The Ultimate Guide to Preventing and Treating Osteoporosis: Strategies for Stronger Bones
This comprehensive guide explores osteoporosis management, covering treatment options like medications, injectable therapies, and surgical procedures. It emphasizes the importance of early diagnosis, personalized care, and lifestyle modifications to prevent fractures and strengthen bones. Learn how targeted treatments and preventive measures can help maintain bone health and improve quality of life, especially in aging populations. Essential reading for those seeking to understand osteoporosis and its effective management strategies.
Comprehensive Approach to Osteoporosis Management and Prevention
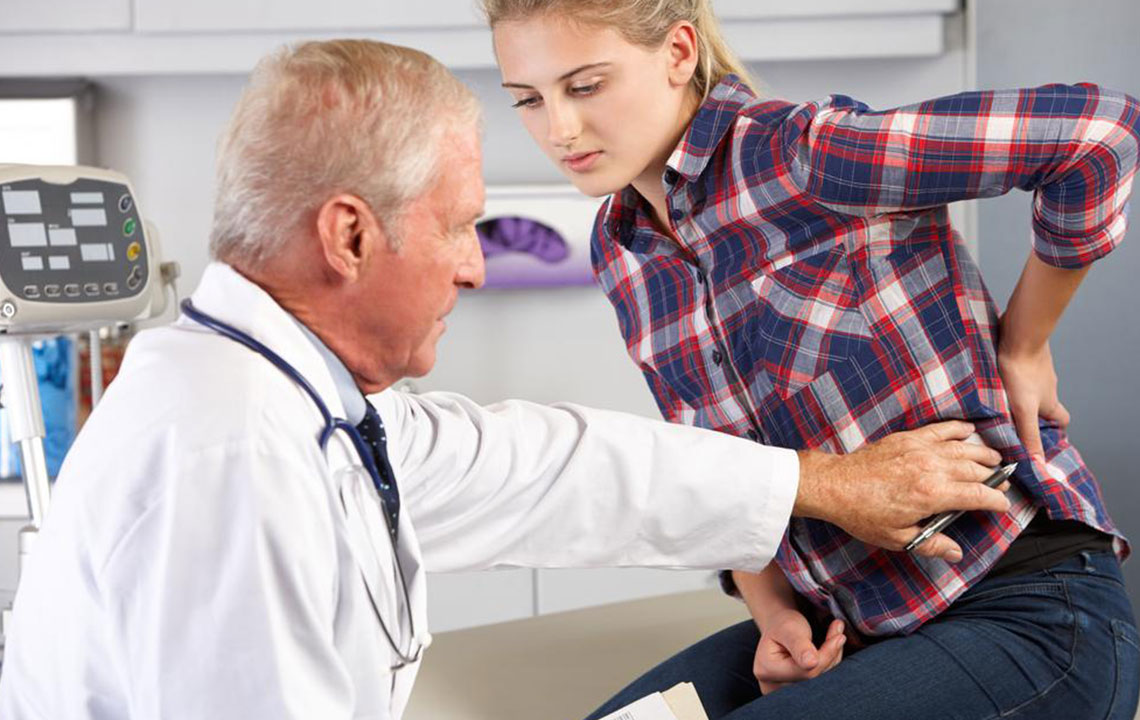
Osteoporosis is a pervasive condition characterized by decreased bone density, leading to fragile bones and heightened susceptibility to fractures. Globally, over 200 million individuals are affected by this silent yet debilitating disease, and the prevalence continues to rise with aging populations. Recognizing the importance of early detection, effective management, and proactive prevention is essential for maintaining quality of life and avoiding severe complications associated with osteoporosis. This detailed guide provides insights into the various treatment options, preventive measures, and lifestyle modifications necessary to combat this common bone health disorder.
What Is Osteoporosis?
Osteoporosis is a medical condition marked by the deterioration of bone tissue, resulting in significantly reduced bone strength. The condition often develops silently, without obvious symptoms in its early stages, making regular screening vital for at-risk populations. As the disease progresses, bones become more fragile and prone to breaks and fractures, especially in the hips, spine, and wrists. If left untreated, osteoporosis can lead to severe disability, chronic pain, and increased mortality risk from related complications.
Effective management of osteoporosis involves a combination of medical treatments, nutritional support, and lifestyle changes. Since individual responses vary, personalized treatment plans under the guidance of healthcare professionals specializing in bone health are crucial for optimal outcomes. Early diagnosis coupled with comprehensive care can significantly slow disease progression and reduce fracture risks.
Key Osteoporosis Treatment Strategies
Choosing the appropriate treatment depends on various factors including age, gender, severity of bone loss, and overall health. An integrated approach combining medication, nutritional supplementation, physical activity, and lifestyle adjustments offers the best chance for maintaining healthy bones well into old age. Consult your healthcare provider to develop a tailored plan suited to your specific needs, ensuring effective osteoporosis management and improved quality of life.
Medications play a central role in osteoporosis treatment by targeting bone turnover and strength. They are often complemented with dietary modifications and exercise routines designed to enhance bone density and reduce fracture risk. Continual monitoring and periodic reassessment are essential for adapting treatment strategies over time.
Medications for Osteoporosis
Pharmacological interventions aim to halt or slow the process of bone loss while promoting bone formation. The most commonly prescribed medication classes include bisphosphonates and selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs).
Bisphosphonates are the frontline therapy for many patients, functioning by inhibiting osteoclast-mediated bone resorption. These drugs help preserve existing bone mass and are available in oral and intravenous formulations.
Examples of bisphosphonates include:
Alendronate (Fosamax)
Ibandronate (Boniva)
Risedronate (Actonel)
Zoledronic acid (Reclast)
Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulators (SERMs), such as Raloxifene (Evista), mimic estrogen's protective effects on bones without some of its adverse effects. These drugs are especially useful for postmenopausal women at risk of osteoporosis.
In addition to these, other medications like hormone replacement therapy (HRT), denosumab, and tibolone may be used under specific circumstances to optimize bone health.
Injectable Osteoporosis Treatments
Injectable therapies are often reserved for patients who cannot tolerate oral medications or require more aggressive treatment. These include bisphosphonate injections, which directly inhibit osteoclast activity, and parathyroid hormone (PTH) analogs that stimulate new bone formation. PTH injections, such as teriparatide, increase calcium availability in bones, enhancing their strength. These therapies have demonstrated significant efficacy in reducing fracture incidence and improving bone density in severe cases of osteoporosis.
Surgical Interventions for Severe Cases
Surgery is generally considered when conservative treatments fail or in cases of severe fractures. These procedures aim to stabilize bones, restore mobility, and alleviate pain, including:
Dental Implants for Bone Support: Used in cases of jawbone deterioration to improve dental stability.
Vertebroplasty and Kyphoplasty: Minimally invasive procedures involving injecting cement into fractured vertebrae to stabilize the spine and prevent collapse.
Hip Replacements: Surgical replacement of damaged hip joints to restore mobility and reduce pain, especially after fractures.
Prevention remains the cornerstone of osteoporosis management. Lifestyle changes such as adequate calcium and vitamin D intake, regular weight-bearing exercise, smoking cessation, and limiting alcohol consumption can significantly reduce risk factors. Early diagnosis through bone density screening and personalized treatment strategies are vital for effectively combating osteoporosis and preserving bone health as you age.