Comprehensive Lifestyle Strategies for Effective Blood Glucose Management
Discover comprehensive, scientifically-supported lifestyle strategies to effectively manage blood glucose levels naturally. This detailed guide covers physical activity, diet, stress management, sleep, and herbal supplements, offering practical tips to prevent diabetes complications and promote overall metabolic health. Implementing these lifestyle changes can lead to better blood sugar control, weight management, and improved well-being. Always consult healthcare providers before making significant adjustments, especially if on medication. Empower yourself with knowledge and practical steps to maintain healthy blood glucose levels for a healthier life.

Scientifically Proven Approaches to Regulate Blood Sugar Levels Naturally
Maintaining balanced blood glucose levels is critical for overall health and preventing the development of diabetes. Elevated blood sugar, or hyperglycemia, occurs when the body’s mechanism for transporting glucose from the bloodstream into body cells becomes inefficient. If left unmanaged, this condition can progress into type 2 diabetes, with significant health consequences.
Recent studies reveal that nearly 50% of adults worldwide are either diabetic or pre-diabetic, emphasizing the importance of effective lifestyle management strategies. Fortunately, making targeted adjustments to daily habits, nutritional intake, and activity levels can significantly influence blood sugar control, reduce risks, and promote long-term health.
Below, we delve into comprehensive lifestyle and dietary modifications grounded in scientific research, offering practical guidance for individuals aiming to optimize blood glucose levels and prevent diabetes-related complications. Let's explore these effective approaches in detail.
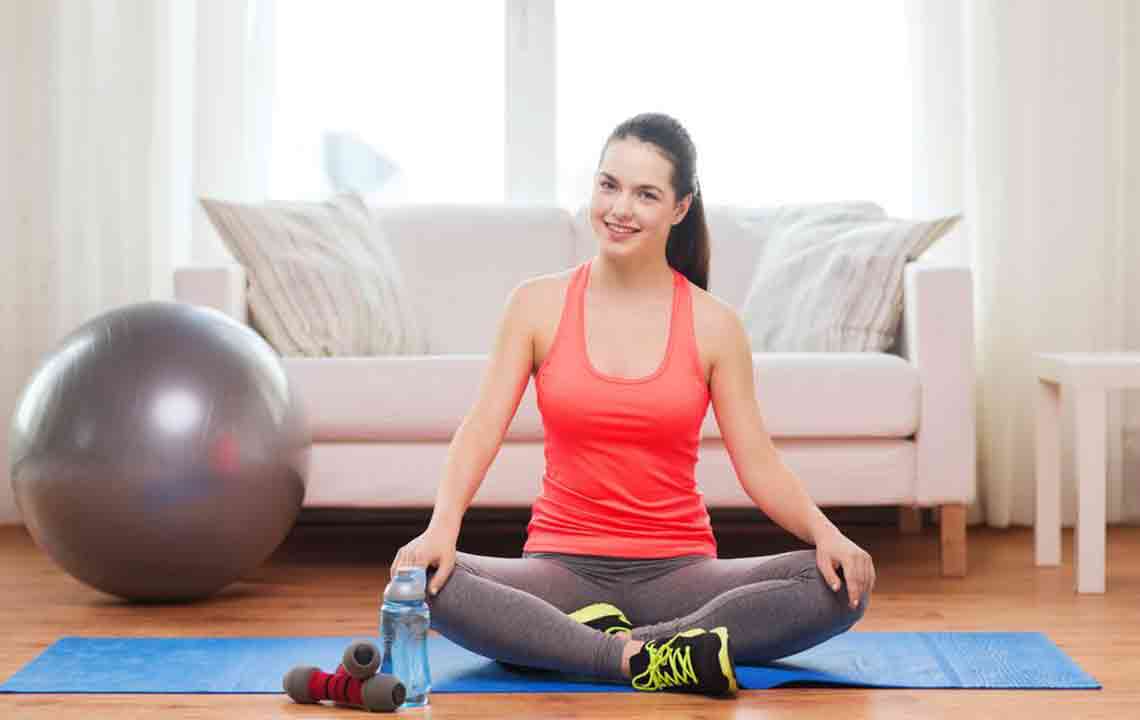
1. Engage in Regular Physical Activity
Physical activity plays a vital role in overall health enhancement and specifically in blood sugar regulation. Regular exercise not only aids in weight management but also improves the body’s sensitivity to insulin, the hormone responsible for transporting glucose into cells for energy use.
When muscles contract during physical activity, they consume glucose, which directly supports lower blood sugar levels. Incorporating various forms of exercise such as walking, cycling, swimming, or strength training into your routine can make a significant difference. Consistency is key—aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week, as recommended by health authorities.
Monitoring how your blood sugar responds to different physical activities can provide insights into your body’s specific needs. Using a blood glucose monitor before and after workouts helps identify which exercises contribute most effectively to glucose control. Over time, this can inform personalized routines that maximize health benefits.
2. Limit Carbohydrate Intake
Carbohydrates are a primary source of glucose, and their digestion leads to increased blood sugar levels. When the body’s insulin response is inadequate or compromised, consuming excess carbs can cause undesirable spikes.
Adopting a low-carb diet—focused on reducing simple sugars and refined grains—can help maintain more stable blood glucose levels. Emphasize complex carbohydrates such as whole grains, vegetables, and legumes, which release glucose more slowly, providing sustained energy without sharp spikes.
This dietary shift not only supports blood sugar management but also promotes better weight control and overall metabolic health. Collaborating with a healthcare professional or dietitian can help tailor an appropriate carbohydrate intake plan suitable for your needs.
3. Increase Dietary Fiber Intake
Dietary fiber is a powerful ally in blood glucose regulation. Soluble fiber, found abundantly in fruits, vegetables, oats, barley, beans, and legumes, forms a gel-like substance in the digestive tract that slows down carbohydrate absorption.
This delayed absorption results in smoother blood sugar levels, reducing the risk of sudden spikes after meals. Additionally, fiber-rich diets promote a healthy gut microbiome and improve overall digestion, contributing to better metabolic health.
Striving for a daily fiber intake of at least 25–30 grams can help stabilize blood glucose. Incorporating high-fiber foods into every meal is an accessible, effective strategy to enhance glycemic control.
4. Practice Portion Control
Controlling portion sizes is crucial in managing calorie intake and preventing blood sugar surges. Eating large quantities of even healthy foods can overwhelm the body’s ability to process glucose efficiently.
Adopting mindful eating habits—such as taking time to chew slowly, savoring flavors, and paying attention to hunger cues—can prevent overeating. Using smaller plates, pre-portioning snacks, and avoiding second servings are simple yet effective tricks to keep portions in check.
Monitoring carbohydrate content per meal and spreading intake evenly throughout the day supports consistent blood sugar levels, reduces insulin resistance, and fosters weight management.
5. Choose Low-Glycemic Index (GI) Foods
Low-GI foods tend to cause smaller, more controlled increases in blood glucose. Foods with a GI score below 55 are ideal for maintaining stable levels and preventing sudden spikes.
Examples include leafy greens, nuts, seeds, legumes, lean meats, fish, sweet potatoes, and quinoa. Incorporating these foods into daily meals can significantly improve glycemic responses, especially when combined with other healthy practices.
Balancing meals with low-GI options helps sustain energy, reduce cravings, and improve overall metabolic health.
6. Manage Stress Effectively
Persistent stress can elevate blood sugar levels through the release of hormones like cortisol and adrenaline. These hormones signal the liver to produce more glucose, leading to hyperglycemia.
Implementing stress reduction techniques—such as yoga, meditation, deep breathing exercises, or engaging in hobbies—can effectively lower cortisol levels and support glucose stability.
Practicing mindfulness and developing healthy coping mechanisms are essential components of a comprehensive approach to blood sugar management.
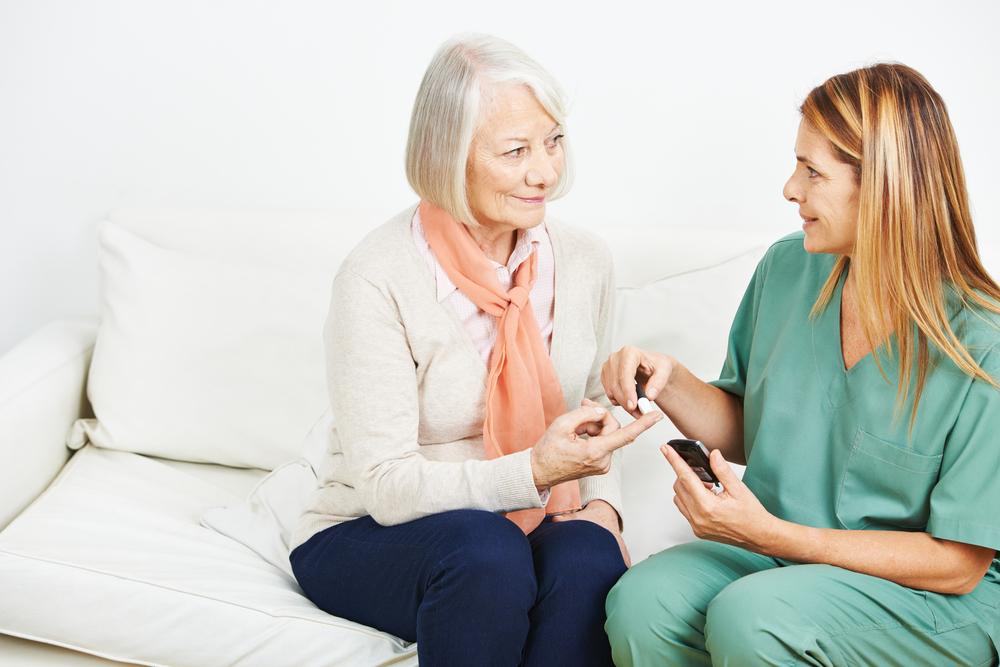
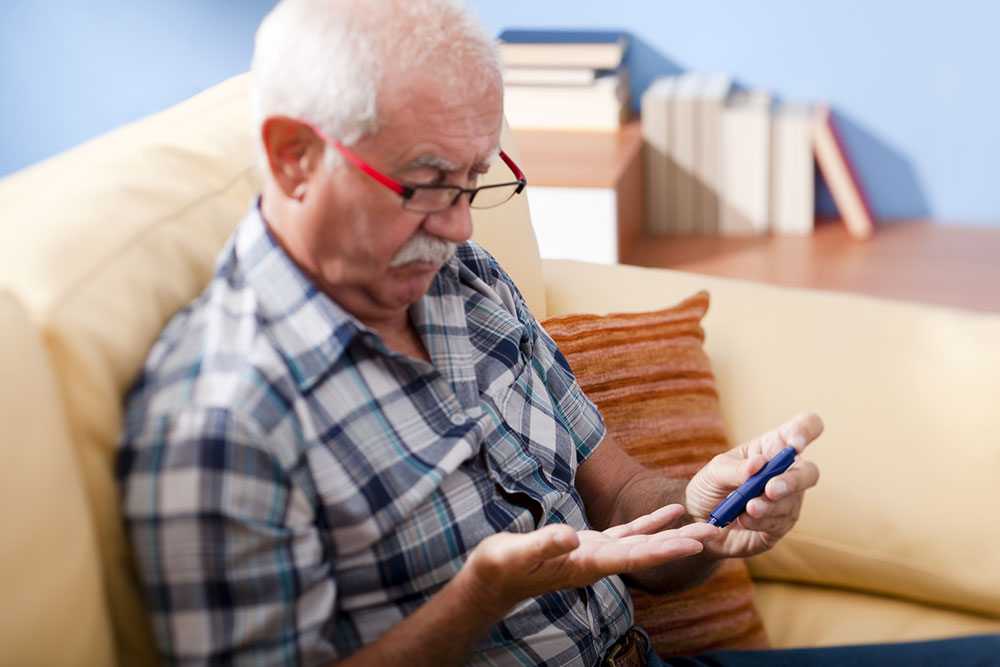
7. Routine Blood Glucose Monitoring
Regularly checking blood glucose levels provides immediate insights into how your lifestyle, diet, and physical activities influence your body. Self-monitoring helps identify patterns, recognize triggers for spikes, and adjust routines accordingly.
Maintaining a log of blood sugar readings, along with dietary and activity notes, can be invaluable for healthcare providers when tailoring treatment plans. Use of modern continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) can also provide real-time data to facilitate better management.
8. Prioritize Quality Sleep
Adequate sleep—at least 7 to 8 hours per night—is essential for hormonal balance and metabolic health. Sleep deprivation impairs insulin sensitivity, increases appetite-regulating hormones, and elevates cortisol, all of which contribute to higher blood sugar levels.
Creating a relaxing bedtime routine, minimizing screen time before sleep, and maintaining a consistent sleep schedule can support restorative rest. Quality sleep enhances the body’s ability to regulate glucose effectively and reduces the risk of metabolic disorders.
9. Incorporate Fenugreek Seeds Into Your Diet
Fenugreek seeds are rich in soluble fiber and bioactive compounds that support glucose tolerance. Research indicates that daily consumption of 2-5 grams of fenugreek—either added to meals or brewed as tea—can improve blood sugar levels in people with insulin resistance or diabetes.
Adding fenugreek to your diet is an easy, natural method to enhance glycemic control. Always consult your healthcare provider before starting new supplements or herbal remedies, especially if you are on medication.
Implementing these scientifically-backed lifestyle modifications can significantly improve your body's ability to maintain healthy blood glucose levels. For personalized guidance and safe practices, always seek advice from healthcare professionals, especially when managing pre-diabetes or diabetes.