Comprehensive Guide to Managing Blood Glucose Levels and Preventing Diabetes-Related Complications
This comprehensive article provides effective strategies for managing blood glucose levels and preventing long-term diabetes complications. It covers medication options, dietary and lifestyle modifications, and technological advances like continuous glucose monitors, offering valuable insights for those living with diabetes to maintain health and prevent serious health issues.

Comprehensive Strategies for Maintaining Healthy Blood Sugar Levels and Avoiding Diabetes Complications
Managing blood glucose effectively is a crucial aspect for individuals diagnosed with diabetes. When blood sugar levels become irregular, particularly when they rise above normal—a condition known as hyperglycemia—they can lead to severe health complications including cardiovascular diseases, kidney failure, vision impairment, and nerve damage. According to global health statistics, approximately 13% of adult populations worldwide are living with diabetes, making it one of the most common chronic illnesses today. The good news is that with proper management—combining medication, lifestyle adjustments, and technological aid—people with diabetes can lead healthy, active lives. This comprehensive guide delves into proven strategies and innovations for controlling blood glucose and preventing long-term complications.
Medical Interventions and Treatment Options
GlucoTrust - An all-natural, FDA-approved supplement designed specifically to support blood sugar regulation. Suitable for both type 1 and type 2 diabetes, this supplement aims to improve insulin sensitivity and promote stable glucose levels.
INVOKANA® (Canagliflozin) - Part of the SGLT2 inhibitors class, INVOKANA® helps lower blood glucose by promoting excess sugar excretion through the urine. It also reduces the risk of kidney damage, a common complication in longstanding diabetes.
Additional Therapeutic Strategies
Kerendia® (Finerenone) - A daily oral medication formulated for patients with type 2 diabetes who are at increased risk for kidney and cardiovascular issues. It works by selectively blocking mineralocorticoid receptors, thereby safeguarding kidney function and improving cardiovascular health.
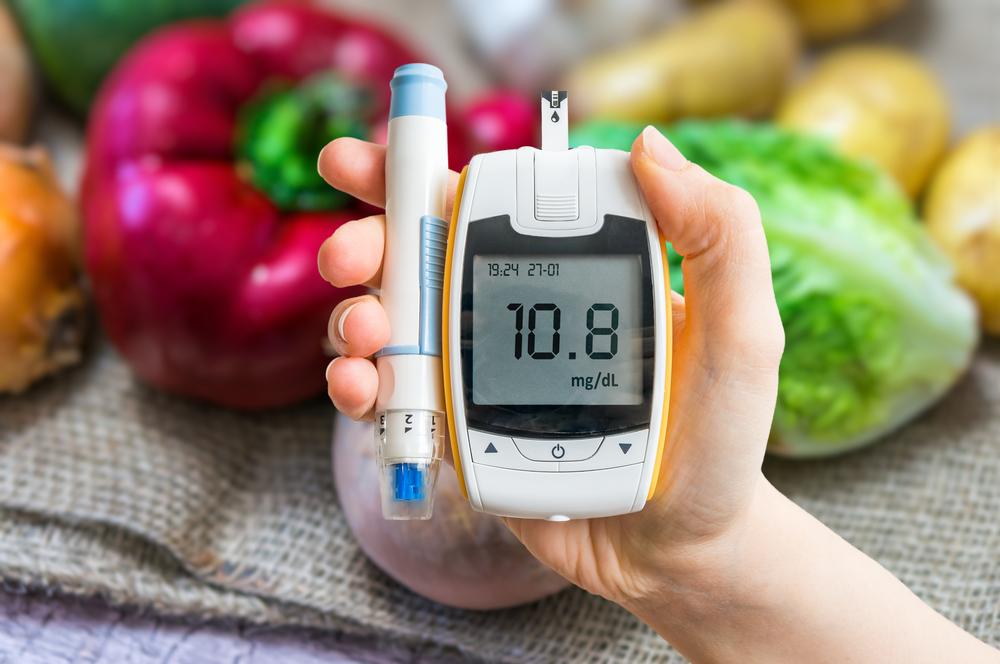
Insulin therapy remains fundamental for managing type 1 diabetes and some cases of type 2 diabetes. Modern devices like continuous glucose monitoring systems—such as the Dexcom G6—are revolutionizing diabetes care. These gadgets continuously measure blood glucose levels, reducing the need for frequent finger pricks and allowing real-time management adjustments, leading to better overall control and fewer complications.
Foods and Habits to Avoid for Better Blood Sugar ControlTo maintain optimal blood glucose levels, certain foods and habits should be minimized or avoided entirely. Fried foods, processed snacks, sugary beverages, and refined carbohydrates such as white rice, white bread, and sweets cause rapid blood sugar spikes. Processed and high-salt, oily meats can also contribute to poor health outcomes. Additionally, exercising on an empty stomach or immediately after a heavy meal should be avoided for safety reasons. Adherence to prescribed medication regimens is crucial, and skipping doses can jeopardize blood sugar stability. Managing stress is equally important since hormones like cortisol and glucagon, released during stressful periods, can elevate blood glucose, making control more challenging. Developing a stress management routine, including relaxation techniques or mindfulness meditation, can be highly beneficial.
Dietary and Lifestyle Modifications for Optimal Blood Glucose Control
Adopting a diet centered around low-glycemic index foods is vital for blood sugar stability. Examples include oats, Greek yogurt, lentils, chickpeas, and a variety of vegetables. These foods cause slower, steadier increases in blood glucose compared to high-glycemic foods. Incorporating high-fiber options such as brown rice, quinoa, and whole grains in meal planning helps regulate blood sugar levels and improves insulin sensitivity. Fruits like berries, apples, and pears can be enjoyed in moderation due to their fiber content and relatively low sugar impact.
Physical activity plays a crucial role in diabetes management. Regular exercise helps muscles absorb glucose more efficiently, reducing blood sugar levels naturally. Activities such as brisk walking, cycling, swimming, and strength training should be engaged in most days of the week. Additionally, relaxation techniques like meditation, deep breathing, or yoga can help lower stress hormones that may interfere with blood sugar control. Ensuring adequate sleep hygiene and getting 7-9 hours of restful sleep each night support metabolic health and hormone balance.
Understanding the two main types of diabetes is key to effective management:
Type 1 Diabetes: An autoimmune condition where the pancreas produces little to no insulin. Patients require daily insulin injections or use insulin pumps to maintain their blood glucose levels within safe ranges.
Type 2 Diabetes: More common, characterized by the body's inefficient use of insulin—a condition known as insulin resistance. It is often associated with obesity, poor diet, and lack of physical activity. Lifestyle interventions, including diet and exercise, along with medications, can effectively manage this form of diabetes.
In conclusion, managing blood glucose and preventing diabetes complications require a multi-faceted approach that combines medication, lifestyle changes, and technological tools. Staying informed about treatment options, maintaining a healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and managing stress are fundamental steps. Advances in medical devices and medications continue to improve prospects for individuals living with diabetes, making it easier to achieve optimal control and a better quality of life.