Comprehensive Guide to Hernia Repair: Choosing the Best Surgical Method for You
This comprehensive article explores hernia repair options, focusing on traditional open and minimally invasive laparoscopic surgeries. It highlights the procedures' benefits, risks, mesh use, recovery tips, and why choosing the right surgical method is critical. Patients can make informed decisions to ensure successful hernia treatment and smoother recovery. Perfect for those seeking detailed insights into modern hernia surgery techniques and advancements.

Comprehensive Guide to Hernia Repair: Choosing the Best Surgical Method for You
Hernias are a common medical condition that often necessitates surgical intervention to restore normal anatomy and prevent complications. Understanding the different hernia repair techniques available today can empower patients to make informed decisions in consultation with their healthcare providers. This extensive guide elaborates on the various surgical options, their advantages, potential risks, and important considerations for a successful recovery. Whether you are facing an initial hernia treatment or exploring minimally invasive options, this article aims to provide comprehensive insights to help you choose the most suitable approach for your specific circumstances.
Varieties of Hernia Repair Procedures
In the realm of hernia treatments, especially in the United States, surgeons primarily endorse two main types of procedures: traditional open repair and advanced minimally invasive laparoscopic surgery. Each approach has distinct features, suitable patient profiles, and recovery profiles. Recognizing these differences is key to selecting an optimal treatment strategy tailored to individual needs and health profiles.
Traditional Open Hernia Repair
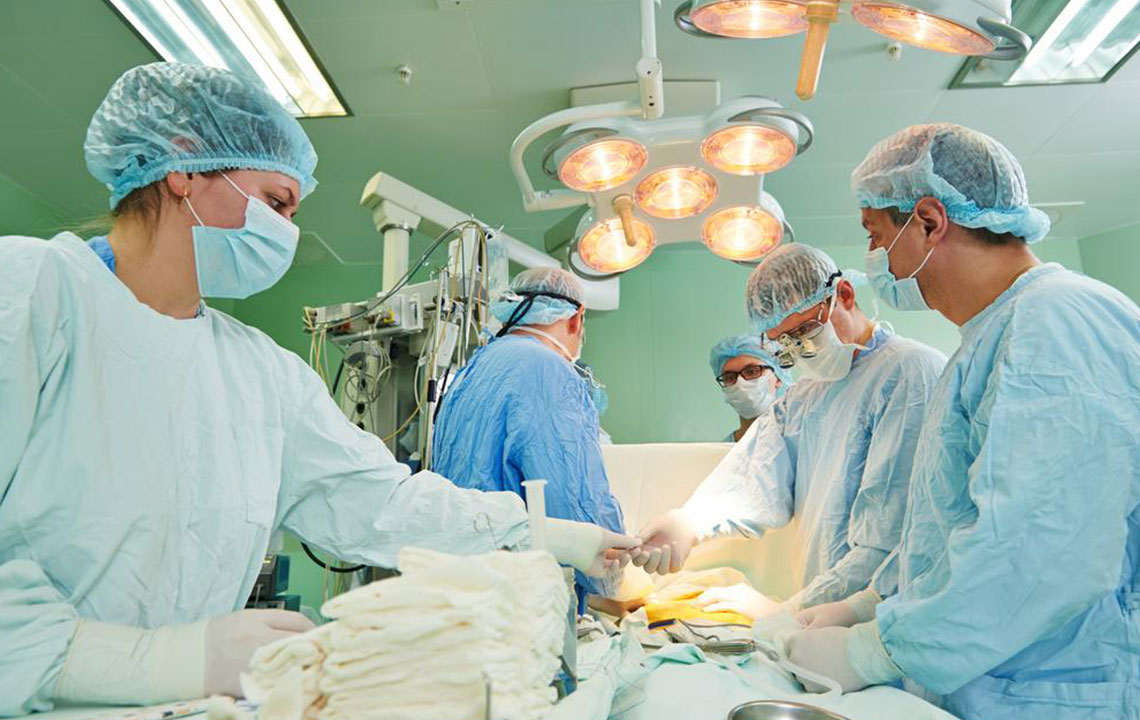
This conventional surgical method involves making a single, well-placed incision directly over the hernia bulge. The surgeon then meticulously pushes the protruding tissue back into its proper place or removes damaged tissue as needed. The repair typically involves suturing the muscle tissue together or reinforcing it with synthetic materials such as surgical mesh to provide additional strength, thereby reducing the chance of hernia recurrence.
Minimally Invasive Laparoscopic Hernia Repair
Laparoscopic hernia repair is a state-of-the-art surgical technique utilizing small incisions, usually less than an inch, through which specialized instruments are inserted. A tiny camera, known as a laparoscope, is used to provide a magnified, high-definition view of the internal structures on a monitor. This advanced visualization allows surgeons to perform precise repairs with less disruption to surrounding tissues, leading to less postoperative pain and quicker healing.
A core component of laparoscopic surgery is the insertion of a camera with integrated lighting, along with miniature surgical tools, through small keyhole incisions. To facilitate the procedure, carbon dioxide gas is introduced into the abdominal cavity, inflating it and creating a workable space for the surgeon. Once the hernia repair is complete, this gas is safely released, allowing the patient to recover more comfortably. The magnified view provides exceptional clarity, reducing risks and improving outcomes, especially in complex hernias.
Role of Mesh in Hernia Reinforcement
The utilization of surgical mesh has revolutionized hernia repairs by significantly reducing recurrence rates. Hernias usually occur through weakened tissues, and placing a synthetic mesh over the defect acts as a sturdy barrier that reinforces the damaged area. The mesh supports tissue regeneration and minimizes tension on sutures, which often leads to less postoperative discomfort. During the healing process, tissue grows into the mesh, securing its position and restoring the integrity of the abdominal wall. This reinforcement reduces the likelihood of hernia recurrence, providing patients with a more durable repair.
Mesh placement is typically straightforward in laparoscopic procedures, bridging the hernia defect with minimal sutures. The choice of mesh type—synthetic, bio-absorbable, or composite—depends on patient factors and surgeon preference. Proper placement and fixation are critical to avoid complications such as mesh migration or infection.
Understanding Keyhole and Laparoscopic Techniques
Often referred to as keyhole surgery due to the small incisions resembling a keyhole shape, laparoscopic hernia repair boasts numerous benefits. The procedure usually takes less than two hours, and most patients can return home within the same day. Postoperative recovery is generally swift, with most individuals resuming normal activities within 2 to 3 weeks. However, strenuous activities and heavy lifting should be avoided for at least two months to ensure proper healing and to prevent hernia recurrence.
Despite its advantages, laparoscopic surgery requires specialized training and experience. Incorrect technique or improper placement of mesh can lead to complications, including chronic pain, mesh infection, or recurrence of the hernia. Consulting with a skilled surgeon is essential for optimal results.
Benefits and Potential Drawbacks of Minimally Invasive Hernia Surgery
The success rates for laparoscopic hernia repair are generally high, particularly in experienced surgical centers. Patients enjoy the benefits of smaller scars, less postoperative pain, and faster recovery times compared to traditional open surgery. These advantages often translate into a better overall patient experience. Nonetheless, these procedures demand considerable surgical expertise; inexperienced surgeons may inadvertently increase the risk of complications such as organ injury or improper mesh placement.
While pain is common during initial recovery as tissues heal, most patients report significant comfort improvements over open surgery. The minimally invasive approach is often the preferred choice for many candidates, especially those with recurrent hernias or bilateral hernias.
Limitations and Risks of Laparoscopic Hernia Repair
However, laparoscopic repairs are not without challenges. The presence of permanent synthetic mesh can sometimes lead to infection, mesh protrusion, or rejection. Such complications may necessitate additional surgeries. Additionally, because the procedure relies heavily on two-dimensional imaging, there is a risk of accidental injury to blood vessels or nearby organs, especially if visualization or technique is suboptimal. Emerging 3D imaging technologies are being integrated into laparoscopic surgery to improve navigation and minimize these risks.
Why Opt for Minimally Invasive Surgery Instead of Traditional Open Repair?
In many cases, minimally invasive laparoscopic hernia repair is favored over open surgery, particularly for bilateral or recurrent hernias. Its smaller incisions mean less scarring and faster return to daily activities. Surgeons generally recommend this approach when suitable, given its lower postoperative pain and metastatic benefits. However, the choice depends on individual patient factors such as hernia size, location, and overall health status.
Essential Preventive Measures and Patient Preparation
Preoperative planning is crucial to ensure a smooth surgical experience and optimal outcomes. Patients should consider the following precautions:
Discuss with your healthcare provider the urgency of the hernia repair, especially if the hernia is reducible or asymptomatic.
Control chronic conditions like diabetes to reduce postoperative complications.
Manage other health issues such as respiratory problems or urinary system conditions that could influence recovery.
Be aware of the potential for hernia recurrence and adhere to doctor’s advice regarding lifestyle adjustments and postoperative care.