Understanding the Top 5 Causes of Fungal Infections and How to Effectively Prevent Them
This comprehensive article explores the top five common causes of fungal infections, including athlete’s foot, ringworm, jock itch, yeast infections, and vaginal yeast infections. It provides detailed insights into their causes, symptoms, and practical prevention tips to promote better health and avoid recurring issues. Understanding these causes empowers individuals to take proactive steps, ensuring effective management and minimizing the risk of persistent fungal infections, especially in vulnerable populations.
Understanding the Top 5 Causes of Fungal Infections and How to Effectively Prevent Them
Fungal infections are a common health concern that can affect various parts of the body, leading to discomfort and, if left untreated, potential health complications. Fungi are a diverse group of organisms; some are beneficial and contribute to processes like fermentation, while others can be harmful and cause infections. Our bodies naturally host some fungi without causing issues, but certain conditions can promote the growth of pathogenic fungi, resulting in infections. Recognizing the primary causes of these infections is crucial for early intervention and prevention. In this comprehensive guide, we explore the top five most common fungal infections, their underlying causes, and effective strategies to prevent them from affecting your health and well-being.
Fungal infections tend to be persistent, with recurrence being common, particularly among individuals with weakened immune systems, those undergoing prolonged antibiotic therapy, or with underlying health conditions like diabetes. While some fungal infections are superficial, affecting skin and mucous membranes, others can become systemic, affecting internal organs. Therefore, understanding their causes and adopting preventive measures is vital for maintaining optimal health.
1. Athlete’s Foot (Tinea Pedis): Causes and Prevention
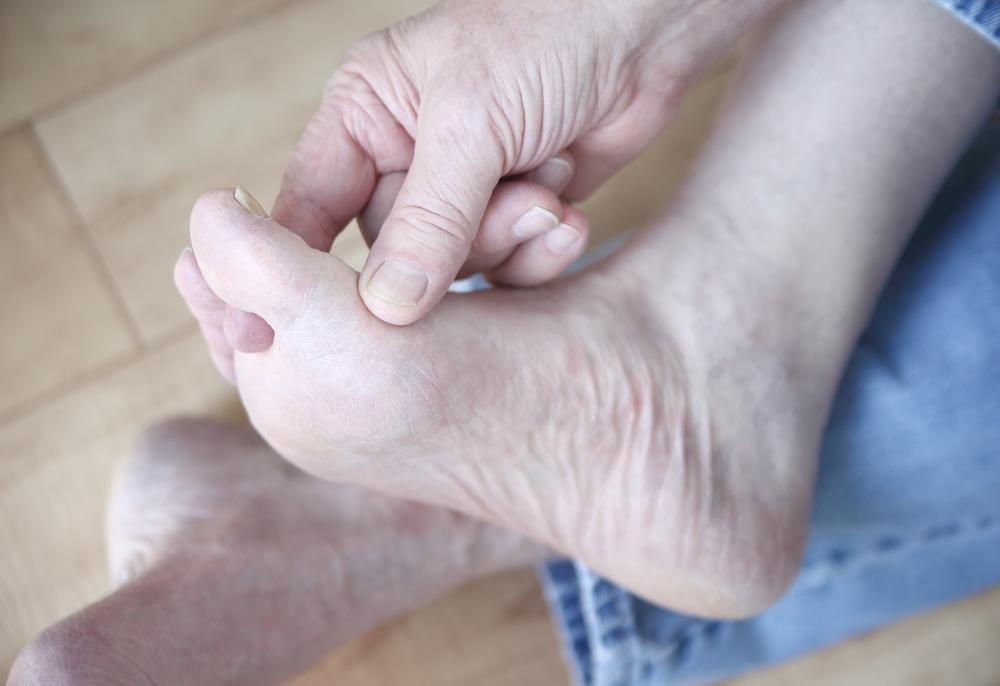
Athlete’s foot, scientifically known as tinea pedis, is a highly prevalent fungal infection affecting the skin of the feet. The causative fungi thrive in warm, moist environments, especially inside shoes, socks, and communal areas like showers and swimming pools. This condition is predominantly seen among athletes, but anyone who frequently wears tight, non-breathable footwear or shares communal facilities is at risk. The fungi infect the outer layer of skin, causing symptoms such as itching, redness, swelling, and blisters, which can sometimes lead to secondary bacterial infections if scratched or not properly treated.
Factors contributing to athlete’s foot include excessive sweating, poor foot hygiene, wearing damp or contaminated footwear, and walking barefoot in public showers. To prevent this common infection, it is essential to practice good foot hygiene: wash feet thoroughly daily, dry them completely, and ensure footwear is breathable and dry before wearing. Using antifungal powders or sprays can further reduce the risk, especially if you are prone to excessive sweating or participate in activities that increase foot moisture. Avoid sharing shoes, socks, or towels, and wear protective footwear in communal showers or pool areas to minimize exposure.
2. Ringworm (Tinea Corporis): Causes and Prevention
Despite its name, ringworm is a fungal infection affecting the skin, hair, or nails caused by dermatophyte fungi. This highly contagious pathogen spreads easily through direct contact with infected individuals, animals, or contaminated objects such as clothing, bedding, towels, or grooming tools. The hallmark of ringworm is the appearance of circular, red or scaly patches with a clear center, often accompanied by itching and inflammation. The infection can affect any age group but is particularly common in children and athletes.
Preventing ringworm involves maintaining proper hygiene: wash hands regularly, keep skin dry and clean, and avoid sharing personal items. Treating infected pets promptly can also prevent transmission, as animals can be asymptomatic carriers. It’s important to isolate contaminated laundry and bedding, wash them in hot water, and disinfect surfaces diligently. If infection occurs, seek early medical treatment with topical or oral antifungal medications, which help eliminate the fungi and prevent spreading to others or re-infection.
3. Jock Itch (Tinea Cruris): Causes and Prevention
Jock itch, medically known as tinea cruris, primarily affects the groin, inner thighs, and buttocks. This fungal infection develops in warm, damp, and sweaty areas where skin folds trap moisture, creating an ideal environment for fungi to thrive. People who sweat excessively, wear tight clothing, or participate in physical activities are at increased risk. Symptoms include itchy, red, and irritated skin that may develop a rash with a defined border.
Effective prevention strategies include wearing loose, breathable clothing, especially during physical activity, showering promptly after sweating, and thoroughly drying affected areas. Maintaining good personal hygiene, particularly in the groin and inner thigh regions, is critical. Avoid sharing towels or clothing, and wash workout gear regularly. Over-the-counter antifungal creams or powders can help manage early signs of infection. For recurrent cases, consulting healthcare professionals for persistent or severe infections is recommended to prevent complications.
4. Yeast Infections (Candidiasis): Causes and Prevention
Candidiasis refers to infections caused by the overgrowth of Candida yeasts, particularly Candida albicans. These infections commonly occur in moist, warm areas of the body, such as the armpits, groin, mouth, and skin folds. Factors like a weakened immune system, antibiotic use, diabetes, obesity, or hormonal changes can disrupt the natural microbial balance, promoting yeast overgrowth. Symptoms include redness, itching, irritation, and sometimes discharge or swelling.
To prevent yeast infections, maintaining dry and clean skin folds is vital, especially after bathing or sweating. Wearing loose, breathable clothing and avoiding irritants like harsh soaps or perfumed products can reduce risk. Management often involves topical antifungal creams prescribed by healthcare professionals. For individuals with recurrent infections, addressing underlying conditions like diabetes or immune deficiencies is essential. Good hygiene and early treatment help prevent the worsening or spreading of yeast-related conditions.
5. Vaginal Yeast Infections: Causes and Prevention
Vaginal yeast infections are among the most common infections affecting women worldwide. They result from an imbalance between Candida yeast and healthy bacteria in the vaginal area, often triggered by factors such as antibiotic use, high blood sugar levels, hormonal shifts during menstruation, pregnancy, or menopause, and compromised immunity. Symptoms include itching, burning sensation, abnormal discharge, swelling, and discomfort.
Preventative measures focus on good personal hygiene: wearing breathable cotton underwear, avoiding unnecessary use of scented products or douches, and keeping the genital area dry. Managing blood sugar levels if diabetic and seeking prompt treatment at the first signs of infection can prevent secondary complications. Healthcare providers may recommend antifungal creams, suppositories, or oral medications for treatment. It’s crucial not to ignore persistent symptoms, as recurring infections can indicate underlying health issues that require medical attention.
Overall, most fungal infections are manageable with proper hygiene, timely treatment, and awareness. Practicing preventive measures can significantly reduce risk and improve quality of life by avoiding recurring discomfort and potential health complications.