Comprehensive Approaches to Alleviating Sciatic Nerve Pain: Effective Strategies for Relief
This comprehensive article explores effective methods for managing sciatic nerve pain, including stretching, thermal therapy, medications, and surgical options. It emphasizes personalized treatment plans, combining conventional and alternative therapies for optimal relief. Suitable for those suffering from persistent sciatic symptoms, the guide highlights when to seek medical help and how lifestyle changes can promote recovery.

Comprehensive Approaches to Alleviating Sciatic Nerve Pain: Effective Strategies for Relief
Sciatic nerve pain, commonly known as sciatica, is a condition characterized by sharp, shooting discomfort that radiates from the lower back down through the buttocks, legs, and sometimes into the feet. This pain results from irritation, compression, or inflammation of the sciatic nerve, the longest nerve in the human body, which plays a crucial role in connecting the spinal cord to the legs and feet. Often caused by herniated discs, spinal stenosis, degenerative disc disease, or muscle spasms, sciatic nerve issues can significantly impair daily activities and diminish quality of life.
Managing sciatic nerve pain involves understanding its root causes and selecting appropriate treatment strategies. While some cases resolve with conservative measures, others may require more intensive interventions like surgery. The good news is that with a well-structured approach combining lifestyle modifications, physical therapy, medications, and possibly complementary therapies, most individuals can find relief and regain their mobility.
Effective Management Strategies for Sciatic Nerve Pain: Explore various treatment options tailored to alleviate discomfort and promote healing, from simple home exercises to advanced medical procedures. Consulting healthcare professionals is vital to develop a personal treatment plan for optimal recovery.
Here are some of the most effective treatment options and lifestyle adjustments for alleviating sciatic nerve discomfort:
Targeted Stretching and Physical Activity
Engaging in specific stretching exercises can alleviate nerve pressure and reduce inflammation. Regular physical activity, particularly low-impact aerobic exercises like walking, swimming, or cycling, has proven beneficial for many middle-aged adults suffering from sciatica. Developing a personalized exercise routine with the help of a physical therapist or healthcare provider can accelerate recovery. Studies suggest that nearly 50% of sciatic patients experience significant improvement within six weeks of consistent exercise, often avoiding the need for surgical intervention.
Thermal Therapy: Cold and Hot Pack Treatments
Applying cold packs during the initial stages of pain can help curb inflammation and numb the affected area, providing immediate relief. After a few days, switching to heat therapy encourages blood flow, relaxes tight muscles, and promotes tissue repair. Alternating between cold and hot treatments, typically for 15-20 minutes each, can effectively reduce pain and speed up recovery. It's crucial to observe proper precautions to avoid skin burns or frostbite.
In addition to these treatments, adopting certain restorative practices such as sleeping in supportive positions—like on your side with a pillow between your knees or on your back with a pillow under your knees—can support spinal alignment and facilitate healing over time.
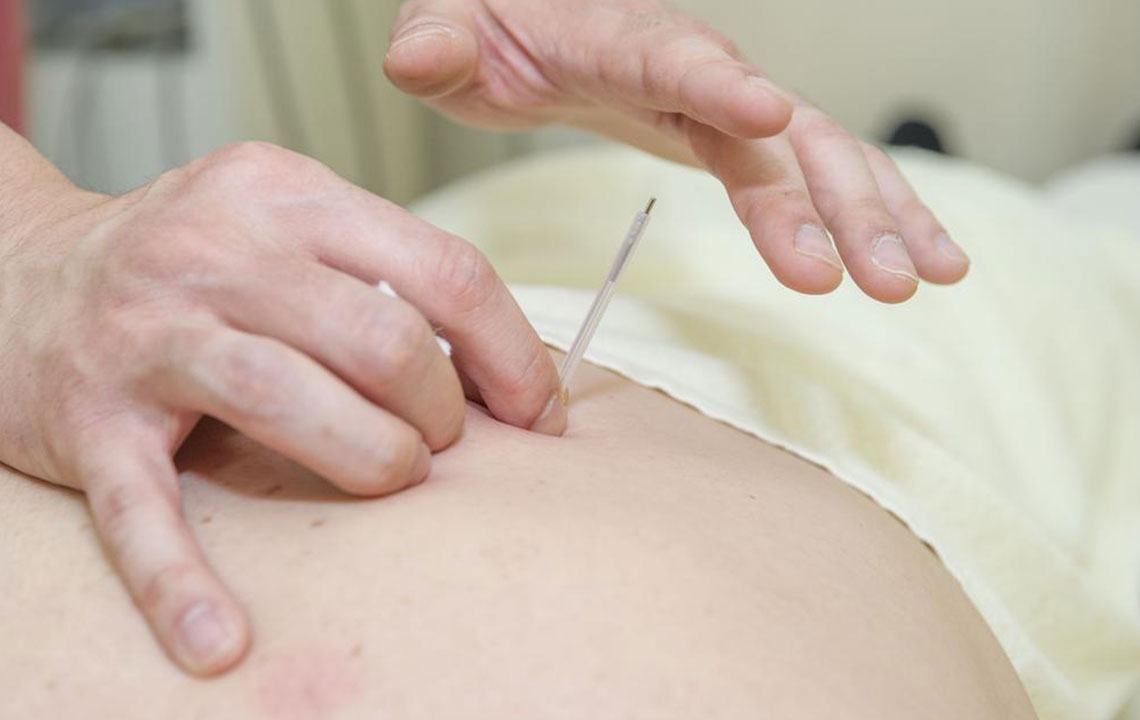
Complementary and Alternative Therapies
Many individuals find relief through alternative methods such as acupuncture, massage therapy, yoga, chiropractic adjustments, and biofeedback. These therapies can relax tense muscles, improve circulation, and stimulate nerves, often providing temporary or even lasting relief from sciatic symptoms. While some of these treatments may not entirely replace traditional medicine, they can be effective adjuncts to a comprehensive treatment plan, especially for those seeking non-pharmacological options.
Medication Management
Over-the-counter medications such as acetaminophen, aspirin, and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen are commonly used to mitigate pain and reduce inflammation. For severe or persistent symptoms, healthcare providers might prescribe muscle relaxants, corticosteroids, or nerve pain medications. It’s important to use these drugs judiciously, under medical supervision, to avoid potential side effects, dependency, or interactions. Medications are typically viewed as short-term solutions to manage acute pain episodes.
Persistent sciatic pain that lasts beyond three to four months or worsens despite conservative measures may necessitate surgical intervention. Surgery is considered a last resort when other treatments fail or if symptoms threaten organ functions or cause significant neurological deficits.
Discectomy
This surgical procedure involves removing herniated disc material compressing the nerve root, providing immediate and often permanent relief from pressure. Discectomy is a common and highly successful operation, particularly suited for cases involving herniated discs that do not respond to non-invasive treatments.
Laminectomy
This operation entails removing a small portion of the vertebral bone called the lamina, which may be enlarging or causing compression due to bone spurs, tissue swelling, or arthritis. Laminectomy can relieve nerve impingement efficiently, with minimal recovery time and a low incidence of complications.
When surgery is necessary, it's essential to select a qualified neurosurgeon or orthopedic surgeon experienced in spinal procedures. Preoperative assessments and postoperative rehabilitation are crucial components to ensure optimal outcomes.
In some cases, spinal manipulation therapy or epidural steroid injections might be offered temporarily to alleviate symptoms, especially during acute episodes. Always consult a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate treatment pathway based on individual circumstances.
Prompt medical attention should be sought if severe pain persists, or if symptoms include weakness, loss of bladder or bowel control, or numbness spreading to the groin or legs, as these could indicate more serious neurological issues requiring immediate intervention.