Comprehensive Guide to Osteoporosis: Causes, Symptoms, and Preventive Measures
Discover comprehensive insights into osteoporosis, including its causes, early signs, and effective prevention strategies. Learn how lifestyle choices and medical interventions can help maintain healthy bones and prevent fractures, especially for at-risk populations like postmenopausal women and the elderly. Early detection and proactive treatment are key to managing this silent disease and ensuring a better quality of life.

Understanding Osteoporosis: Causes, Early Signs, and Prevention Tips
Osteoporosis is a widespread bone disease characterized by reduced bone density and deterioration of bone tissue, leading to fragile bones that are highly susceptible to fractures. It primarily affects older adults, especially postmenopausal women, but can impact individuals of various ages due to a range of contributing factors. To effectively prevent and manage osteoporosis, understanding its underlying causes, early warning signs, and preventive strategies is essential.
Bones play a critical role in supporting the body, protecting vital organs, and enabling movement. They are dynamic structures composed mainly of collagen, a protein that gives bones some flexibility, intertwined with mineral deposits such as calcium phosphate that provide the necessary hardness and strength. The harmony between bone formation by osteoblasts and bone resorption by osteoclasts is vital to maintaining healthy bone density. When this balance is disturbed—due to nutritional deficiencies, hormonal changes, or lifestyle choices—osteoporosis can develop, leading to fragile bones prone to fractures.
Several factors contribute to the development of osteoporosis. These include hormonal deficiencies, particularly reduced estrogen levels in women after menopause, insufficient intake of calcium and vitamin D, sedentary lifestyles, smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, certain medical conditions like rheumatoid arthritis or hyperthyroidism, and long-term use of steroid medications. Age-related decline in bone mass is also a significant risk factor, as bones naturally lose density over time.
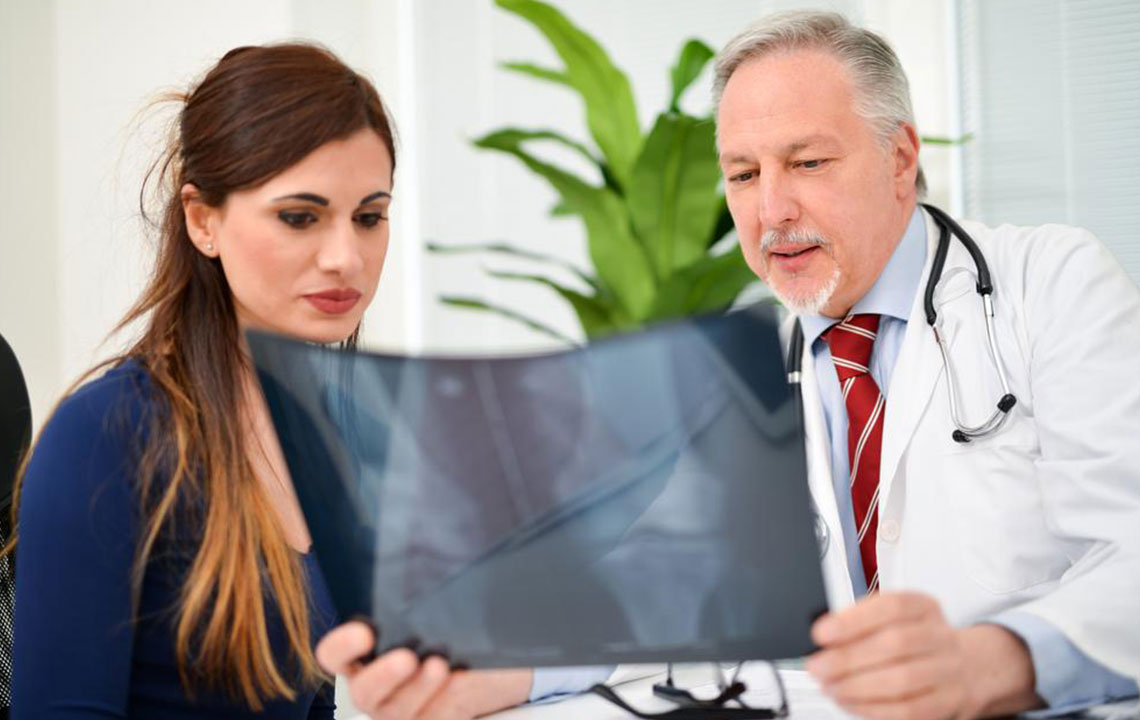
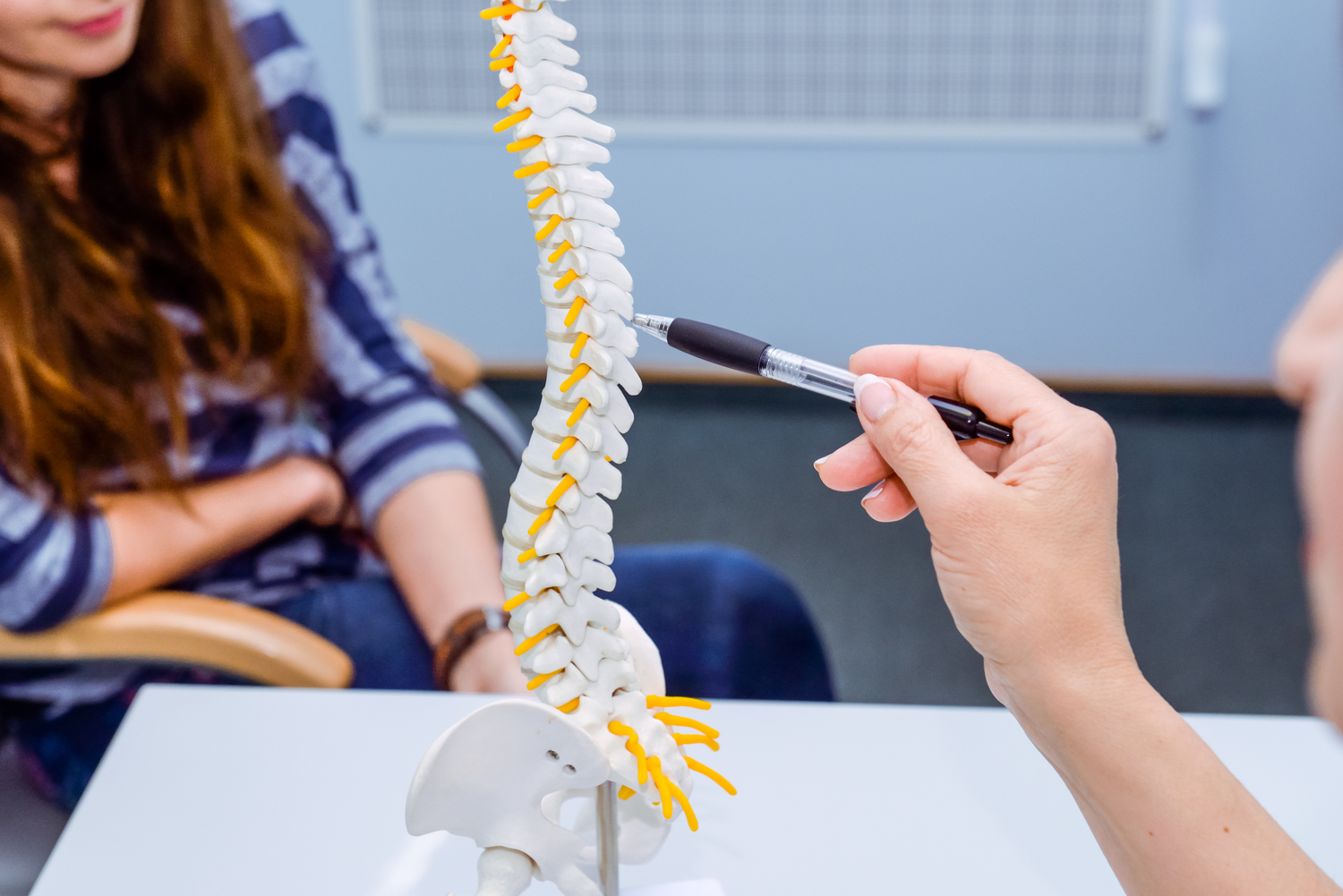
Recognizing the early signs of osteoporosis can be challenging because symptoms often do not manifest until a fracture occurs. However, some subtle signs may include receding gums, brittle nails, decreased grip strength, and mild joint aches. As the disease progresses, individuals may notice persistent back or neck pain due to vertebral fractures, a noticeable reduction in height, and postural changes such as stooping. These signs should prompt timely medical evaluation to prevent serious complications.
Prevention is the cornerstone of osteoporosis management. Maintaining a well-balanced diet rich in calcium and vitamin D, engaging in weight-bearing and resistance exercises, avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption, and ensuring hormone levels are balanced are vital strategies. Getting regular screenings can help detect early bone loss, enabling early intervention through lifestyle modification or medications if necessary.
In addition to lifestyle modifications, medical treatments such as bisphosphonates, hormone replacement therapy, and other medications can help increase bone density and reduce fracture risk. Personalized treatment plans should be developed in consultation with healthcare providers. Early diagnosis and proactive management can significantly improve quality of life and reduce the risk of debilitating fractures associated with osteoporosis.