Comprehensive Guide to Fast-Acting Remedies for Toenail Fungus Healing
This comprehensive article delves into effective, fast-acting remedies for toenail fungus, exploring causes, symptoms, and treatment options. It emphasizes early diagnosis, preventive measures, and a mix of medical and natural solutions. Suitable for those seeking quick relief and long-term nail health restoration, this guide provides valuable insights into managing toenail onychomycosis effectively. Whether mild or severe, understanding the fungus and applying the right treatments can help restore nails and prevent recurrence.
Comprehensive Guide to Fast-Acting Remedies for Toenail Fungus Healing
Effective Strategies for Rapid Treatment of Toenail Fungal Infections
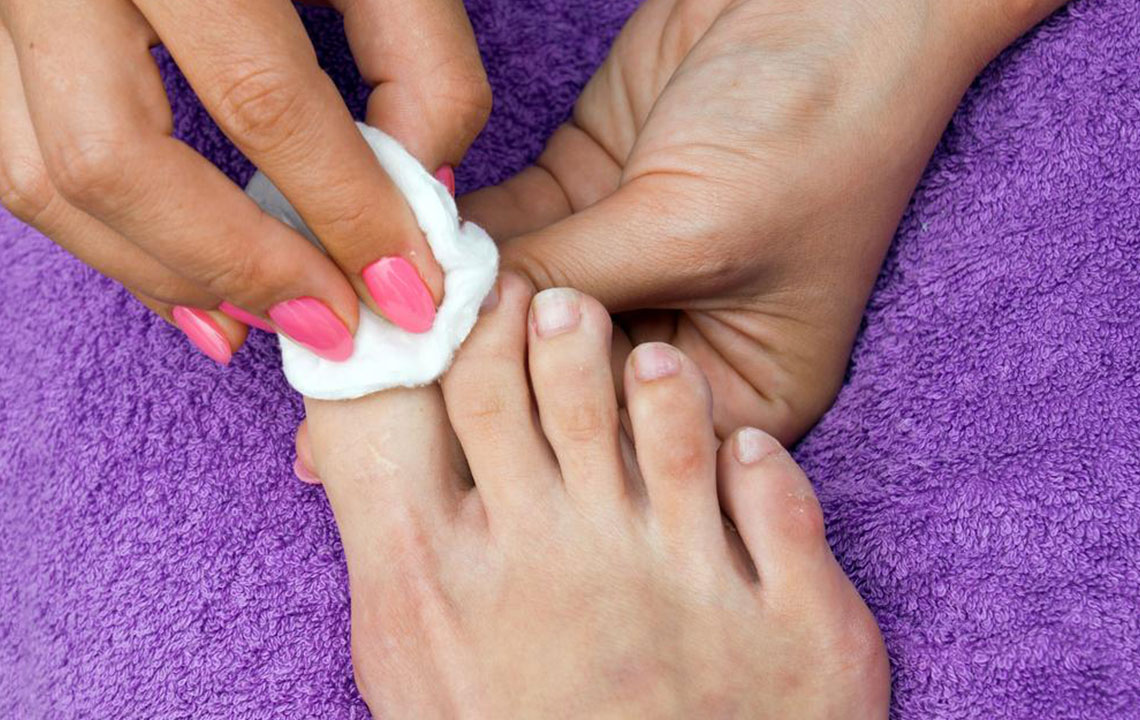
Maintaining impeccable personal hygiene is a cornerstone of overall health, and it becomes especially crucial when dealing with conditions that affect your nails. Toenail fungus, medically known as onychomycosis, is a common issue that many individuals face, often exacerbated by improper hygiene, damp footwear, and environmental factors. Recognizing the importance of early intervention, this comprehensive guide explores the most effective remedies—both medical and natural—for quickly alleviating toenail fungus, preventing its spread, and restoring nail health.
Nail infections, if neglected, can worsen and lead to more severe complications such as cellulitis or permanent nail damage. Fortunately, with a correct diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan, most cases are manageable and reversible. This article offers a detailed overview of toenail fungus, including causes, symptoms, types, and diverse treatment options that you can adapt based on severity and personal preferences.
What Exactly Is Toenail Fungus?
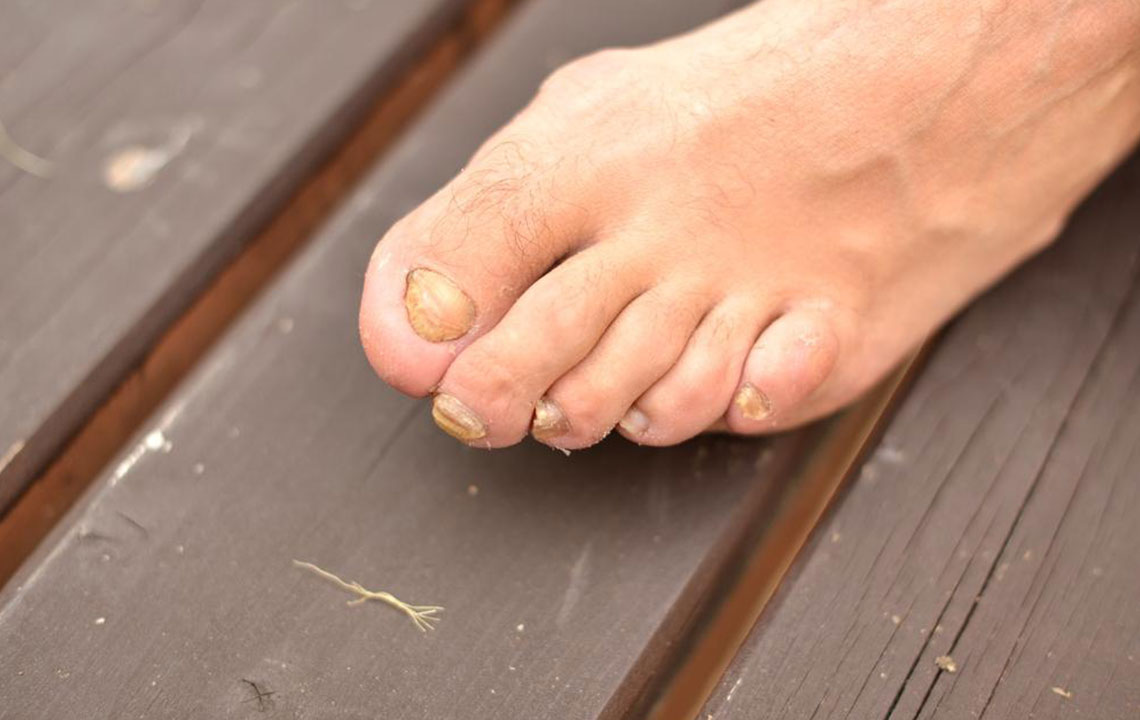
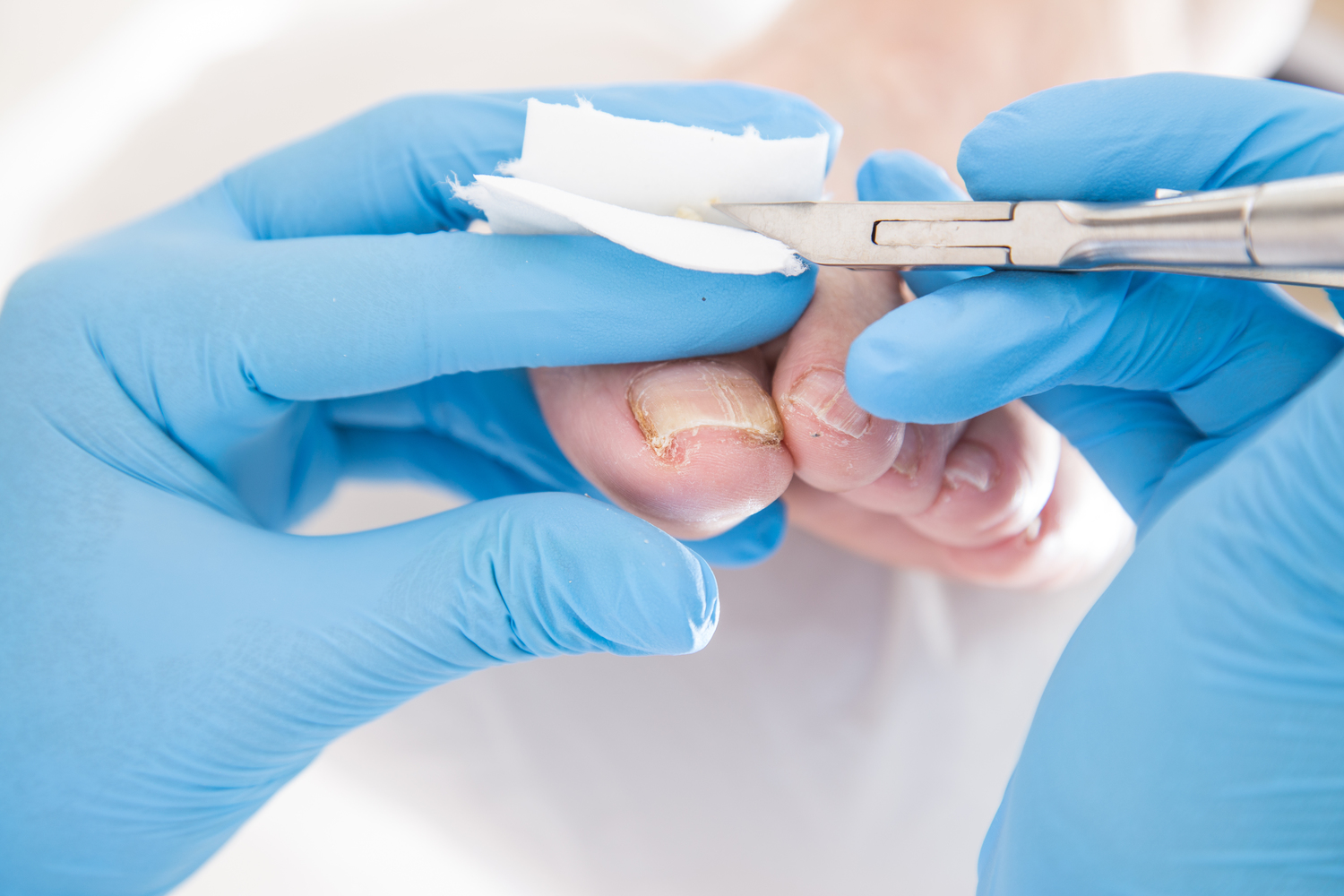
It is known as onychomycosis, a fungal infection that targets the nails.
Commonly beginning on the toenails but can also affect fingernails.
Initial signs include nail discoloration, thickening, and fragility, which can escalate if untreated.
Early recognition through visual cues allows for simple interventions like trimming infected parts, but recurring infections remain a concern even after proper cleaning or trimming.
Consistently replacing worn-out footwear and practicing good foot hygiene are essential to prevent reinfection and ensure successful treatment.
Types of Toenail Fungal Infections
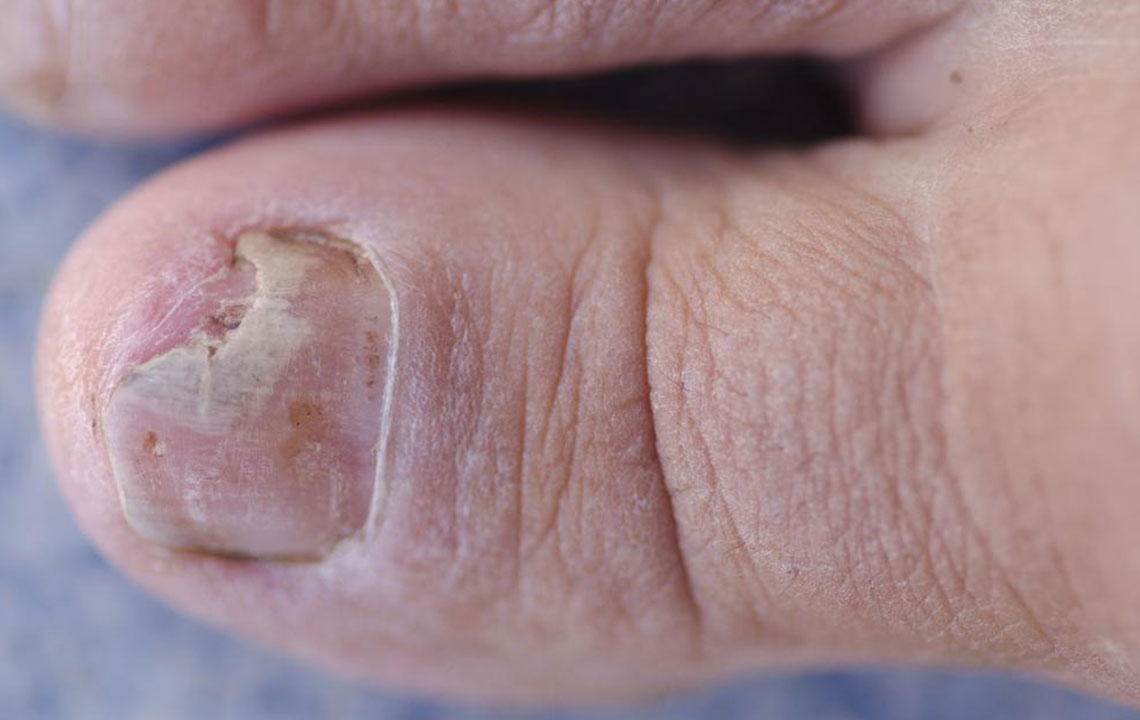
Distal subungual onychomycosis: The most prevalent form caused by Trichophyton rubrum, which invades the nail bed and beneath the nail plate, leading to thickening and discoloration.
White superficial onychomycosis: Characterized by chalky white patches on the surface of the nails, often affecting the top layers, making it easier to treat.
Proximal subungual onychomycosis: A rarer type where fungi infiltrate through the cuticle and underside of the nail plate, often associated with immunodeficiency conditions.
Candidal onychomycosis: Caused primarily by Candida species, commonly affecting individuals with frequent water exposure or nail damage, leading to infections that sometimes involve adjacent skin.
Root Causes and Risk Factors
Dermatophytes: Such as Trichophyton rubrum, are the primary culprits behind most toenail fungal infections.
Other pathogens: Fungi like Candida and molds such as Aspergillus can also cause infection, especially in older adults with weaker nails.
Aging: Age-related decline in blood circulation and immune response increases vulnerability.
Excessive moisture and sweating: Humid environments, moist footwear, and water exposure create ideal conditions for fungal growth.
Recognizing the Symptoms
Thickened, discolored nails—white, yellow, black, or green hues.
Fragile, brittle nails that easily break or crumble.
Pain, swelling, or tenderness around the affected areas.
Yellowish patches or spots near the nail bed.
Unpleasant odor and scaling skin near the nails.
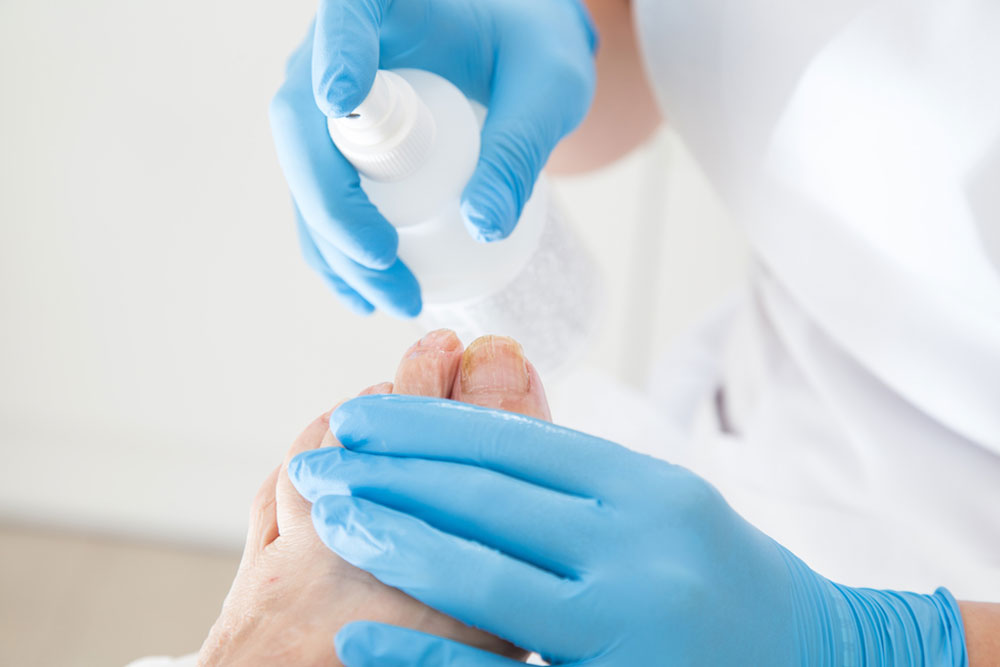
Diagnosis and Treatment Strategies
Diagnosing toenail fungus involves visual inspection backed by laboratory tests such as potassium hydroxide (KOH) smear, fungal culture, PCR analysis, or histopathology to confirm the presence of fungal elements. Treatment options vary depending on severity and patient health, including:
Oral Antifungal Medications: Such as terbinafine or itraconazole, known for high efficacy in eradicating fungal infections from within.
Medicated Nail Lacquers: Examples include ciclopirox, applied directly to the nails to inhibit fungal growth over time.
Topical Antifungal Creams and Ointments: Used on the surrounding skin and nails to reduce fungal load and assist healing.
Natural Remedies and Home Treatments: A combination of herbal extracts, essential oils, and lifestyle changes can improve outcomes for mild cases or as adjunct therapy.