Comprehensive Guide to Managing Common Dermatitis and Skin Reactions Effectively
This comprehensive guide offers in-depth information on managing common dermatitis and skin reactions such as eczema, granuloma annulare, lichen planus, and pityriasis rosea. It details symptoms, causes, and scientifically proven treatments, emphasizing the importance of professional diagnosis and personalized care for effective management and symptom relief. Learn practical skincare strategies, medication options, and when to seek medical advice to ensure optimal skin health and comfort.
Effective Strategies for Managing Common Skin Conditions and Reactions
Skin reactions and dermatitis are prevalent concerns that affect millions worldwide, leading to discomfort, itching, redness, and various skin irregularities. Proper management and treatment are essential not only for relief but also to prevent potential complications or worsening of the condition. This comprehensive guide explores the most common types of dermatitis and skin reactions, their causes, symptoms, and scientifically backed treatment options, providing valuable insights for both patients and healthcare professionals.
Understanding the diverse nature of skin conditions is crucial for effective management. Since symptoms can sometimes overlap or resemble other dermatological issues, consulting with a healthcare provider for accurate diagnosis is highly recommended. Additionally, leveraging visual aids such as skin rash images available online can assist in initially identifying your skin condition, but definitive diagnosis should always be confirmed by a professional.
The primary types of dermatitis discussed include eczema, granuloma annulare, lichen planus, and pityriasis rosea. Each condition has unique features, but effective treatment strategies can significantly alleviate symptoms and improve quality of life.
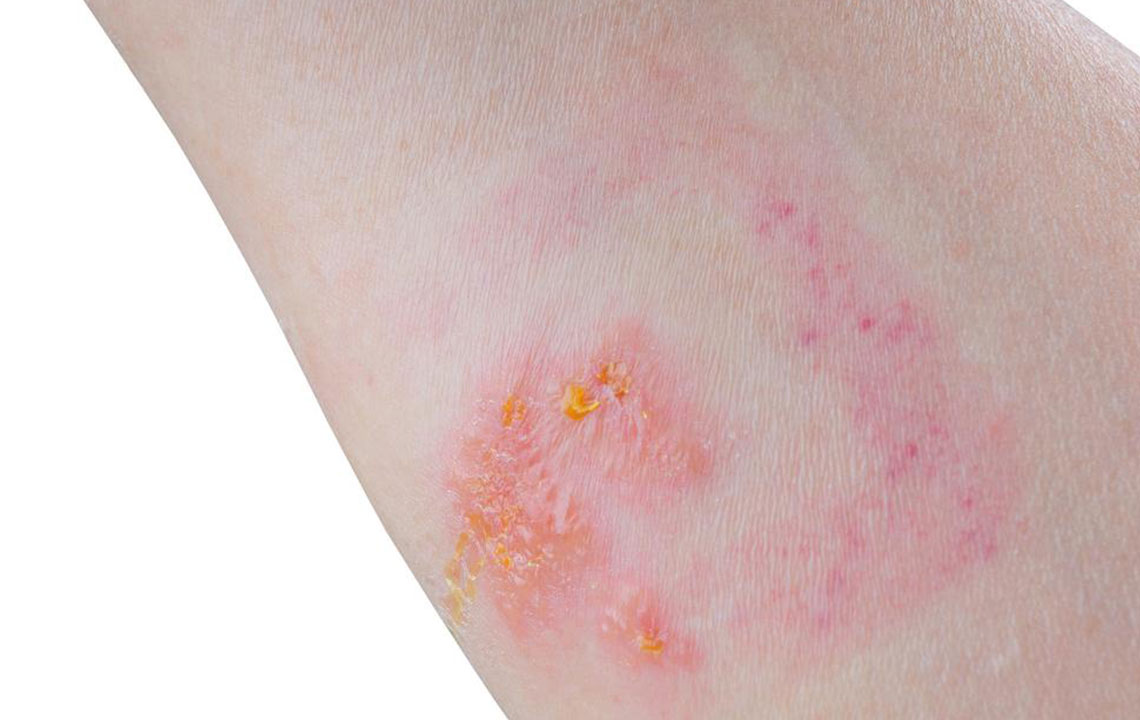
Eczema (Atopic Dermatitis): One of the most common skin issues, eczema presents as dry, inflamed, red, itchy patches on the skin. Atopic eczema is especially prevalent among children but can affect individuals of all ages. The condition is characterized by skin barrier dysfunction, leading to increased susceptibility to irritants and allergens. Treatment usually involves topical medications such as hydrocortisone creams, which help reduce inflammation, itching, and redness. For more stubborn cases, healthcare providers might recommend cortisone-based pills or injections to control severe inflammation. Additionally, skin moisturizers and avoiding known irritants are critical in managing eczema effectively. Proper skincare routines, including gentle cleansing and hydration, play an essential role in preventing flare-ups and maintaining skin health.
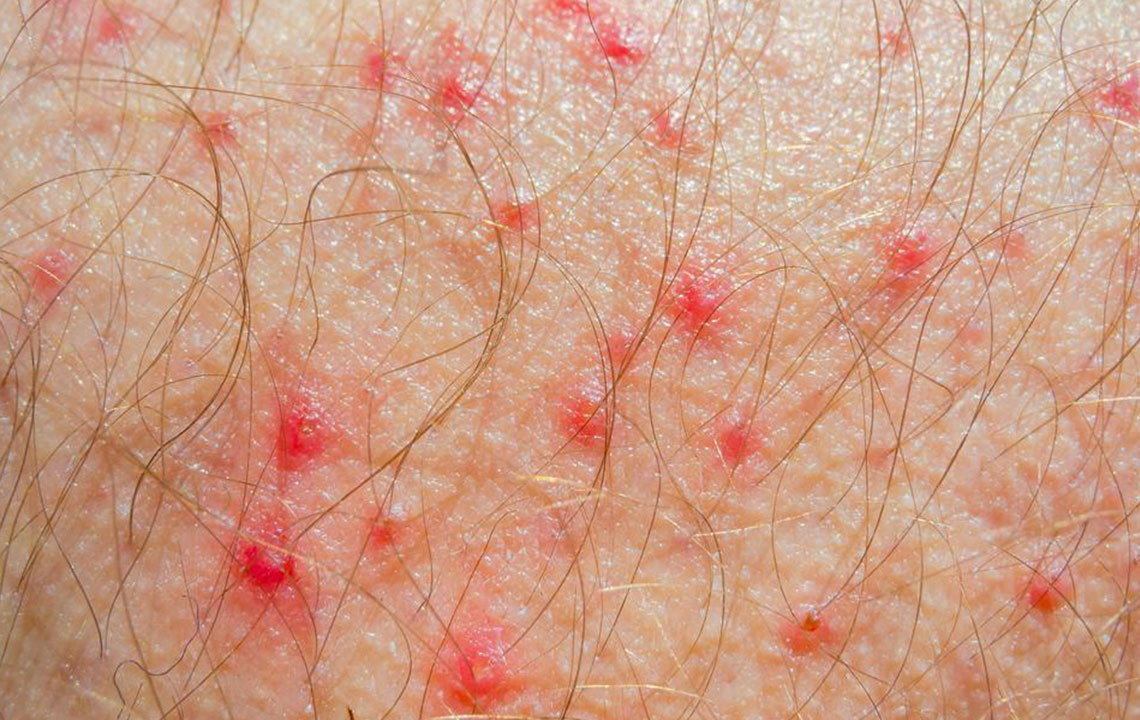
Granuloma annulare manifests as circular skin lesions with reddish or skin-colored bumps, commonly affecting children and young adults. These lesions are often located on the hands, fingers, or forearms. While the exact cause remains unknown, treatment options focus on reducing inflammation and promoting healing. Steroid creams and ointments are typically the first-line treatment, sometimes combined with corticosteroid injections directly into the lesions to decrease swelling and redness. In persistent or severe cases, dermatologists may suggest ultraviolet (UV) light therapy or prescribe oral medications to help control the condition. Although granuloma annulare can resolve spontaneously over time, prompt treatment may hasten recovery and reduce discomfort.
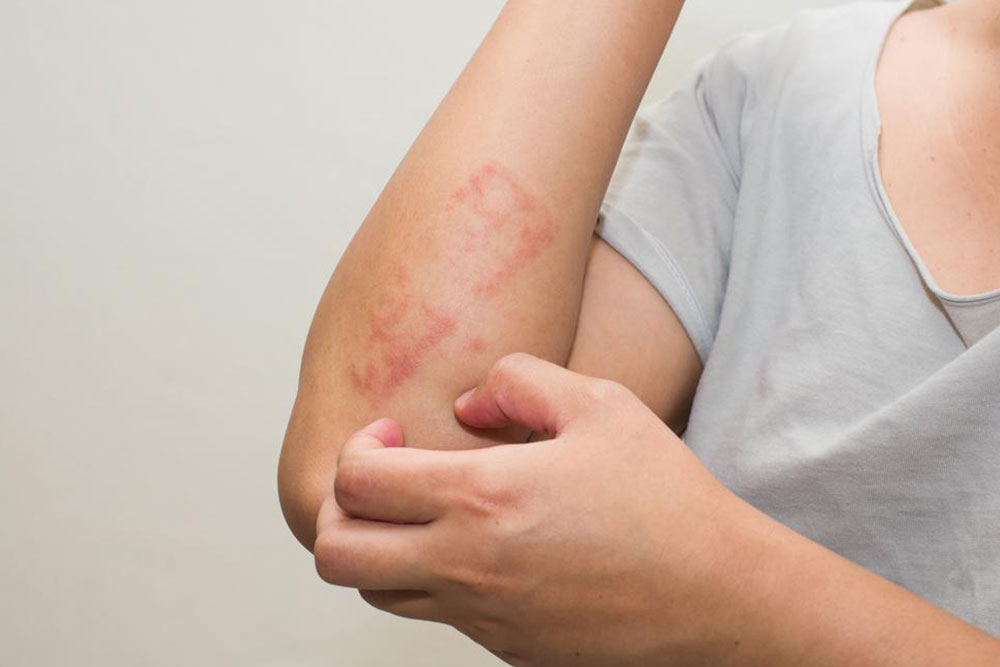
Lichen planus appears as shiny, flat-topped, reddish-purple bumps, usually found on the wrists, ankles, legs, back, or neck. It can cause significant itching and discomfort but does not have a known cure. Management focuses on relieving symptoms through antihistamines and anti-itch topical agents. Corticosteroid creams may also be prescribed to reduce inflammation. Patients are advised to avoid triggers such as stress, certain medications, or skin irritants. Although lichen planus may persist for months or years, consistent treatment can help control symptoms and prevent secondary infections.
Pityriasis rosea begins with a single large, scaly, pink patch called a ‘herald patch’ typically appearing on the chest or back. This initial lesion is followed by smaller spots that can vary in size and distribution. The condition is usually self-limited, resolving spontaneously within several weeks to a few months. Nonetheless, antihistamines can be used to relieve itching and discomfort during the course of the rash. Maintaining skin hydration, avoiding irritants, and wearing loose clothing are also recommended to manage symptoms effectively. Proper diagnosis is essential for distinguishing pityriasis rosea from other skin conditions, and consulting a healthcare provider ensures appropriate management.
Overall, understanding these common skin conditions, their symptoms, and the most effective treatment approaches can significantly improve patient outcomes. Using visual aids such as skin rash images online can aid in initial identification, but professional medical consultation is essential for accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plans. Maintaining good skin hygiene, avoiding known triggers, and adhering to prescribed treatments are key steps toward healthier skin and better quality of life.