down carbohydrate absorption and reduce post-meal blood sugar surges. Eating smaller, balanced meals more frequently can stabilize your blood glucose, prevent cravings, and support ongoing metabolic health. Be mindful of portion sizes and opt for nutrient-dense foods that provide essential vitamins and minerals while maintaining blood sugar stability.
Choose Low-Glycemic Index Foods for Better Stability
Selecting foods with a low glycemic index (GI) is an effective strategy to prevent rapid blood sugar increases. Low-GI foods include a variety of vegetables, whole grains like oats and brown rice, legumes such as lentils and chickpeas, and organic dairy products. These foods contain fewer simple carbohydrates and are rich in fiber, which slows digestion and glucose absorption. Consuming low-GI foods helps maintain stable blood sugar levels, supports digestion, reduces inflammation, and boosts immunity. Additionally, they help diminish cravings for sugary foods, promoting better adherence to a healthy diet. Over time, prioritizing low-GI options can enhance insulin sensitivity and reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes or other metabolic disorders.
In conclusion, managing blood sugar after consuming excess sugar involves a combination of hydration, physical activity, vigilant monitoring, meal planning, and choosing the right foods. By adopting these strategies, individuals can effectively control their blood glucose levels, minimize health risks, and promote overall well-being. Educating oneself about dietary choices and lifestyle modifications is crucial for long-term diabetes management and maintaining optimal health.