Complete Guide to Hip Replacement Surgery: Procedures, Preparation Tips, and Alternative Options
Discover comprehensive insights into hip replacement surgery, including different surgical options, how to prepare effectively, and viable alternative treatments. This guide aims to equip patients with knowledge to make informed healthcare decisions, ensuring a smooth recovery and long-term joint health. From total replacements to minimally invasive options and regenerative therapies, learn what suits your condition best and how to optimize your pre- and post-surgery care for optimal results.
Complete Guide to Hip Replacement Surgery: Procedures, Preparation Tips, and Alternative Options
Hip problems caused by conditions such as osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and traumatic injuries can significantly impair quality of life. Persistent hip pain, stiffness, limited mobility, and difficulty performing everyday tasks often prompt individuals to seek surgical solutions when conservative treatments prove inadequate. Hip replacement surgery has become a standard and highly effective method to restore function and relieve pain for millions worldwide. Understanding the various types of hip replacement procedures, preparing adequately for surgery, and knowing about alternative treatments can empower patients to make informed decisions about their healthcare.
Understanding the Types of Hip Replacement Procedures
There are several surgical options available for hip replacement, each tailored to the patient's specific needs, age, activity level, and the severity of joint damage. The primary types of hip replacements include total hip arthroplasty, partial hip replacement, and hip resurfacing. Each approach has unique benefits and considerations, and your orthopedic surgeon will recommend the most suitable option based on your condition.
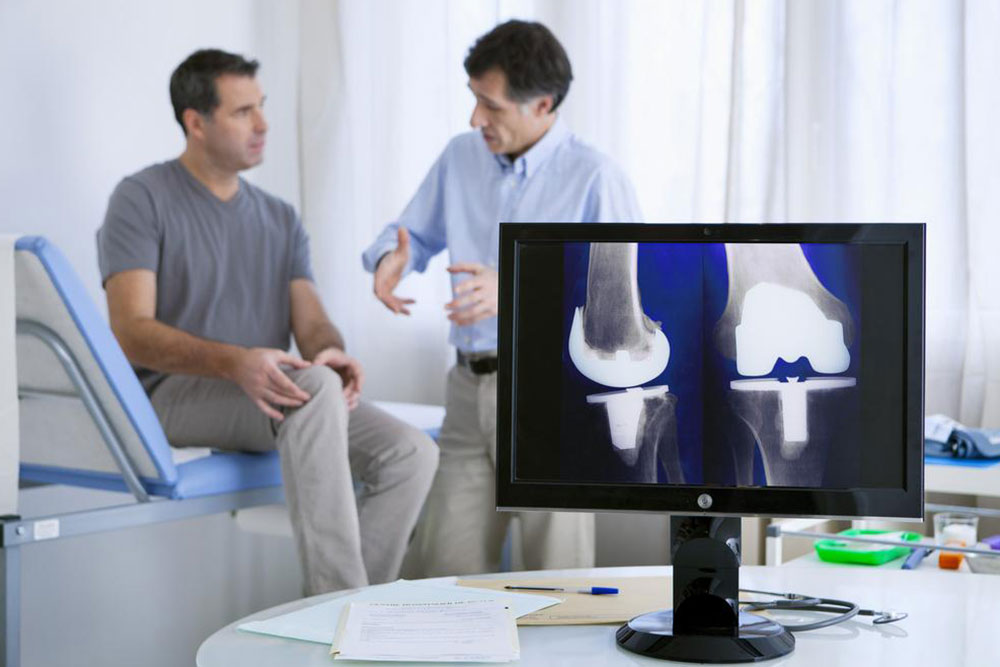
Total Hip Replacement: This is the most common form of hip surgery, often referred to as total hip arthroplasty. During this procedure, the entire joint is replaced. The damaged socket (acetabulum) is removed and replaced with a durable plastic or ceramic cup. The femoral head (ball) is also removed and replaced with a specially designed metal or ceramic ball attached to a metal stem inserted into the thigh bone (femur). This procedure aims to restore joint function, reduce pain, and improve mobility significantly.
Partial Hip Replacement: Also known as hemiarthroplasty, this procedure involves replacing only the damaged part of the hip joint, typically the femoral head. It’s often recommended for elderly patients with specific types of fractures or localized joint damage. Since it preserves more of the natural bone and tissue, recovery may be quicker, but it may not be suitable for all conditions.
Hip Resurfacing: An alternative to full joint replacement, this technique involves capping the existing femoral head with a metal prosthesis after reshaping it slightly. The process preserves more bone tissue, which can be advantageous for younger, active patients. However, not everyone qualifies for this option, especially those with significant osteoporosis or deformities.
Preparing for Hip Replacement Surgery
Proper preparation for hip replacement surgery enhances recovery outcomes and minimizes complications. Patients should start by understanding the surgical process, implant materials, potential risks, and post-operative expectations. Preoperative planning typically involves several steps:
Medical Evaluation: Comprehensive health assessment, including blood tests, imaging studies, and heart evaluations, to ensure fitness for surgery.
Optimizing Health: Addressing weight management, controlling blood sugar levels for diabetics, quitting smoking, and managing chronic conditions such as hypertension or heart disease improve surgical success and recovery.
Physical Readiness: Engaging in pre-surgical exercise routines focusing on strengthening the upper body and core muscles can aid in rehabilitation. Physical therapists can recommend tailored exercises to improve mobility and balance.
Home Environment Adjustment: Preparing a safe, accessible space at home by removing tripping hazards, adding supportive railings, and arranging furniture to facilitate easier movement during recovery.
Planning Post-Operative Support: Arranging for assistance during the initial recovery phase, as well as understanding the role of caregivers and rehabilitation services.
Understanding implant materials—such as ceramic, metal, and high-grade plastics—is crucial, as these affect the durability and compatibility of the prosthesis. Discuss implant options thoroughly with your surgeon and ensure you’re aware of the expected outcomes. Additionally, it’s recommended to avoid certain medications, such as blood thinners, prior to surgery under your doctor’s guidance.
Hospital stays typically last between 3 to 5 days, depending on individual health and recovery progress. Early post-operative pain management, coupled with physical therapy, is critical to regaining joint mobility and strength. Patients are encouraged to start gentle movement exercises as soon as possible to prevent blood clots, improve circulation, and facilitate healing.
Recovery and Postoperative Exercises
Rehabilitation focuses on gradually restoring joint function, strength, and flexibility. Physical therapy plays an integral role, involving exercises designed specifically for hip joint recovery. These exercises should always be performed under professional supervision or following a tailored plan prescribed by your healthcare team. Typical post-surgery exercises include ankle pumps to improve circulation, quad sets to strengthen the thigh muscles, gluteal squeezes to stabilize the pelvis, and gentle range-of-motion stretches.
As healing progresses, patients may start more active routines like standing heel raises and knee flexion exercises to improve muscle strength and joint stability. Adherence to physical therapy routines significantly influences long-term success, helping to reduce pain, improve mobility, and prevent future complications.
Exploring Alternative Treatments for Hip Conditions
Not all patients opting for surgery are suitable candidates, or they may wish to explore less invasive options first. There are various alternative treatments available, especially for seniors or individuals with less severe joint degeneration. These options can help manage symptoms and maintain a good quality of life without the need for surgery.
Minimally Invasive Techniques: Focused on symptom management through physical therapy, injections, and lifestyle modifications. These methods aim to reduce pain and improve functions without extensive surgery.
Resection Arthroplasty: For patients with severe joint damage and mobility issues, this procedure involves removing damaged joint tissues to relieve pain, often used in specific clinical scenarios.
Hip Osteotomy: A surgical procedure that realigns the bones around the hip to reduce joint stress and slow degeneration, suitable for younger patients with certain deformities.
Regenerative Medicine: Emerging therapies like stem cell injections and platelet-rich plasma aim to repair damaged cartilage and tissues, potentially delaying or avoiding the need for full joint replacements. While promising, these treatments are still under research and not yet widely available.