Comprehensive Guide to Recognizing and Treating Nail and Toenail Fungal Infections
This comprehensive guide explores the symptoms, causes, and treatment options for nail and toenail fungal infections. From early detection to medical treatments like antifungal medications and surgical options, learn how to effectively manage and prevent this common condition. Emphasizing hygiene and preventive measures, the article offers valuable insights for maintaining healthy, fungus-free nails across all age groups.

Understanding and Managing Nail and Toenail Fungal Infections for Better Nail Health
Identifying symptoms and exploring effective treatment options for nail and toenail fungal infections
Nail fungal infections, medically known as onychomycosis, are a widespread dermatological condition that affects people across all age groups but is particularly prevalent among older adults. This condition begins subtly, often unnoticed, but can progress rapidly if left untreated, leading to significant discomfort and cosmetic concerns. Recognizing early signs and understanding the available treatment options are crucial steps toward maintaining healthy nails.
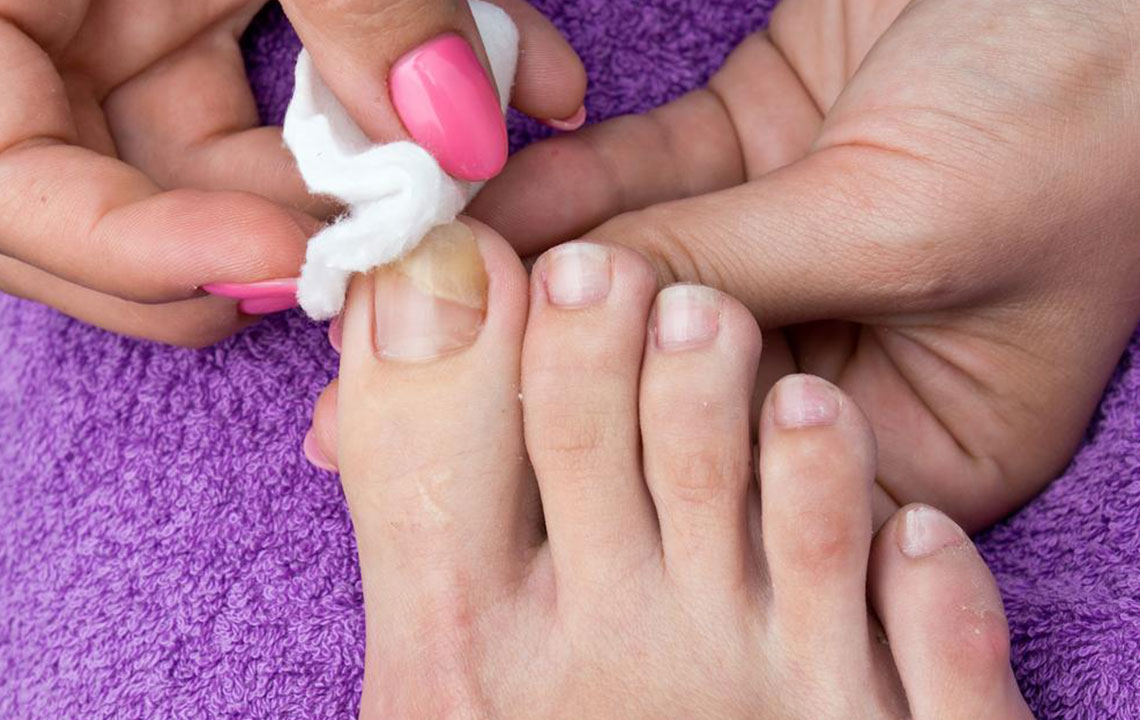
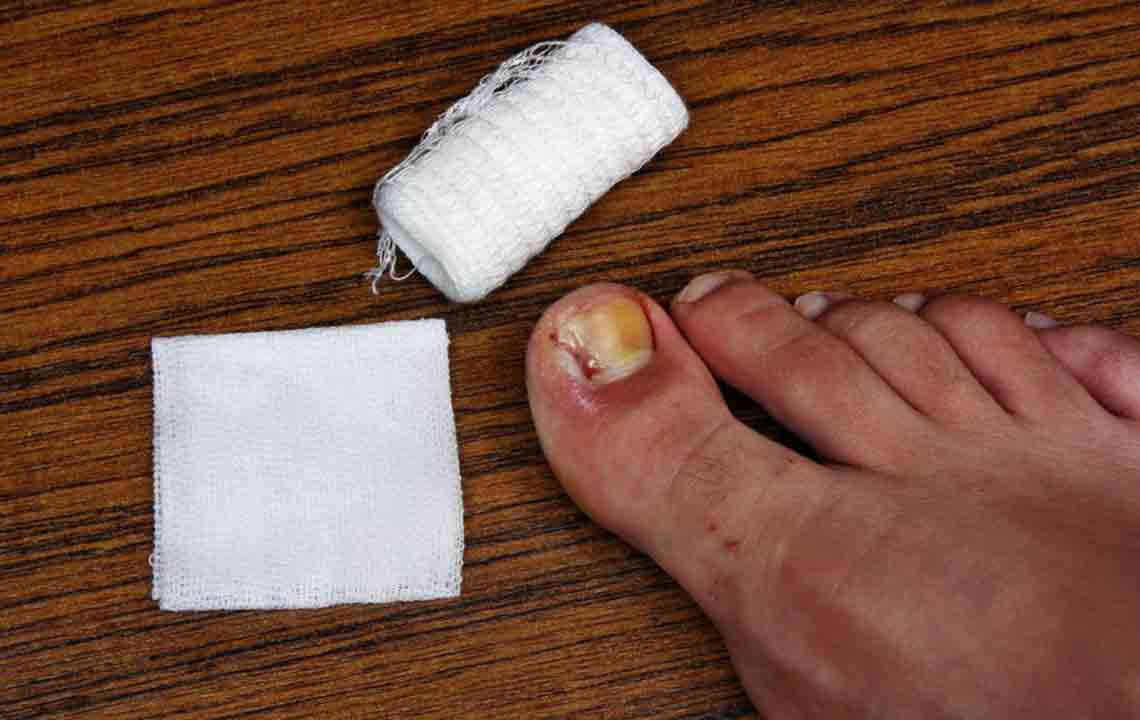
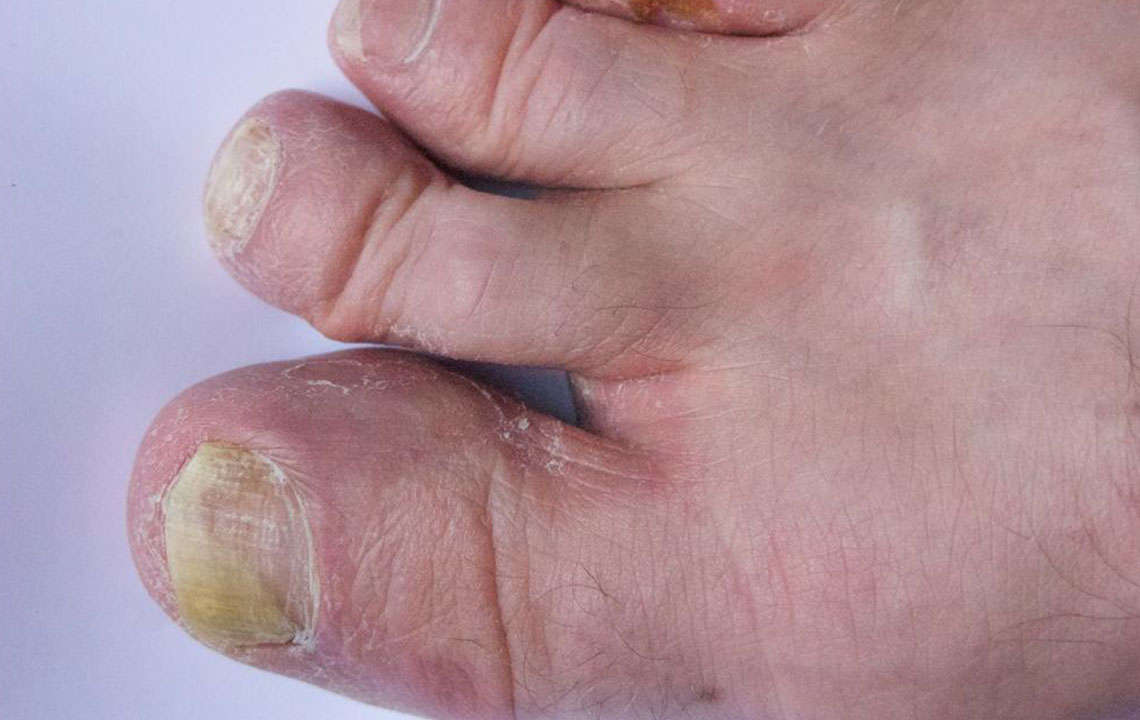
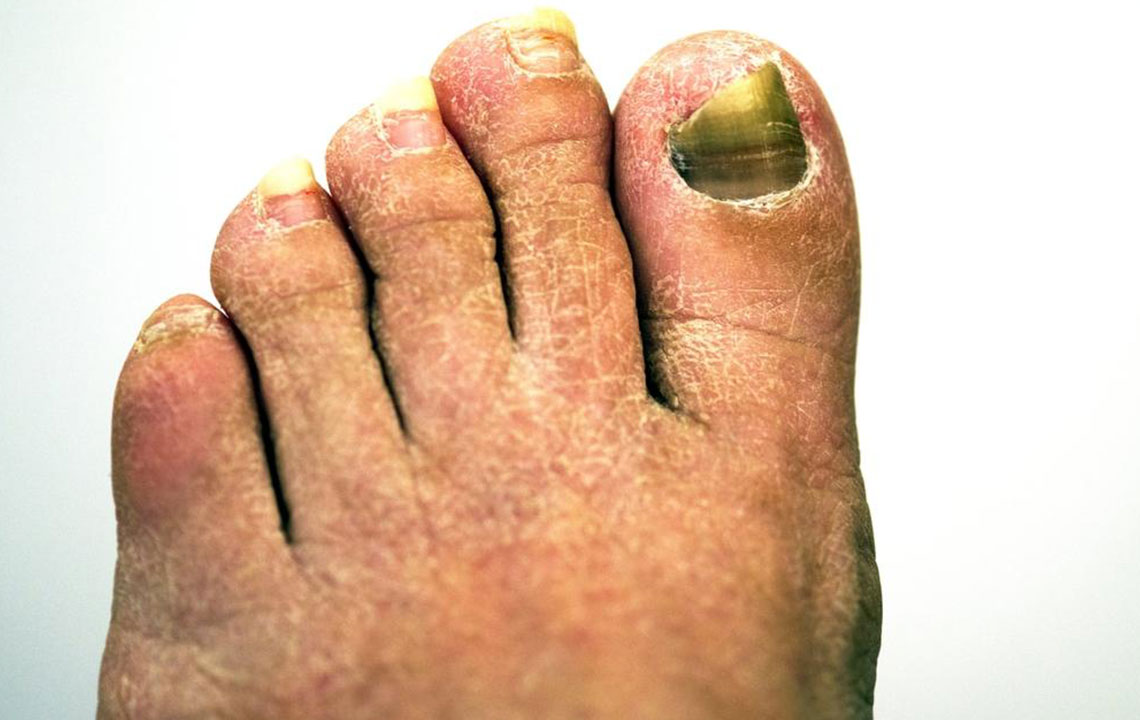
Nail fungus typically starts with a small white or yellow spot at the edge of a fingernail or toenail. Over time, this discoloration can deepen, and the affected nail may become thicker, brittle, and prone to crumbling. In some cases, the infection causes nails to become misshapen or emit an unpleasant odor due to debris accumulation underneath the nail plate. These changes not only impact appearance but can also cause discomfort or pain, especially when the infection worsens.
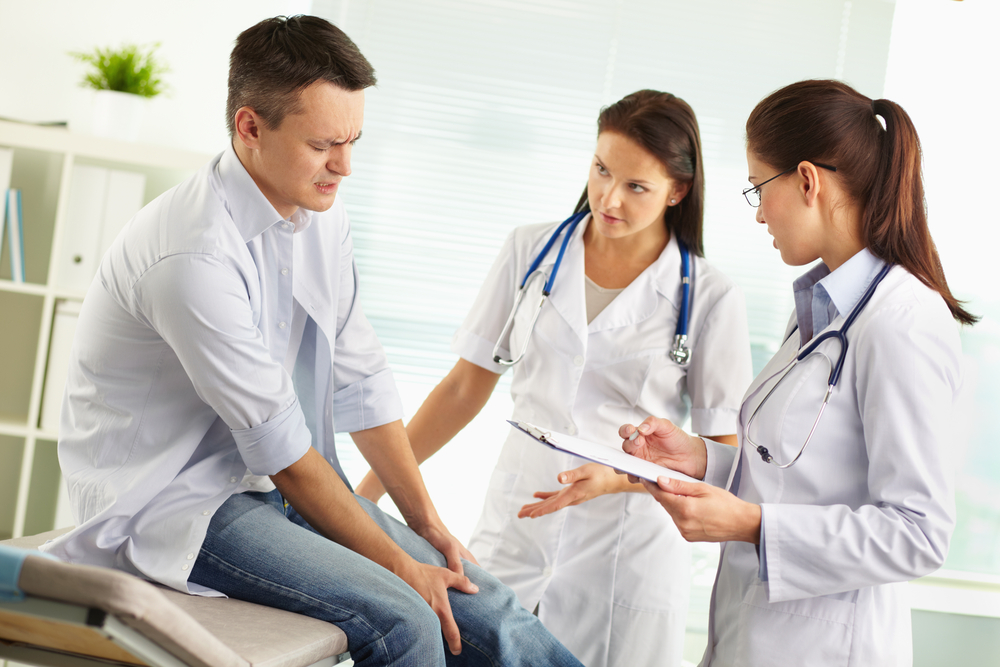
Most mild fungal infections might not require immediate medical intervention, especially if they do not cause pain or interfere with daily activities. However, if symptoms escalate—such as increased thickening, pain, or spreading redness—prompt medical assessment becomes essential. Fungal infections can recur even after successful treatment, emphasizing the importance of preventive care and early detection.
Nail fungal infections are primarily caused by various fungi, including yeasts, molds, and dermatophytes. They tend to be more common among older adults due to decreased blood circulation and slower nail growth. These infections are often associated with athlete’s foot and can spread from skin to nails, underscoring the importance of overall foot hygiene.
Early-stage infections may be effectively managed with over-the-counter antifungal treatments. Topical antifungal creams, medicated nail polishes, and powders can help contain and eradicate mild cases. For persistent or severe infections, healthcare providers often recommend oral antifungal medications such as terbinafine and itraconazole. These systemic treatments require medical supervision to monitor potential side effects and interactions but are generally effective within 6 to 12 weeks, resulting in healthier nail regrowth.
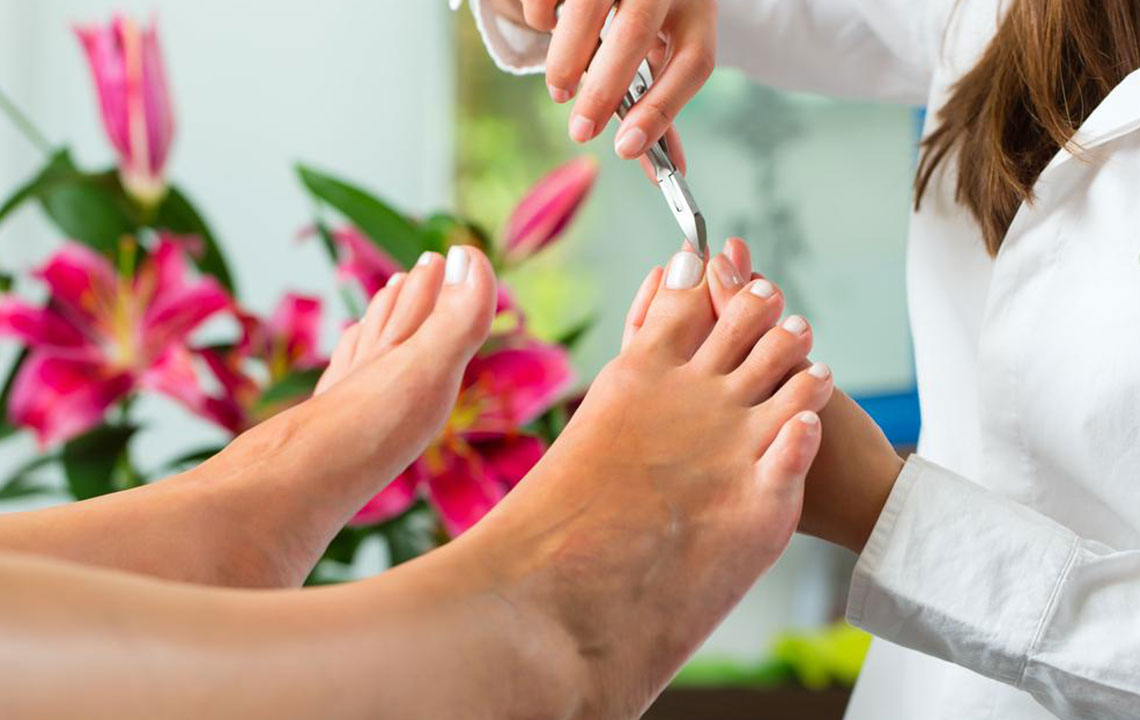
In addition to medications, some cases warrant surgical intervention, especially when infections are resistant to topical or oral therapy. Procedures include partial or complete nail removal to eliminate the infected tissue and allow for proper treatment application. This approach is usually reserved for stubborn cases, severe pain, or fungus that has severely damaged the nail structure.
Preventive measures play a significant role in avoiding fungal infections or reducing recurrence. Maintaining good foot hygiene, such as washing and drying feet thoroughly, is fundamental. Wearing breathable footwear and moisture-wicking socks help minimize fungal growth environments. Regularly changing socks and shoes, disinfecting footwear with antifungal powders or sprays, and avoiding walking barefoot in public places like pools, gyms, and locker rooms can significantly reduce infection risk. Applying antifungal powders or sprays in shoes and on feet provides an added layer of protection.
Choosing clean, reputable salons for manicures and pedicures is crucial, as contaminated tools can harbor fungi. Limit the use of artificial nails and nail extensions, which can trap moisture and create breeding grounds for fungi. Regularly inspecting nails for early signs of infection allows prompt intervention, preventing progression to more severe stages.