Comprehensive Strategies to Relieve Stiff Neck Pain Quickly and Effectively
Discover comprehensive methods to quickly relieve a stiff neck, including effective home remedies, professional treatments, and lifestyle tips. Learn about common causes, symptoms, and prevention strategies to manage neck pain effectively and regain comfort promptly.

Proven Methods to Alleviate a Stiff Neck Fast
Experiencing a stiff neck can be incredibly disruptive to your daily life, causing discomfort that hampers movement and activities. Whether it’s due to poor posture, sudden movements, or underlying medical conditions, neck stiffness can range from mild soreness to severe pain. Fortunately, there are numerous effective strategies to relieve neck stiffness promptly, helping you restore comfort and normal function. This article explores in detail the causes, symptoms, and best treatment options available, including home remedies, lifestyle adjustments, and when to seek medical attention.
The neck is a complex structure comprising bones (vertebrae), muscles, ligaments, and connective tissues that work together to support head movement and protect the spinal cord. Any disruption in this delicate system—be it inflammation, injury, or structural abnormalities—can lead to neck pain. Understanding the anatomy and common causes of neck stiffness is essential for effective relief and prevention.
Neck pain often stems from strained or torn muscles, ligaments, or tendons, generally caused by overuse, strain, or injury. The pain can be mild to severe, depending on the extent of tissue damage. Mild discomfort may resolve naturally over a few days with proper care, but intense or persistent pain often requires targeted treatment. Recognizing common causes enables better management of neck stiffness and helps prevent future episodes.
Understanding the Main Causes of a Stiff Neck
Neck discomfort results from various factors impacting the cervical region, which spans from the base of the skull down to the upper shoulders. The complex tissues supporting this area can become strained or injured due to multiple reasons, including:
Muscle overstrain or tension: Prolonged poor posture, such as slouching at a desk or sleeping with inadequate support, can overstretch neck muscles. Sudden or awkward movements during exercise or daily activities may also cause strain.
Trauma or injury: Accidents involving falls, whiplash from car collisions, or sports injuries can cause significant neck trauma. These injuries may result in sprains, strains, or more serious conditions requiring medical intervention.
Underlying medical conditions: Certain health issues, including arthritis, spinal stenosis, herniated discs, or osteoporosis, can contribute to chronic neck stiffness. These degenerative conditions tend to worsen with age and require specialized care.
Infections and systemic illnesses: Rarely, infections such as meningitis or other inflammatory diseases can cause neck stiffness along with fever, headache, and other systemic symptoms. Immediate medical attention is crucial in such cases.
Additional factors: Poor ergonomics, stress, or even dehydration can exacerbate muscle tension, leading to a stiff neck.
Recognizing the symptoms early and understanding the root causes is key to effective treatment and prevention of recurrent neck stiffness.
Effective Treatment Options for Stiff Neck Relief
The appropriate treatment for neck stiffness depends on its cause, severity, and duration. While minor strains often resolve with simple home care, more serious issues like herniated discs or spinal abnormalities require professional medical management. Consulting a healthcare provider ensures accurate diagnosis and tailored treatment plans to promote recovery and prevent further injury.
Here is a comprehensive overview of the treatments available:
Medication Therapy: Over-the-counter pain relievers such as acetaminophen or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can reduce inflammation and alleviate pain. Muscle relaxants may be prescribed for severe muscle spasms. In cases of infection, antibiotics or antiviral medications are necessary. Corticosteroid injections can also provide short-term relief for inflammation.
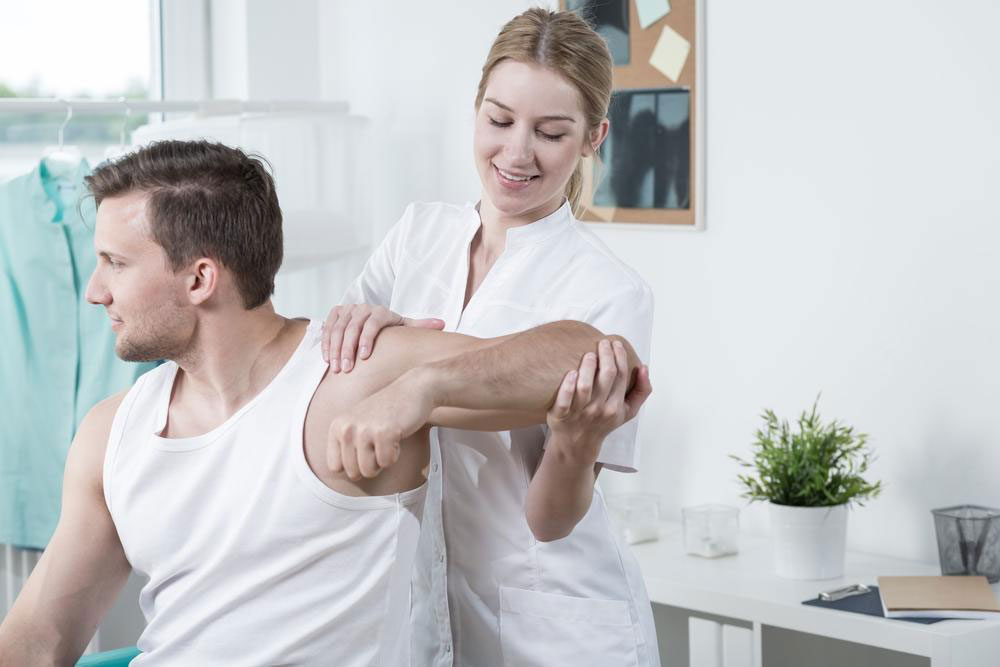
Physiotherapy and Manual Therapy: A trained physical therapist can guide you through gentle stretching exercises designed to restore flexibility and strengthen neck muscles. Manual therapy techniques, including massage and mobilization, can relieve muscle tension. Applying heat or cold packs before or after therapy sessions aids recovery.
Supportive Devices and Immobilization: Using a cervical collar temporarily can reduce movement and allow tissues to heal in cases of acute injury. However, prolonged use is discouraged as it may weaken muscles.
Traction and Spinal Decompression: These methods are used primarily in chronic cases linked to disc herniation or nerve compression. They help relieve pressure on cervical discs and nerves.
Surgical Intervention: Reserved for severe cases involving structural abnormalities, fractures, or nerve impingement resistant to conservative treatments. Surgery aims to correct structural problems and alleviate pain.
Home Remedies and Preventive Measures for Neck Pain
For mild to moderate neck pain, several home remedies can effectively provide relief. Applying ice packs initially can help reduce swelling and inflammation, especially if pain results from recent injury. After 48 hours, heat pads or warm compresses promote blood flow and relax tense muscles. Maintaining a proper posture, especially during prolonged sitting, is vital to prevent recurrence.
Additional self-care tips include:
Engaging in gentle neck stretches and exercises recommended by healthcare providers.
Practicing good ergonomics at work and during daily activities to minimize strain.
Ensuring adequate hydration to keep tissues healthy.
Managing stress through relaxation techniques like deep breathing or meditation.
Scheduling regular breaks from screen time to avoid posture-related strain.
Alternative therapies such as acupuncture, chiropractic adjustments, and massage therapy can complement conventional treatments and promote faster recovery. However, persistent or worsening pain warrants professional medical evaluation to rule out serious conditions.