Effective Approaches to Maintain Optimal Blood Glucose Levels for Better Health
This comprehensive guide explores effective strategies for maintaining healthy blood glucose levels. It emphasizes the importance of balanced nutrition, regular exercise, portion control, medication adherence, and consistent monitoring to prevent complications and enhance overall health. Suitable for diabetics and those seeking to prevent metabolic disorders, it offers practical tips to achieve stable blood sugar and improve quality of life.
Effective Approaches to Maintain Optimal Blood Glucose Levels for Better Health
Maintaining healthy blood glucose levels is a fundamental aspect of managing diabetes and overall health. Blood sugar regulation depends primarily on insulin, a vital hormone produced by the pancreas. When you consume food, especially carbohydrates, blood glucose levels rise. This prompts the pancreas to release insulin, which facilitates the absorption of sugar into cells to be used as energy or stored for future use. A well-functioning insulin response ensures that blood glucose returns to a normal range. However, in individuals with insulin resistance or pancreatic issues, blood sugar can stay elevated longer, increasing the risk of serious complications like organ damage, nerve impairment, and vision problems. Therefore, understanding and implementing effective strategies to regulate blood glucose is crucial for individuals with diabetes and for those looking to prevent metabolic disorders.
Normal fasting blood sugar levels should ideally be below 100 mg/dL, while post-meal levels typically peak around 140 mg/dL. For diabetics, fasting blood glucose can often be above 200 mg/dL, highlighting the importance of diligent blood glucose management. Achieving and maintaining stable blood sugar levels requires a comprehensive approach that includes dietary modifications, regular physical activity, consistent blood glucose monitoring, and adherence to prescribed medication regimens. This holistic approach not only helps prevent complications but also enhances overall quality of life.
Comprehensive Dietary Strategies for Blood Glucose Control
One of the most fundamental pillars of blood sugar management is diet. Eating the right types of food in appropriate amounts can significantly influence blood glucose levels. Focus on incorporating nutrient-dense, low glycemic index foods such as fresh fruits, legumes, whole grains, and low-fat dairy products. These foods release glucose more slowly into your bloodstream, preventing sharp spikes. It's critical to limit highly processed foods and refined carbohydrates like white bread, pastries, sugary cereals, and sweets, which can cause quick, dramatic increases in blood sugar.
Integrating healthy fats and proteins with carbohydrate-rich meals is another essential tactic. Combining carbs with sources of healthy fats—such as avocados, nuts, and olive oil—and lean proteins like chicken, fish, or tofu helps slow down digestion and sugar absorption. This stabilization effect results in steadier blood glucose levels, reducing the risk of hyperglycemia episodes.
Importance of Protein-Powered Breakfasts and Portion Control
Starting your day with a protein-rich breakfast can be highly effective in managing post-meal blood sugar spikes. Aiming for 25-30 grams of protein during breakfast—through options like egg whites, low-fat yogurt, or cottage cheese—has been shown to moderate subsequent blood sugar increases. Consuming balanced, smaller meals throughout the day helps avoid large fluctuations and keeps energy levels consistent.
Portion control plays a critical role in preventing excessive caloric intake and rapid blood glucose escalations. Use smaller plates, measure portions, and avoid second servings. Incorporate healthy snacks such as nuts or seeds, which provide vital nutrients and help maintain blood sugar stability. These strategies collectively support weight management, which is vital for insulin sensitivity and overall metabolic health.
Exercise and Weight Management: Key Components of Blood Sugar Regulation
Physical activity is a cornerstone of blood glucose control. Regular exercise enhances insulin sensitivity, allowing the body to utilize glucose more effectively. Aerobic activities such as walking, swimming, cycling, and jogging, along with resistance training, can substantially improve metabolic health. Engaging in at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise weekly is recommended for most adults.
Maintaining a healthy weight further improves insulin function and reduces the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Achieving weight loss through dietary adjustments and increased physical activity helps lower blood sugar levels, decrease insulin resistance, and improve overall health. It’s important to practice mindful eating—listening to hunger cues and avoiding emotional or habitual snacking that could lead to overeating.
Role of Alcohol and Medication in Blood Glucose Stability
Alcohol consumption can influence blood glucose levels; it tends to lower blood sugar temporarily but can cause hypoglycemia if not managed properly. Moderation is key, and individuals should measure their blood sugar before, during, and after alcohol intake. Consulting healthcare professionals for personalized advice is recommended, especially if you are on diabetes medications.
Adherence to prescribed medication plans is equally critical. Diabetes medications such as insulin or oral hypoglycemics assist in controlling blood sugar levels, especially when lifestyle measures alone are insufficient. Always follow your healthcare provider’s instructions and have regular check-ups to adjust treatment plans as needed.
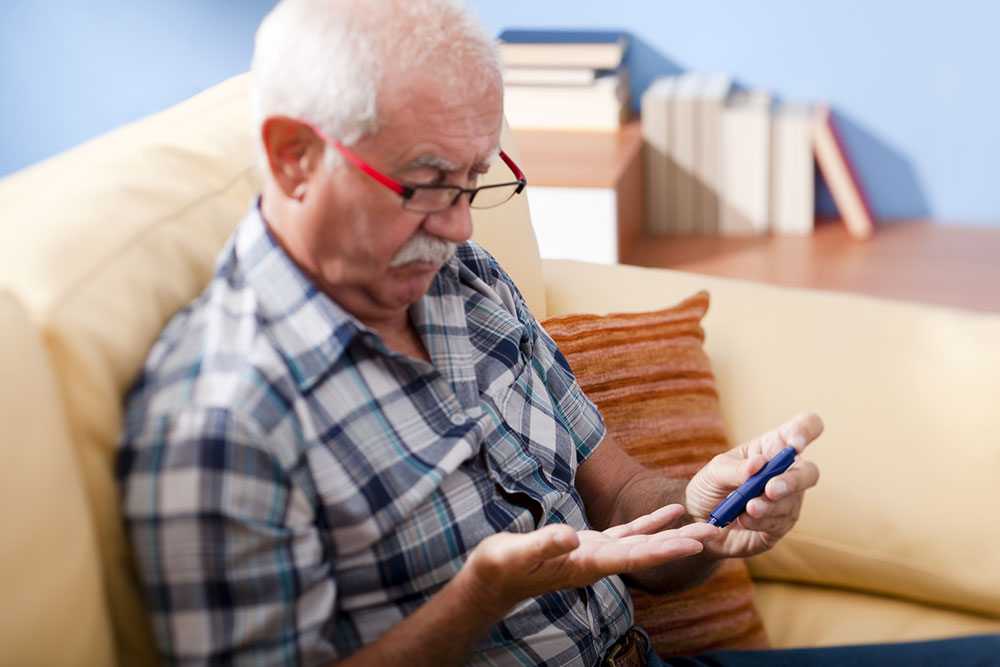
The Significance of Regular Blood Glucose Monitoring
Consistent blood sugar monitoring provides valuable insights into how lifestyle, diet, activity, and medications influence your levels. Using glucometers or continuous glucose monitoring devices helps detect fluctuations early, preventing long-term complications like kidney disease, nerve damage, and cardiovascular issues. Keeping a log of your readings facilitates better communication with healthcare providers and adjustments to your management plan.
In conclusion, maintaining optimal blood glucose levels necessitates a multi-faceted approach. A balanced diet, regular physical activity, diligent medication adherence, moderate alcohol consumption, and consistent monitoring together form the foundation for effective blood sugar management. These strategies empower individuals to prevent complications, improve well-being, and enjoy a healthier life.