Comprehensive Guide to Hepatitis C: Recognizing Early Symptoms and Skin Manifestations
Hepatitis C presents with subtle early signs, including jaundice and fatigue, and skin reactions like urticaria and lichen planus. Recognizing these symptoms early and understanding skin manifestations are vital for prompt diagnosis and effective management. This comprehensive guide covers hepatitis C's symptoms, skin rashes, and prevention tips, helping patients and healthcare providers stay alert for signs of infection and prevent severe liver complications.

Understanding Hepatitis C: Recognizing Its Early Signs and Skin Symptoms
Hepatitis C is a viral disease that primarily affects the liver, leading to inflammation and potential long-term damage if not diagnosed and treated early. It is caused by the hepatitis C virus (HCV), which enters the bloodstream and targets liver cells. This infection can be asymptomatic in its early stages, making awareness of subtle signs crucial for early detection. In addition to internal symptoms, hepatitis C often manifests through various skin reactions, including rashes, which can serve as visual cues for underlying infection. Regular screening, particularly for high-risk populations, coupled with attention to skin changes, can significantly improve prognosis and prevent severe complications like cirrhosis or liver cancer.
Understanding the Early Signs of Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C can present in two forms: acute and chronic. The acute phase occurs shortly after infection and may be mild or asymptomatic, while the chronic phase can develop insidiously over years. This latency often results in delayed diagnosis, emphasizing the importance of awareness. Since the virus impacts liver function primarily, early symptoms often relate to liver impairment and include distinctive signs such as jaundice, fatigue, and digestive disturbances.
Common Early Symptoms of Hepatitis C
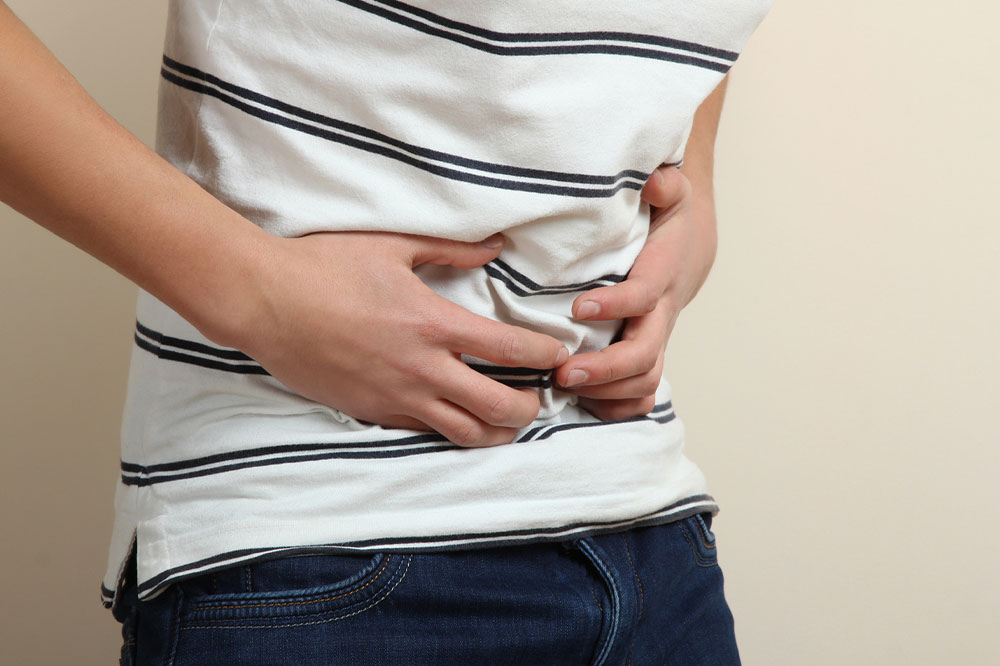
Jaundice, which causes yellowing of the skin and eyes, is among the most recognizable signs indicating liver dysfunction.
Abdominal discomfort or pain, especially in the upper right quadrant, signifies liver inflammation or enlargement.
Dark-colored urine is another indicator, often resulting from excess bilirubin processing issues.
Light-colored stools can also appear, reflecting bile flow disruption.
Fever and chills may occur during acute infection, often accompanied by flu-like symptoms.
Extreme fatigue or prolonged tiredness is a common complaint among infected individuals.
Hepatitis C-Related Skin Rashes: An External Clue to Internal Issues
Persistent hepatitis C infection can trigger various skin reactions. In the early stages, some patients may experience itching and rashes as the immune system responds to the viral presence. These skin manifestations can serve as visual cues to prompt further medical assessment. The rashes associated with hepatitis C are generally seen on the torso, chest, arms, and sometimes on the face. Recognizing these skin changes is vital for early intervention, especially since internal liver damage may be asymptomatic initially.
Types of Rashes and Skin Conditions Linked to Hepatitis C
The skin reactions associated with hepatitis C vary depending on the stage and immune response. Below are some common rashes and skin conditions linked with the infection:
1. Urticaria (Hives)
One of the most prevalent skin reactions during acute hepatitis C is urticaria, characterized by itchy, raised patches that are red or skin-colored. These hives can appear suddenly, swell, and last for hours. They are often allergy-related, triggered by immune responses to the virus or other allergens. Urticaria can recur in waves, causing persistent discomfort requiring appropriate antihistamine treatment.
2. Lichen Planus
This chronic inflammatory condition is more common among individuals with long-standing hepatitis C. It presents as flat, shiny, scaly bumps which often appear in the mouth, scalp, or wrists. The lesions are typically reddish-purple with white striae and can be confused with eczema. Due to its chronic nature, accurate diagnosis by a dermatologist is crucial for effective management, which may include topical steroids and immune-modulating therapies.
3. Purpura
Associated with vasculitis—an inflammation of blood vessels—purpura manifests as purple or red patches on the skin that do not blanch when pressed. These spots result from blood vessel rupture under the skin, indicating bleeding phenomena linked with hepatitis C. The size of these patches varies, and they can sometimes be accompanied by other signs of bleeding or skin fragility.
4. Pruritus (Itchy Skin)
Itching without an obvious rash is a common complaint among hepatitis C patients. Pruritus can significantly impact quality of life, and its severity may vary. To minimize skin damage, patients are advised to avoid scratching, keep the skin well-moisturized, and use soothing creams. Topical antipruritics or antihistamines may be prescribed by healthcare providers to alleviate discomfort.
Other Notable Skin Conditions Related to Hepatitis C
Porphyria cutanea tarda: characterized by fragile skin prone to blistering, especially in sun-exposed areas, often accompanied by hyperpigmentation.
Necrolytic acral erythema: a rare rash resembling psoriasis that may involve itching and burning sensations.
Raynaud’s phenomenon: episodes of finger, toe, or facial discoloration due to blood vessel spasms triggered by cold or stress.
Sicca syndrome: autoimmune dry syndrome affecting the mouth, eyes, and skin, often coexisting with hepatitis C.
It is important to note that while hepatitis C is contagious, these skin rashes are immune responses and are not transmissible through skin contact. Early recognition of skin symptoms through online resources and consultation with healthcare professionals can improve early diagnosis. Managing skin symptoms involves protective measures such as limiting sun exposure, wearing loose natural fabrics, regular moisturizing, avoiding harsh chemicals, and maintaining skin hygiene.