Comprehensive Guide to Spinal Surgery: When It’s Needed, Types, and Recovery Strategies
This comprehensive guide explores when spinal surgery is necessary, the common types of procedures like fusion and discectomy, and essential recovery tips to ensure optimal healing. It emphasizes early diagnosis, tailored treatment plans, and the importance of postoperative care in improving quality of life for patients suffering from chronic back pain. Ideal for those considering surgical options, the article highlights advancements in spinal surgery and recovery strategies to promote a safe and effective healing process.

The human spine plays a crucial role in supporting our entire body structure and enabling a wide range of movements essential for daily life. Comprising complex components like vertebrae, intervertebral discs, nerves, and the spinal cord, this intricate system maintains stability, flexibility, and protection for vital neural pathways. While the spine is remarkably resilient, various factors such as aging, physical exertion, and stress can lead to chronic back pain, significantly affecting quality of life. Most cases of back discomfort can be managed through conservative treatments, but when pain persists beyond several months without improvement, surgical intervention may become necessary.
Understanding When Spinal Surgery Becomes Necessary
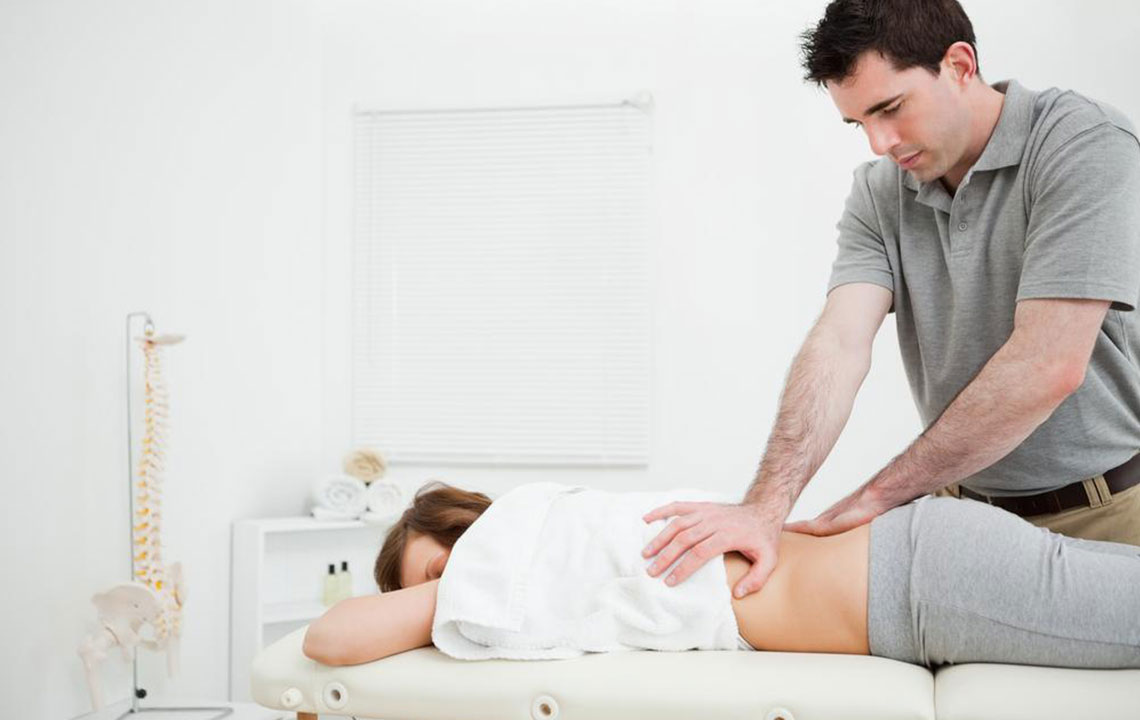
Deciding on spinal surgery involves careful assessment by healthcare professionals, typically after exploring all non-invasive options. Surgery is particularly indicated for patients suffering from persistent back pain that interferes with daily activities and fails to respond to medication, physiotherapy, or lifestyle modifications. The goal of intervention is to alleviate nerve compression, stabilize the spine, and restore mobility.
Several conditions warrant surgical correction, including:
Herniated or ruptured discs that compromise the cushioning between vertebrae, leading to nerve impingement.
Spinal stenosis, where the spinal canal narrows, causing pressure on the spinal cord or nerve roots.
Spondylolisthesis, a condition where one vertebra slips out of alignment, resulting in instability and pain.
Vertebral fractures resulting from traumatic injury or osteoporosis, which threaten spinal integrity.
Degenerative disc disease, often associated with aging, which leads to deterioration of disc structure and function.
Major Types of Back Surgeries and Their Purposes
When conservative treatments such as physical therapy, medications, or lifestyle changes do not provide relief, surgical options are considered to correct structural problems, decompress nerves, or stabilize the spine. Although undergoing surgery can be intimidating, advances in medical technology and surgical techniques have made procedures safer with quicker recovery times. Proper selection of surgical method tailored to the specific condition can greatly improve symptom relief and overall quality of life.
Common surgical procedures include:
Spinal Fusion: This procedure involves fusing two or more vertebrae together using bone grafts, hardware, or a combination of both. The goal is to eliminate painful movement between vertebrae, providing stability, reducing deformity, and alleviating nerve pressure. It’s often used to treat degenerative disc disease, spondylolisthesis, or spinal instability.
Laminectomy: In this surgery, part of the vertebral bone called the lamina is removed to enlarge the spinal canal. This helps relieve pressure caused by bone spurs, herniated discs, or thickened ligaments pressing on the spinal cord or nerve roots. It’s particularly common in cases of spinal stenosis.
Discectomy: This minimally invasive procedure involves removing herniated or ruptured disc material pressing on nearby nerves. Discectomy can significantly reduce pain, numbness, and weakness associated with nerve compression.
Postoperative Recovery Tips for a Smooth Healing Process
Recovery after spinal surgery is a critical phase that influences long-term outcomes. While each patient’s healing process varies based on age, overall health, and the specific procedure performed, certain general principles can help promote effective recovery. Following a comprehensive postoperative plan designed by healthcare professionals maximizes the chances of a successful outcome.
Key recovery tips include:
Prioritize Nutritious Eating and Hydration: Consuming a balanced diet rich in vitamins, minerals, and protein supports tissue repair and immune function. Staying well-hydrated aids in reducing inflammation and promotes healing.
Maintain Quality Sleep: Restorative sleep is essential for tissue regeneration. Creating a sleep-friendly environment and following good sleep hygiene practices help optimize recovery, even amid discomfort.
Engage in Prescribed Exercises: Physical therapy exercises tailored to your condition enhance spinal stability, flexibility, and strength. Adherence to rehab routines accelerates recovery and prevents future issues.
Practice Proper Posture and Body Mechanics: Keeping correct alignment during daily activities minimizes undue stress on the healing spine. Learning safe movement techniques protects against setbacks.
Follow Medical Advice and Rehab Protocols: Regular check-ins with your healthcare team and adhering to prescribed medications, therapies, and activity restrictions are vital for optimal recovery.
In summary, early consultation with healthcare providers enables accurate diagnosis and the formulation of effective treatment plans for persistent back pain. When conservative measures cannot provide adequate relief, surgical options serve as a valuable means to restore spinal function, relieve nerve pressure, and improve overall quality of life. Many health systems also offer financial assistance programs to help offset the costs of surgery, making these procedures accessible to more patients. With proper care and management, individuals can aim for full recovery and a return to active, comfortable living.