Comprehensive Guide to Recognizing Common Fungal Infections and Their Symptoms
This comprehensive guide discusses common fungal infections, including athlete’s foot, ringworm, scalp fungus, nail infections, and oral thrush. It explains their symptoms, causes, transmission, and treatments, emphasizing early detection and hygiene for effective management and prevention of complications.
Comprehensive Guide to Recognizing Common Fungal Infections and Their Symptoms
Understanding the early signs of health issues can be vital in receiving prompt and effective treatment. Among these, fungal infections are often overlooked or misdiagnosed because their initial symptoms—such as skin rashes, scalp flakes, or persistent itching—are frequently mistaken for minor conditions like sunburn, dryness, or dandruff. However, timely recognition of these symptoms is essential because fungal infections can affect various parts of the body and, if left untreated, may lead to more serious health problems. Recognizing early indicators not only facilitates swift intervention but also helps prevent the spread of infection, avoid complications, and reduce stigma associated with fungal diseases.
Fungal infections are caused by different types of fungi present in our environment, and they can affect individuals of all ages, genders, and health backgrounds. Though common, these infections require appropriate diagnosis and treatment to eliminate symptoms and prevent recurrence. Several factors contribute to the development of fungal infections, with poor immunity, inadequate hygiene, sweating, and exposure to contaminated surfaces being some of the leading causes. Protecting oneself and maintaining good hygiene practices are key strategies to prevent these common fungal conditions.
In this detailed guide, we will explore the most prevalent types of fungal infections, their symptoms, causes, modes of transmission, and available treatment options. Recognizing these infections early can make a significant difference in health outcomes, as most fungal conditions are treatable with appropriate medication, lifestyle adjustments, and care.
Let’s delve into the common fungal infections you should be aware of:
Athlete’s Foot (Tinea Pedis): A highly contagious skin condition primarily affecting the feet, especially between the toes. It is caused by fungi belonging to the Tinea genus. Symptoms include intense itching, burning sensations, raw and cracked skin, blisters, and peeling on the soles and sides of the feet. Moist environments, such as sweaty shoes or public showers, foster fungal growth, making athletes' foot common among athletes and individuals with poor foot hygiene. Proper foot care, dry feet, and antifungal treatments are effective in managing this infection.
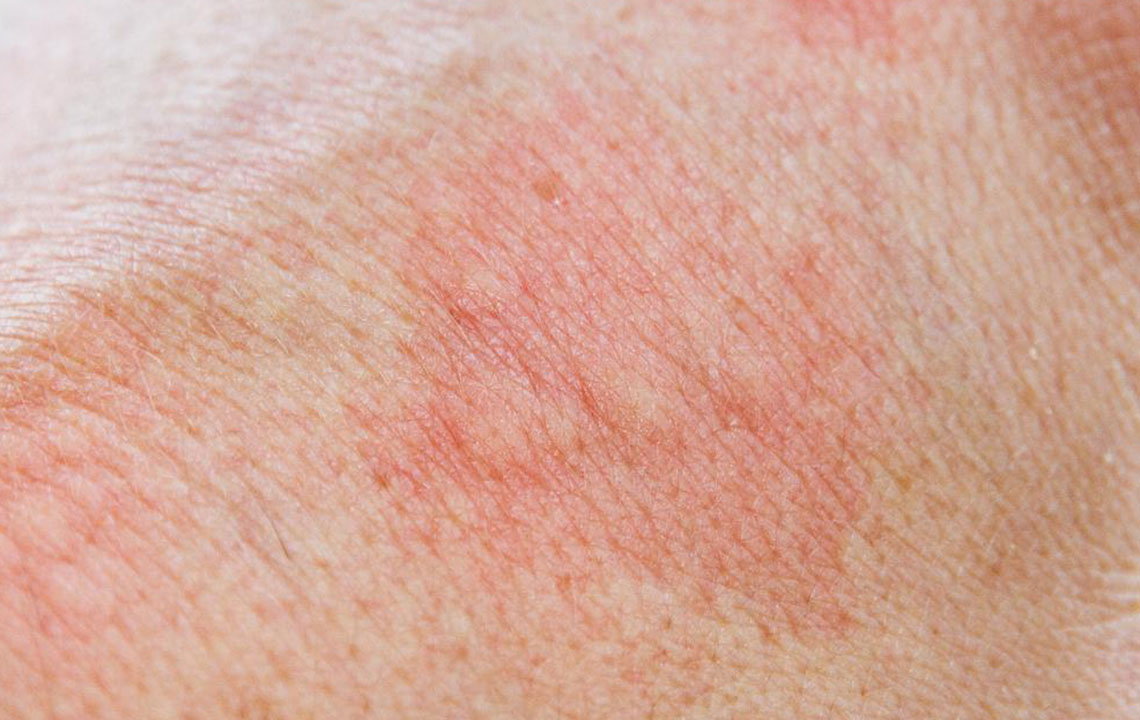
Ringworm (Tinea Corporis): A common fungal skin infection characterized by ring-shaped, scaly, and itchy patches that can appear on any part of the body. Despite its name, ringworm is not caused by worms but by dermatophyte fungi. Transmission occurs through contact with contaminated objects, pets, or infected individuals. The rings typically have clear centers with inflamed borders. Maintaining hygiene and avoiding contact with infected surfaces are crucial preventive measures. Topical or oral antifungal medications are usually prescribed for treatment.
Tinea Capitis (Scalp Ringworm): A contagious fungal infection affecting the scalp, often leading to dandruff, hair loss, and bald patches. It mainly affects children but can also occur in adults. The fungi responsible are dermatophytes that invade hair shafts and scalp skin. Symptoms include scaly patches, itching, and hair breakage. Early diagnosis and antifungal therapy are necessary to prevent scarring and persistent hair loss.
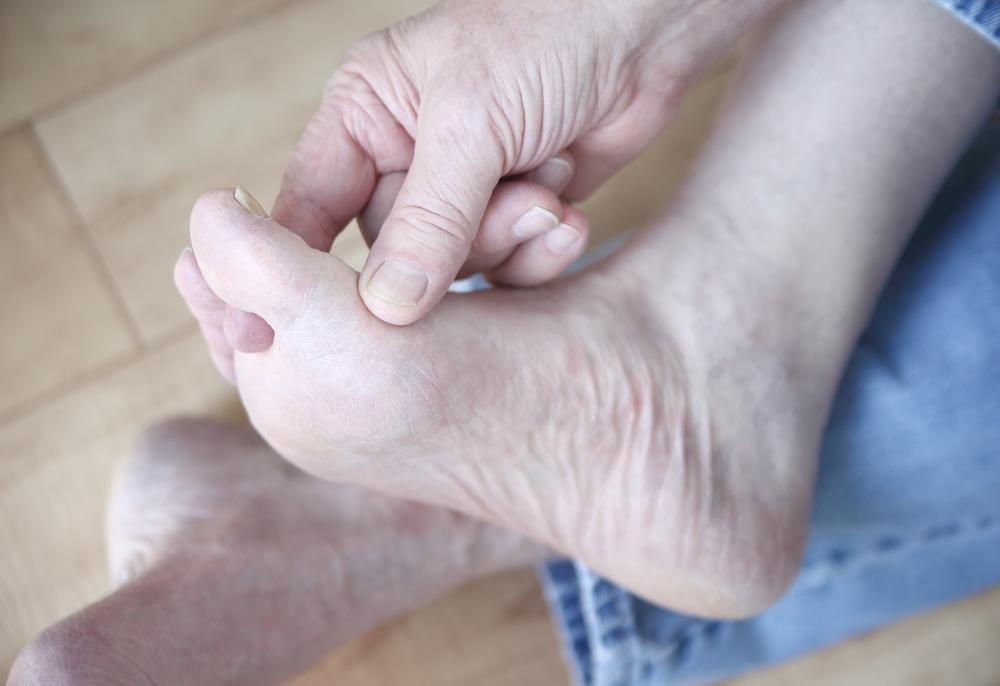
Onychomycosis (Nail Fungal Infection): Fungal infection of the nails caused by yeasts, molds, or dermatophyte fungi. It leads to thickened, brittle, discolored, and possibly deformed nails. Infections often begin at the edges or underneath the nail, making it difficult to detect initially. Poor hygiene, frequent exposure to moist environments, or nail trauma predispose individuals to onychomycosis. Treatment may include topical antifungal lacquers, oral medications, or in some cases, nail removal.
Oral Thrush (Candidiasis): An infection caused by Candida yeast, which naturally exists in the mouth but can overgrow under certain conditions. Symptoms include white patches on the tongue, inner cheeks, or the roof of the mouth, soreness, pain during swallowing, and sometimes a fever if infection spreads. People with weakened immune systems, those taking antibiotics, or wearing dentures are more susceptible. Oral antifungal medications are the common treatment for thrush, and maintaining good oral hygiene is vital for recovery.
While these infections are prevalent, they are generally preventable and treatable. Good hygiene practices, staying dry, avoiding sharing personal items, and maintaining immunity are fundamental measures to reduce risk. If you notice any symptoms of a fungal infection, consulting a healthcare professional for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment is crucial. Early treatment not only alleviates discomfort but also prevents the spread to others and avoids long-term health issues.