Comprehensive Guide to Osteoporosis: Detection Methods and Diagnostic Procedures
Osteoporosis often develops silently, increasing fracture risk by weakening bones. This comprehensive guide explores early detection methods and diagnostic techniques such as DEXA scans and blood tests. Regular screening is crucial, especially for postmenopausal women and the elderly, to identify osteoporosis early and implement effective treatment plans. Understanding bone health assessments can prevent severe fractures and improve quality of life. Learn about risk factors, symptoms, and the importance of proactive diagnosis to maintain strong bones and avoid long-term complications associated with osteoporosis.

Comprehensive Guide to Osteoporosis: Detection Methods and Diagnostic Procedures
Osteoporosis is a pervasive medical condition characterized by diminished bone strength and density, which significantly elevates the risk of fractures. Often dubbed the 'silent disease' because it progresses without noticeable symptoms in its early stages, osteoporosis can silently weaken bones, making routine activities like coughing, bending, or even mild trauma potentially life-altering. Primarily affecting the hip, spine, and wrist, this condition stems from an imbalance between bone resorption and formation, leading to deterioration of bone tissue over time.
While osteoporosis can develop in anyone as they age, it is predominantly observed among postmenopausal women, especially those belonging to Asian and Caucasian populations. The decline in estrogen levels after menopause accelerates bone loss, making early detection and proactive management essential to prevent severe fractures and associated complications.
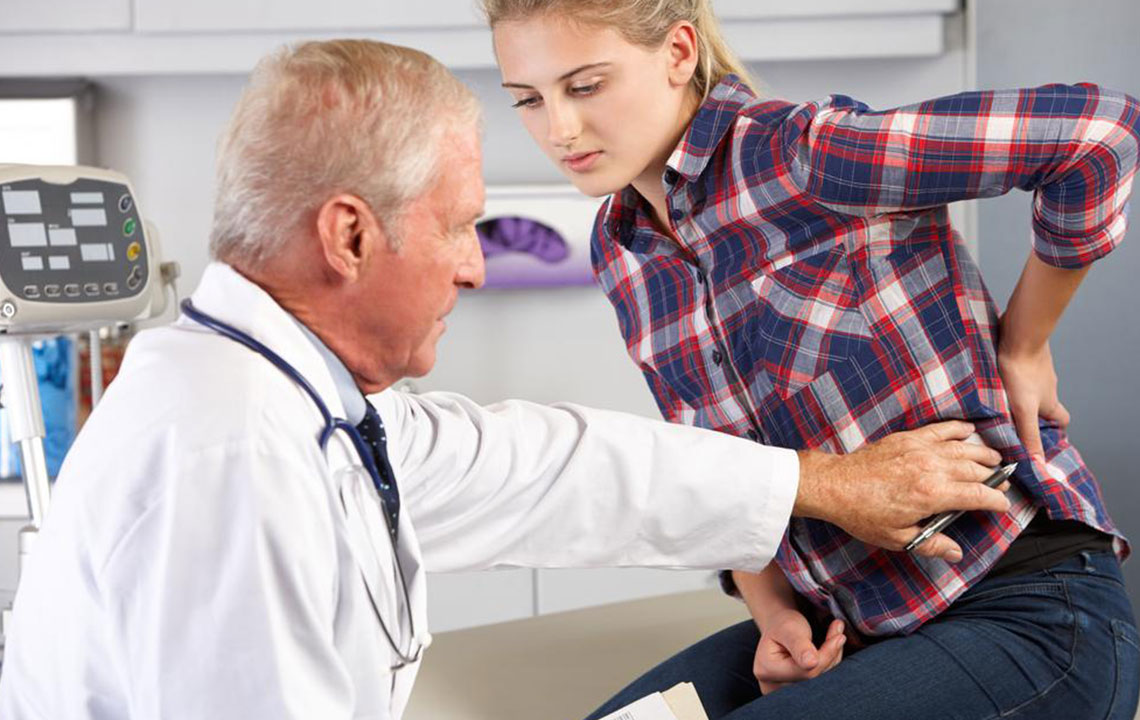
Understanding the early signs and diagnostic techniques of osteoporosis is crucial for early intervention. Though initial symptoms are often absent, advanced stages may manifest through persistent back pain, noticeable decrease in height over time, a stooped posture known as kyphosis, and fractures resulting from minor injuries that would rarely cause concern in healthy bones.
Proactive detection strategies play a vital role in effective osteoporosis management. Regular screening programs are recommended particularly for individuals over the age of 60, as bone density tends to decline with age. The process of diagnosing osteoporosis involves a comprehensive review of a patient’s medical background along with detailed physical examinations.
Medical history assessment
Healthcare providers evaluate past medical conditions, family history of osteoporosis or fractures, dietary habits, lifestyle choices—including smoking and alcohol consumption—and medications that may influence bones. This comprehensive review helps identify individuals at greater risk and uncovers potential underlying causes.
Physical examination
During physical exams, clinicians look for signs such as height loss, which can be indicative of vertebral fractures or bone degradation. Comparing current measurements with previous records enables the detection of subtle changes. Blood tests are also conducted to assess vitamin D status and metabolic activity, providing further insights into bone health and early disease indicators.
To establish a definitive diagnosis, specific imaging and laboratory tests are employed:
Bone density scan (DEXA)
Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DEXA) is the gold standard for measuring bone mineral density (BMD). This quick, painless, and radiation-based imaging technique offers precise data on bone strength, fracture risk, and disease progression. It is particularly recommended for postmenopausal women and older adults. However, due to radiation exposure, it is contraindicated during pregnancy.
Blood and urine tests
Laboratory analyses evaluate parameters such as calcium levels, vitamin D status, thyroid function, and hormonal balance. These tests help identify secondary causes of osteoporosis and provide comprehensive insights into bone metabolism, facilitating targeted treatments.
Advantages of osteoporosis screening
Early detection through screening and diagnostic testing allows for timely intervention, enabling healthcare providers to implement personalized treatment plans aimed at preventing fractures, improving quality of life, and maintaining bone mass. Regular monitoring also helps track disease progression and adjust therapeutic strategies accordingly.
In summary, osteoporosis is a silent yet serious condition that requires vigilant screening, accurate diagnosis, and proactive management. Understanding the methods available for early detection empowers individuals, especially at-risk populations, to seek appropriate care and reduce the risk of debilitating fractures. Advances in imaging and laboratory testing continue to refine diagnostic accuracy, ensuring better outcomes for patients worldwide. Regular bone health assessments should be a priority for aging populations, and individuals with risk factors should consult healthcare professionals about appropriate screening plans.