Comprehensive Guide to Managing Sciatic Nerve Pain Effectively
Discover comprehensive strategies to effectively manage sciatic nerve pain, including medications, physical therapy, alternative therapies, and surgical options. Learn how lifestyle changes and targeted treatments can alleviate discomfort, improve mobility, and enhance quality of life. This detailed guide offers insights into preventing and managing sciatic pain for long-term relief and better health outcomes.
Comprehensive Strategies for Effectively Managing Sciatic Nerve Pain
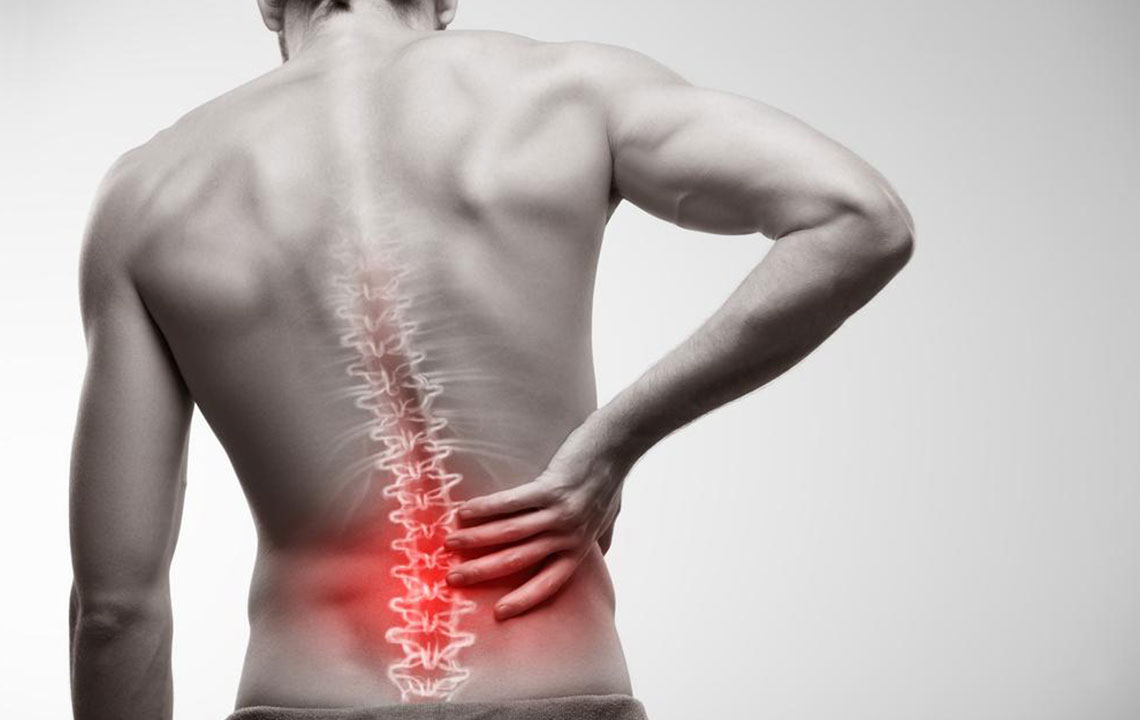
Sciatic nerve pain is a common condition that can significantly impair daily life and mobility. It originates from irritation or compression along the sciatic nerve, which is the longest nerve in the human body. This nerve begins in the lower back, passes through the pelvis, and extends down each leg to the feet. When this nerve becomes inflamed or pinched, it can cause intense discomfort, often radiating along the back of the leg, with symptoms including pain, numbness, tingling, and burning sensations. Understanding the causes, prevention methods, and treatment options is crucial to managing this condition effectively.
Sciatic nerve pain, also known as sciatica, can range from mild discomfort to debilitating pain. The sensation typically follows the pathway along the back of the thigh, splitting at the knee into the calf and foot. It can severely affect mobility, making simple activities arduous. The root cause often involves nerve root compression, commonly due to herniated discs, spinal stenosis, or degenerative disc disease. This compression leads to nerve irritation, triggering inflammation and pain signals. Certain factors like prolonged sitting, heavy lifting, sudden movements, or obesity can worsen symptoms or trigger episodes.
Managing sciatic pain effectively requires a multifaceted approach. The treatment plan often involves medications, physical therapy, and lifestyle modifications. Non-prescription medications such as acetaminophen and NSAIDs like ibuprofen are frequently used to alleviate pain and reduce inflammation. Muscle relaxants may be prescribed to ease muscle spasms, and antidepressants or anticonvulsants might be recommended for nerve pain management. However, it is important to avoid certain drugs like aspirin in children and teenagers due to the risk of Reye’s syndrome.
In addition to medication, healthcare professionals may recommend steroid injections near the affected nerve to provide temporary relief from severe inflammation and pain. These injections can help reduce swelling and nerve irritation, allowing for better participation in physical therapy and daily activities. Physical therapy forms a cornerstone of conservative management, especially for those with persistent or moderate symptoms. A structured exercise program tailored by a professional can help strengthen core muscles, improve flexibility, and alleviate pressure on the sciatic nerve.
Rather than prolonged bed rest, gentle activities like walking, swimming, or water aerobics are recommended as they help decrease inflammation, improve blood circulation, and promote healing. Your physiotherapist might introduce specific stretching and strengthening exercises targeting the lower back, hips, and leg muscles. Consistent physical activity can mitigate nerve inflammation and prevent future episodes. For best outcomes, it is essential to follow personalized advice from healthcare providers to ensure exercises are safe and effective, preventing further injury.
Beyond traditional treatments, several alternative therapies have proven beneficial for sciatic nerve pain relief. Acupuncture is widely favored, providing relief by stimulating specific points and reducing nerve inflammation. Many patients report significant improvement after multiple acupuncture sessions. Massage therapy, especially trigger point therapy, can be particularly effective in relieving muscle tension around the piriformis muscle—often a culprit in compressing the sciatic nerve. Regular massage sessions can alleviate pinched nerves, reducing pain levels within weeks.
Other complementary approaches include yoga, which enhances flexibility and strengthens supporting muscles, potentially reducing nerve pressure. Gentle yoga routines targeting the lower back, hips, and legs are highly recommended. Hot and cold packs can help manage pain and muscle spasms—cold packs reduce inflammation, while heat promotes blood flow and muscle relaxation. Biofeedback techniques teach patients to control muscle tension and stress, thereby decreasing symptom severity. Some herbal remedies, topical anti-inflammatory ointments, and natural supplements can further support pain relief when used under medical supervision.
While conservative measures are preferred, surgery remains a last resort for cases unresponsive to non-invasive therapies. Surgical interventions are considered only when pain persists or worsens despite adequate conservative management, or when neurological deficits threaten permanent damage. Common procedures include a discectomy, where herniated disc material compressing the nerve is removed, or laminectomy, which involves removing part of the vertebra to decompress the nerve roots. In emergency situations, such as cauda equina syndrome—a rare but serious condition—urgent surgical intervention is necessary to prevent permanent nerve damage and restore function.
Overall, managing sciatic nerve pain involves understanding its underlying causes, adopting a comprehensive treatment approach, and making necessary lifestyle adjustments. Early intervention and consistent therapy are key to preventing chronic pain and improving quality of life. Consulting with healthcare professionals—such as neurologists, orthopedists, or physical therapists—is essential for developing a tailored treatment plan. With proper management, most individuals can experience significant pain relief, regain mobility, and return to normal activities, ultimately enhancing their overall health and well-being.