Comprehensive Guide to Effectively Treat Toenail Fungus and Restore Nail Health
This comprehensive guide explores effective strategies for treating toenail fungus, including medical options like antifungal medications and surgical interventions, as well as home remedies and lifestyle changes. Understanding symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options can help individuals restore healthy nails, prevent recurrence, and avoid complications, especially among high-risk groups like diabetics. Consistent care, patience, and early diagnosis are key to success in managing toenail infections and maintaining overall foot health.
Comprehensive Strategies for Treating Toenail Fungus and Restoring Nail Wellness
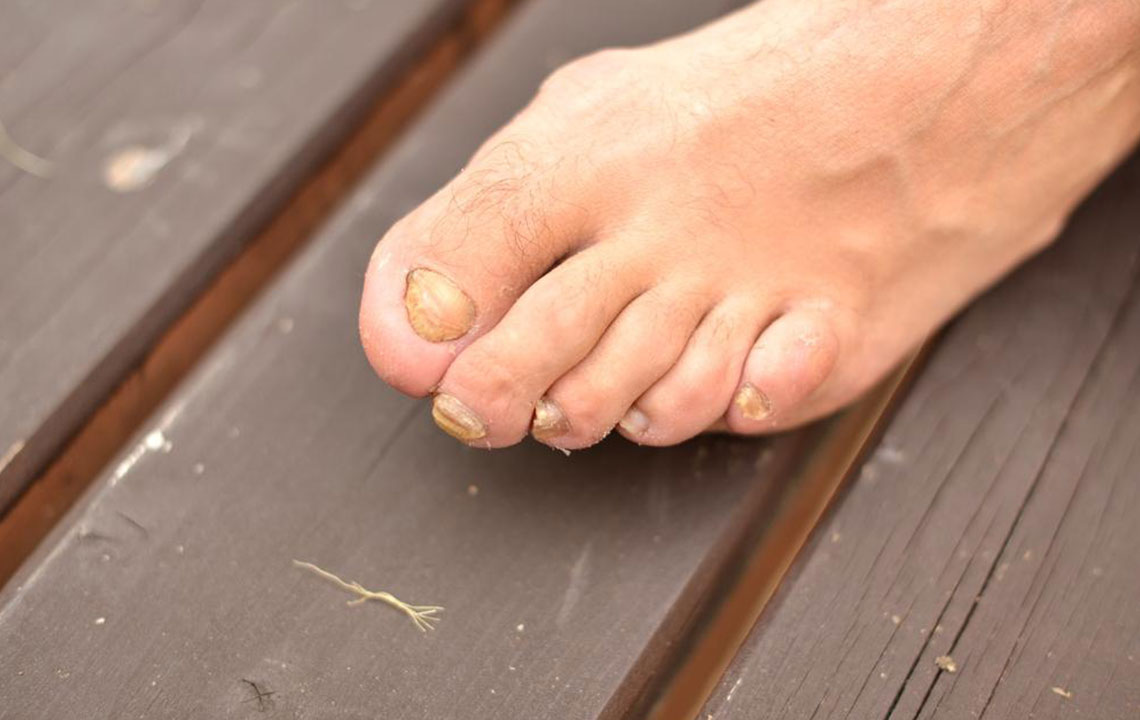
Toenail fungal infections are a prevalent concern affecting many individuals worldwide. These infections often begin subtly, with a small white or yellow spot appearing underneath the tip of the toenail. Without prompt attention, the infection can deepen, leading to the thickening of the nail, discoloration, and even the crumbling of the affected nail. Any toenail, regardless of age or health status, can succumb to this fungal invasion, though certain populations such as diabetics or immunocompromised individuals may face higher risks of complications. Mild infections might not require immediate intervention; however, once symptoms such as discomfort, thickening, or discoloration appear, treatment becomes crucial to prevent further damage and potential spread to other nails or skin.
Recognizing the Signs and Symptoms of Toenail Fungus
While toenail infections are most commonly observed, fingernails can also be affected, especially in individuals with certain risk factors. Proper diagnosis and management are essential to prevent progression and complications. Symptoms of toenail fungus include a variety of tell-tale signs such as:
Thickened nails that feel heavy or uneven
Discoloration, ranging from white patches to yellowish-brown hues
Brittle, ragged, or deformed nails that may crack or crumble easily
Debris accumulation under the nail, causing darkened appearances or foul odor
Potential discomfort or pain, especially when footwear exerts pressure on the affected toenail
Now, understanding these symptoms can prompt timely intervention, minimizing the risk of escalation. Although toenail infections typically don't trigger serious health issues in healthy individuals, those with underlying health conditions such as diabetes, peripheral vascular disease, or compromised immune systems need to seek medical advice promptly to avert potential complications such as secondary bacterial infections or tissue damage.
Effective Treatment Approaches for Toenail Fungus
Addressing toenail fungus requires comprehensive treatment strategies tailored to the severity of the infection and individual health status. The following options are widely utilized by healthcare providers and supported by clinical research:
Prescription Medications - The cornerstone of fungal nail treatment involves antifungal drugs that are administered either topically or orally. These medications work to eliminate the fungus and facilitate healthy nail regrowth. Combination therapy—using both topical and oral antifungals—may be recommended for stubborn or severe infections.
Oral Antifungal Drugs - Systemic medicines, such as terbinafine or itraconazole, are often the most effective in eradicating toenail fungus swiftly. They help promote the growth of a healthy, clear nail by gradually replacing the infected tissue. Treatment typically lasts from 6 to 12 weeks. Complete nail regrowth can take several months, often up to 12 months, because nails grow slowly. Importantly, these drugs may have side effects, including skin rashes, gastrointestinal disturbances, or liver enzyme alterations, necessitating regular blood tests. Individuals with liver disease, heart failure, or other contraindications should discuss options thoroughly with their healthcare provider.
Antifungal Nail Polish - For milder infections, medicated nail lacquers are a convenient option. These topical treatments are applied daily to the affected nail and surrounding skin, with weekly removal and reapplication over an extended period—often around a year. Consistency in use is critical for achieving results, as the medication gradually penetrates the nail and targets the fungus.
Topical Antifungal Creams and Ointments - Applying antifungal creams or ointments directly on the nail after soaking or softening can be effective, especially in early or mild cases. Pre-treatment softening of thickened nails using urea-based creams enhances medication absorption and efficacy. It's important to apply these medications thoroughly under and around the nail to ensure maximal contact with the infected areas.
Surgical and Laser Treatments - In cases where topical and oral therapies are ineffective or the infection is particularly invasive, surgical intervention might be necessary. Procedures include removing the diseased nail either temporarily or permanently, allowing direct access to the infection and facilitating faster healing. Laser therapy, an emerging non-invasive option, uses focused light beams to destroy the fungus without damaging surrounding tissue. These treatments are typically considered as last resorts after conservative methods fail.
Home Remedies and Lifestyle Modifications to Support Treatment
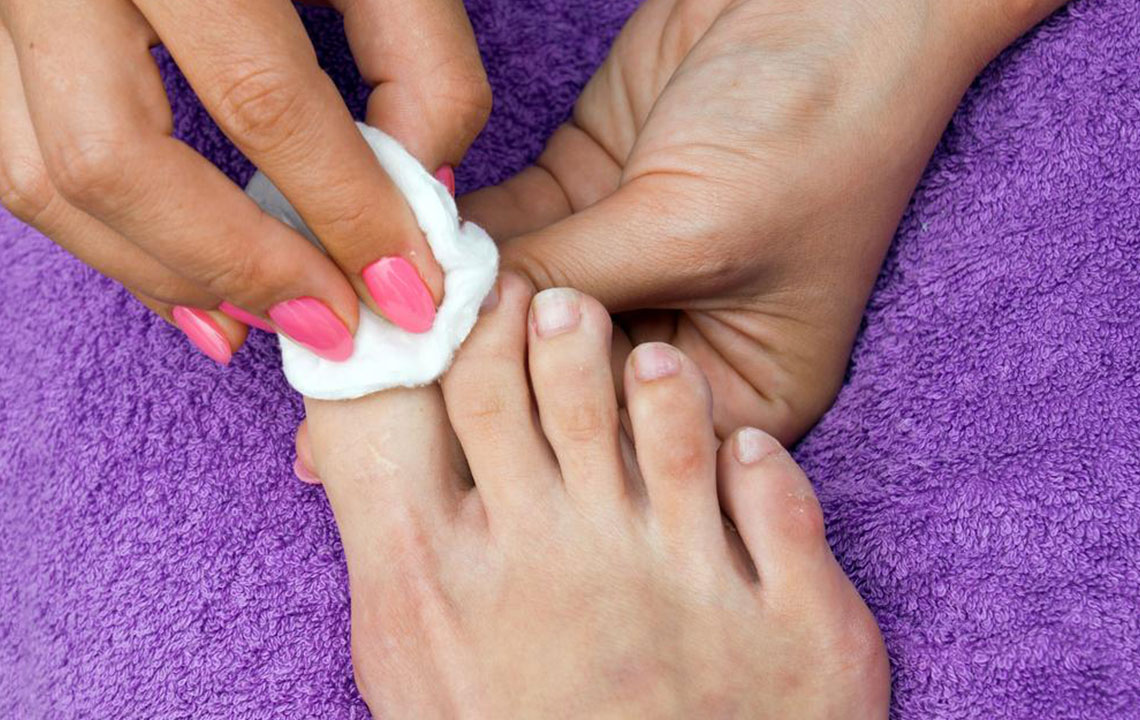
Utilizing over-the-counter antifungal creams, ointments, and medicated polishes can aid in managing mild infections. Regularly filing down the affected nails reduces fungal load and improves medication penetration. Soaking the feet in warm water with salt or antifungal solutions can also provide symptom relief and prevent the spread of fungi.
Maintaining good foot hygiene is essential: wash feet daily, dry thoroughly, and change socks regularly, especially if feet get sweaty. Wear breathable footwear to minimize moisture buildup, which fosters fungal growth. Using urea-containing creams can soften thickened nails for easier removal or trimming.
People with health conditions that impair nail trimming, such as arthritis or poor vision, should seek professional podiatric care. Early diagnosis and consistent treatment are vital to prevent the infection from worsening, spreading, or causing additional complications.
In conclusion, effective management of toenail fungus combines medical treatment, lifestyle adjustments, and patience. Since fungal infections tend to recur, persistence, adherence to prescribed therapies, and ongoing foot care are essential for complete recovery. Early intervention not only restores nail health but also helps maintain overall foot wellness, reducing discomfort and enhancing quality of life.