Comprehensive Guide to the Top 10 Causes of Skin Hives and Effective Management Strategies
This comprehensive guide explores the top 10 causes of skin hives, detailing their triggers and offering practical prevention and management strategies. Understanding these factors enables individuals to reduce outbreaks, improve skin health, and enhance overall well-being, with tips suitable for all affected by this common skin condition.

In-Depth Exploration of the Top 10 Causes of Skin Hives and Practical Tips for Prevention and Treatment
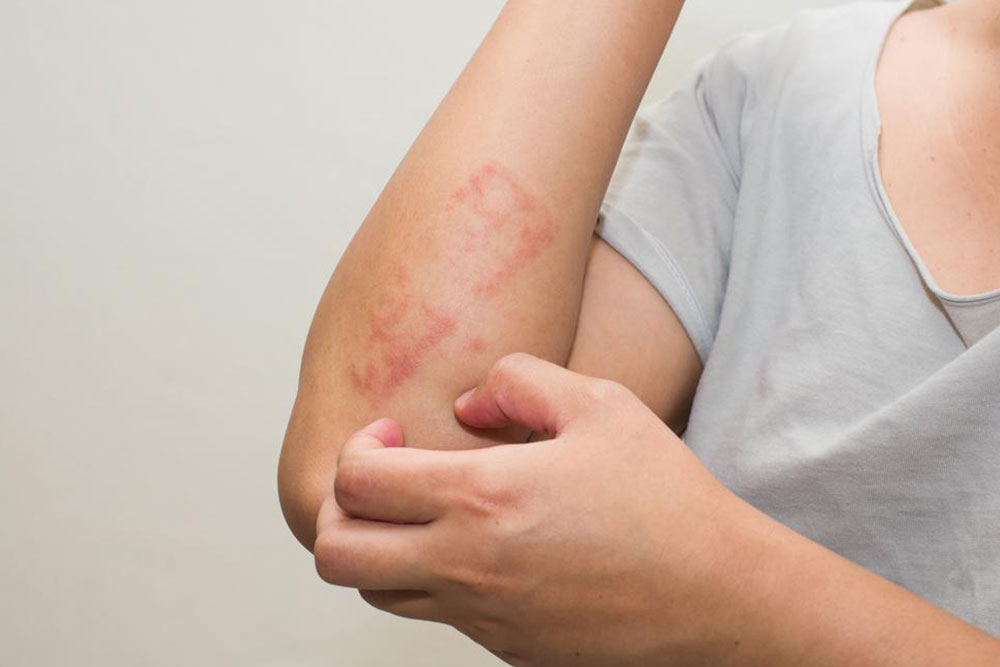
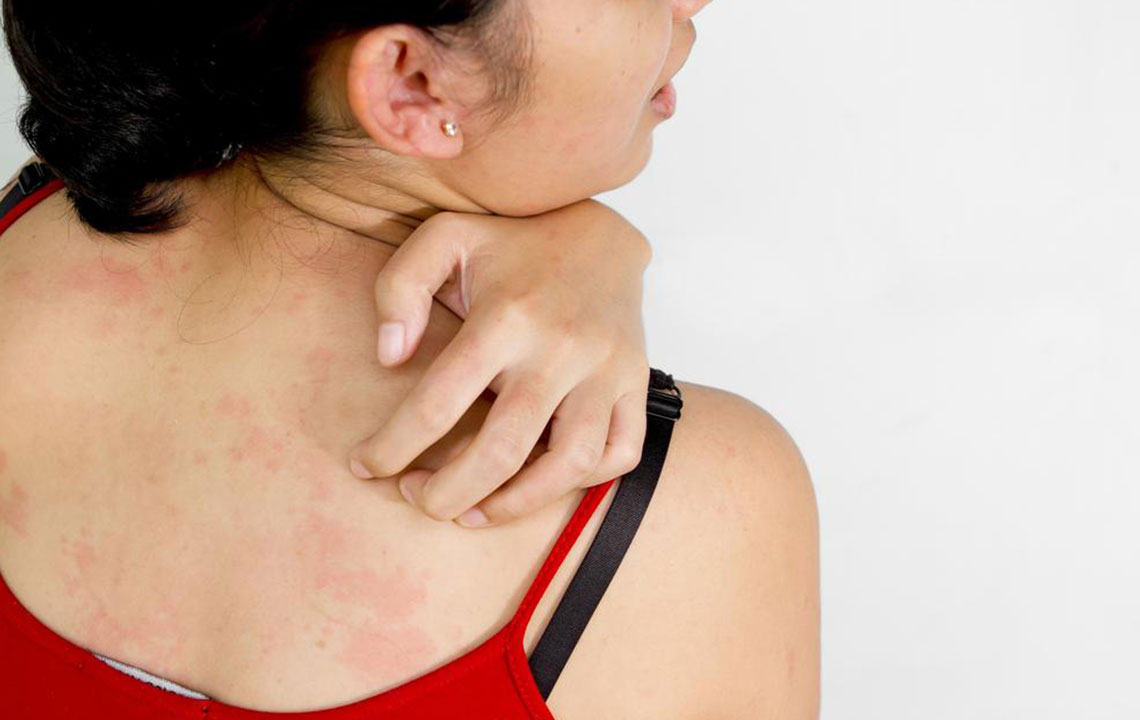
Skin hives, medically referred to as urticaria, are a common dermatological condition characterized by the sudden appearance of raised, red, and intensely itchy bumps on various parts of the body. These skin reactions can develop rapidly and often disappear within a few hours, typically between 6 to 12 hours. Sometimes, individual hives can merge together to form larger, more extensive patches called plaques, which can be more uncomfortable and visually prominent. Although hives are usually temporary and benign, their sudden onset and itching can be quite distressing, affecting daily life and emotional well-being.
Understanding the triggers behind hives is essential for effective management and prevention. They often serve as signs of allergic reactions or other underlying factors influencing the immune response. Recognizing these causes allows individuals to make informed lifestyle adjustments and seek appropriate medical care when necessary.
Hives may appear in various locations including sensitive areas like lips, eyelids, ears, or more prominent regions such as the face, shoulders, chest, and back. They are frequently accompanied by a burning or stinging sensation, which can exacerbate discomfort and embarrassment, especially in social or professional settings. Moreover, the persistence or recurrence of hives may necessitate a thorough investigation to identify potential underlying health conditions that could be contributing to the skin reactions.
To help you better understand and manage skin hives, this comprehensive guide details the top ten causes and offers practical advice on how to prevent and treat these allergic reactions effectively. By identifying and avoiding common triggers, you can reduce the frequency and severity of hive outbreaks, improving your skin health and overall quality of life.
Top 10 Causes of Skin Hives and How to Manage Them Effectively
External Triggers and Allergens
Many cases of hives are triggered by external environmental factors. When your skin comes into contact with certain substances, your immune system reacts by releasing histamine, a chemical that causes blood vessels to expand and results in raised bumps. Common external triggers include dust mites, pollen from trees and grasses, pet dander, insect bites and stings, and contact with certain chemicals or dyes. Recognizing these external allergens plays a crucial role in managing occurrences. Wearing protective clothing, using air purifiers, and minimizing exposure to known allergens can significantly reduce incidents.
Food Allergies and Sensitivities
Food plays a prominent role in causing hives for many individuals. Certain foods are more likely to trigger allergic responses, including nuts, dairy products, eggs, shellfish like shrimp and crab, berries, and foods with artificial additives such as colors, flavors, and preservatives. The reaction can be immediate, occurring within minutes, or delayed, appearing hours after consumption. Maintaining a food diary and conducting allergy tests can help identify specific dietary triggers. Avoiding known allergens and reading food labels carefully are practical steps to prevent food-induced hives.
Infections
Viral and bacterial infections can provoke hives as part of the body's immune response. Common viral illnesses associated with hives include influenza, mononucleosis, and hepatitis. These infections often present with additional symptoms like fever, fatigue, and sore throat. In some cases, hives are among the first signs of illness, appearing before other symptoms manifest. As the infection resolves, the hives typically disappear. Proper treatment of the underlying infection, along with symptom relief for the hives, can hasten recovery and reduce discomfort.
Clothing Choices and Skin Friction
Wearing tight or rough clothing can cause friction against the skin, exacerbating irritation and potentially triggering hives. This is especially true in hot and humid weather when sweating increases, and fabrics trap moisture. Opting for loose-fitting, breathable clothing made from natural fibers helps minimize skin friction and irritation. Additionally, choosing clothing without harsh dyes or chemicals can further decrease the risk of skin reactions.
Medications and Drug Reactions
Many medications, including antibiotics like penicillin, aspirin, and certain pain relievers, can induce allergic reactions manifesting as hives. If you notice hives after starting a new medication, consult your healthcare provider promptly. They may recommend alternative drugs or adjust dosages. Always inform your doctor about any adverse reactions to medications and avoid self-medicating without professional guidance to prevent serious allergic responses.
Stress and Psychological Factors
Psychological stress and anxiety can significantly impact skin health, including the development of hives. Stress triggers the release of stress hormones, which may impair immune regulation and increase skin sensitivity. Incorporating stress-management practices such as meditation, yoga, deep breathing exercises, and adequate sleep can reduce the frequency and intensity of hives. Recognizing stress as a contributing factor is vital for comprehensive treatment and improved mental health.
Sun Exposure and Solar Urticaria
Some individuals develop hives directly triggered by sunlight, a condition known as solar urticaria. These red, itchy bumps tend to appear upon direct exposure to sunlight and may persist despite the use of sunscreen. To manage this, individuals should limit sun exposure during peak hours, wear protective clothing, and use broad-spectrum sunscreens with high SPF. Consulting a dermatologist can provide personalized strategies and possible treatments such as antihistamines or phototherapy.
Temperature Extremes and Sensitivities
Extreme temperatures can trigger hives in susceptible persons. Heat hives often occur in hot weather or after physical exertion, while cold hives develop after cold exposure, including water or air. Managing environmental conditions, such as staying in climate-controlled environments or wearing appropriate clothing, can help prevent these reactions. For individuals sensitive to temperature changes, gradual acclimatization and avoiding sudden temperature shifts are beneficial.
Sweating and Physical Exertion
Intense physical activity leading to sweating can induce hives in some people, a condition known as cholinergic urticaria. Post-exercise or hot water showers may also act as triggers. To minimize this, stay hydrated, wear loose clothing, and gradually increase activity levels. Cooling down appropriately after exercise and avoiding hot showers in susceptible individuals can help prevent outbreaks.
Underlying Medical Conditions
Persistent or recurrent hives may be symptomatic of other health issues such as autoimmune diseases (like lupus), thyroid disorders, or hepatitis. In such cases, addressing the primary condition often alleviates the hives. If hives are prolonged, recurrent, or accompanied by other symptoms such as swelling, difficulty breathing, or dizziness, seek immediate medical evaluation. Proper diagnosis and management are essential to rule out serious underlying health concerns.
In conclusion, while most cases of hives are temporary and resolve without extensive treatment, understanding the diverse triggers and implementing effective management strategies can significantly improve your skin health. Avoiding known triggers, maintaining good skincare habits, and seeking medical advice when needed are key components of managing this common skin condition. With proper care, individuals can minimize the frequency and severity of hives, leading to healthier and more comfortable skin.