Comprehensive Guide to Toenail Fungal Infections: Causes, Symptoms, and Prevention
This comprehensive article explores toenail fungal infections, shedding light on their causes, symptoms, risk factors, and preventive strategies. It emphasizes the importance of hygiene, early diagnosis, and proper treatment, especially for vulnerable populations like older adults. Foot health tips and infection prevention practices are detailed to help readers maintain healthy nails and avoid spreading fungi in public or shared spaces.
Comprehensive Guide to Toenail Fungal Infections: Causes, Symptoms, and Prevention
Toenail fungal infections, medically known as onychomycosis, are among the most common nail disorders affecting millions worldwide. This condition results in abnormal nail appearance, including discoloration, thickening, and crumbling, which can be both unsightly and uncomfortable. While it may seem like a minor issue, if left untreated, toenail fungus can become persistent and may lead to more serious complications. Understanding the underlying causes, risk factors, symptoms, and preventive measures is essential for effective management and treatment.
Understanding Toenail Fungus and Its Localization
Contrary to some misconceptions, toenail fungus tends to stay localized within the affected nail without spreading uncontrollably across the entire foot. The infection usually begins at the nail bed or underneath the nail plate and remains confined unless proper hygiene and treatment are neglected. Despite its localized nature, once a toenail develops an infection, it poses a risk to neighboring nails due to close proximity and shared environmental factors.
To prevent the spread of infection, it’s important to maintain good hygiene practices. Regularly cleaning and drying your feet thoroughly, wearing clean socks, and using medications as prescribed by a healthcare provider are crucial steps. If you develop a toenail infection, avoid sharing towels, shoes, or socks with others to minimize the risk of transmission.
Age and Its Role in Susceptibility
While anyone can develop toenail fungus, certain populations are more vulnerable. Elderly individuals, particularly those over the age of 60, are at a significantly increased risk. As we age, our immune system’s ability to fight off fungal infections diminishes, and nail growth slows down, creating an ideal environment for fungi to thrive. Additionally, age-related decline in circulation and the presence of comorbid conditions such as diabetes further elevate the risk.
Therefore, adopting special precautions becomes vital for older adults. Regular foot inspections, proper foot hygiene, and prompt treatment of any injuries or nail abnormalities are essential measures to reduce susceptibility.
Toenail Fungus Is Highly Contagious
Because of its contagious nature, toenail fungus can easily spread among family members, friends, or gym buddies. The primary modes of transmission include direct contact with infected nails or surfaces contaminated with fungal spores. Public spaces such as locker rooms, swimming pools, communal showers, and gym floors are common hotspots for fungal transmission.
To combat this, individuals should take preventive steps like wearing flip-flops or shower shoes in public facilities, avoiding walking barefoot in shared spaces, and disinfecting shoes regularly. Proper footwear, good personal hygiene, and avoiding walking in damp environments significantly reduce the risk of acquiring or spreading the infection.
Protective Measures to Prevent Infection
Foot injuries provide an entry point for fungi, making it crucial to protect your toes from trauma. Wear well-fitting shoes that do not cause blisters or cuts, and treat any injuries immediately with appropriate cleaning and antiseptic care. Using antifungal powders or sprays can help reduce fungal colonization on the skin and nails.
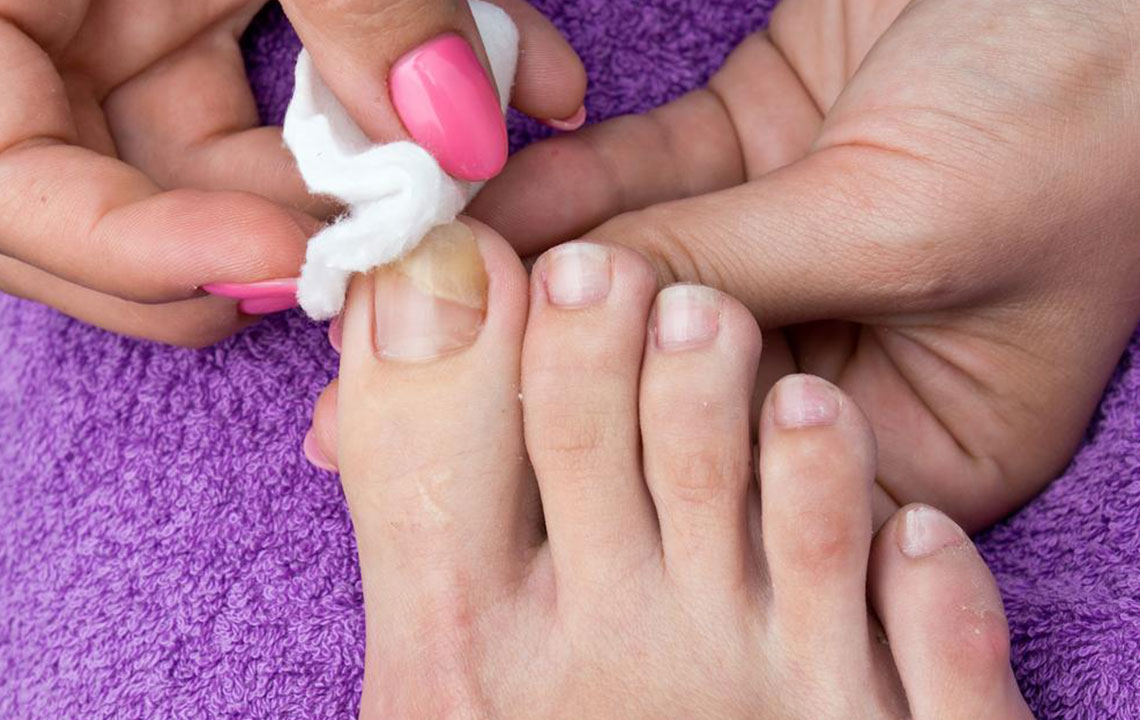
In addition, practicing regular foot hygiene by washing feet daily, thoroughly drying all areas, especially between toes, and avoiding sharing personal items enhances overall foot health. Keeping nails trimmed, clean, and free from debris prevents fungi from gaining footholds.
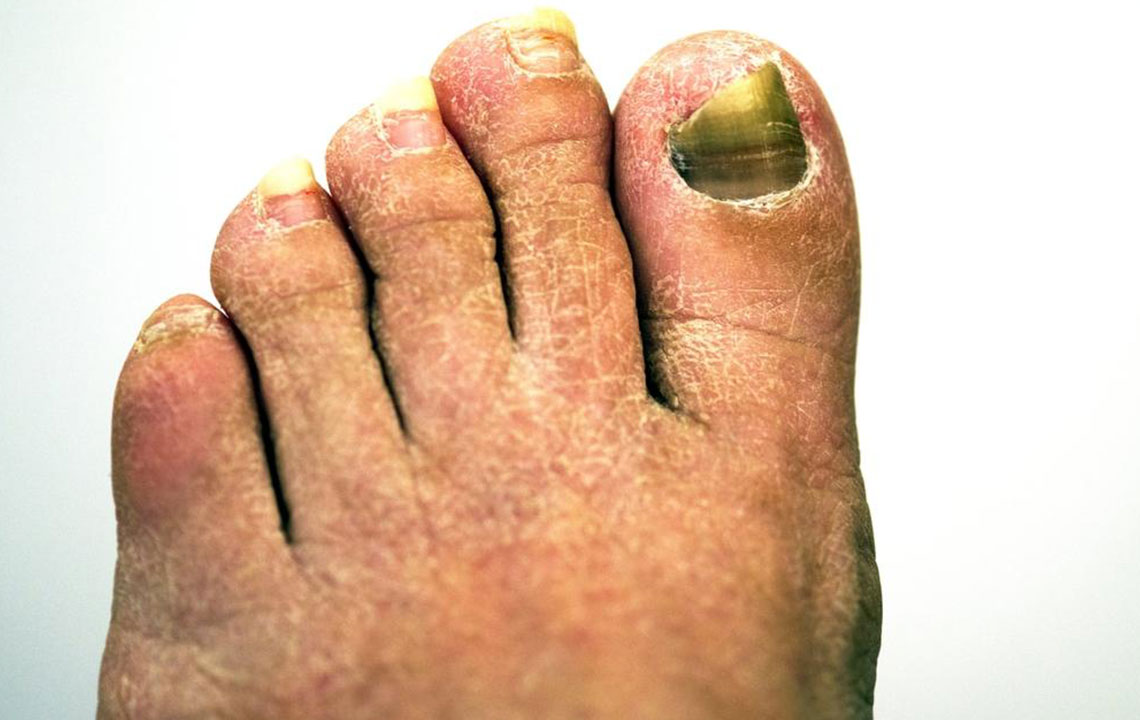
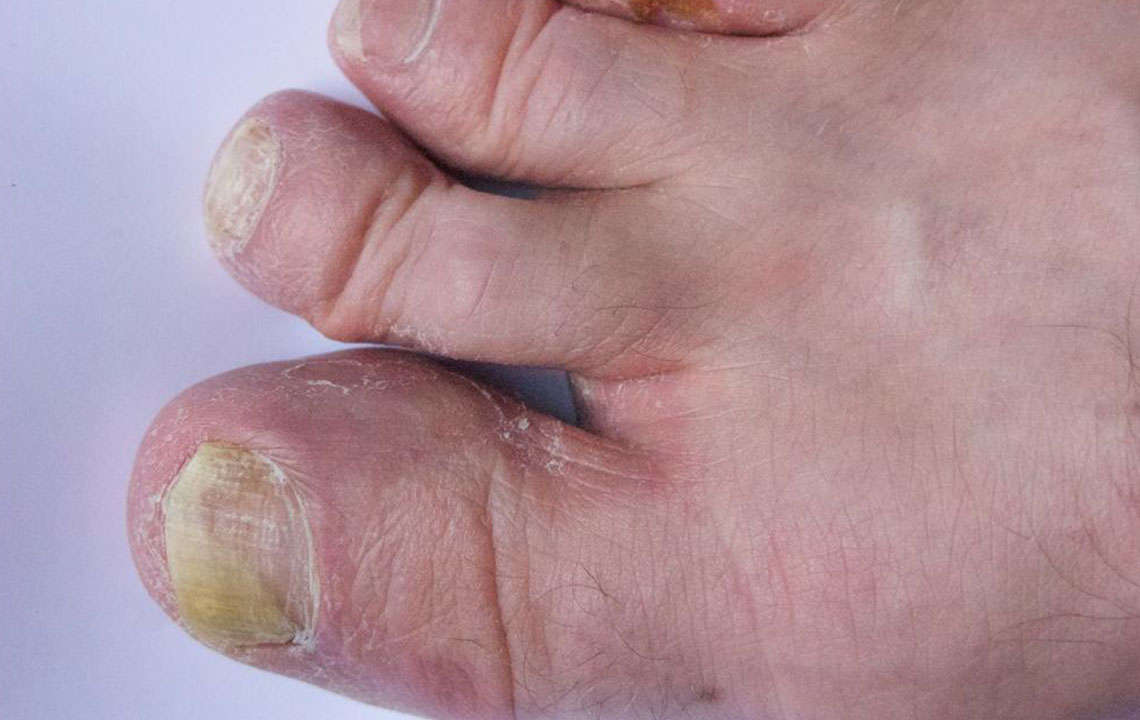
Recognizing Symptoms of Toenail Fungal Infection
Common signs include nail discoloration (yellow, brown, or white), thickening, brittleness, and crumbling edges. Some individuals may notice a foul smell, but often, symptoms are minimal at early stages. The infection rarely causes pain unless it becomes severe, in which case, the nail may detach from the nail bed or cause discomfort during walking.
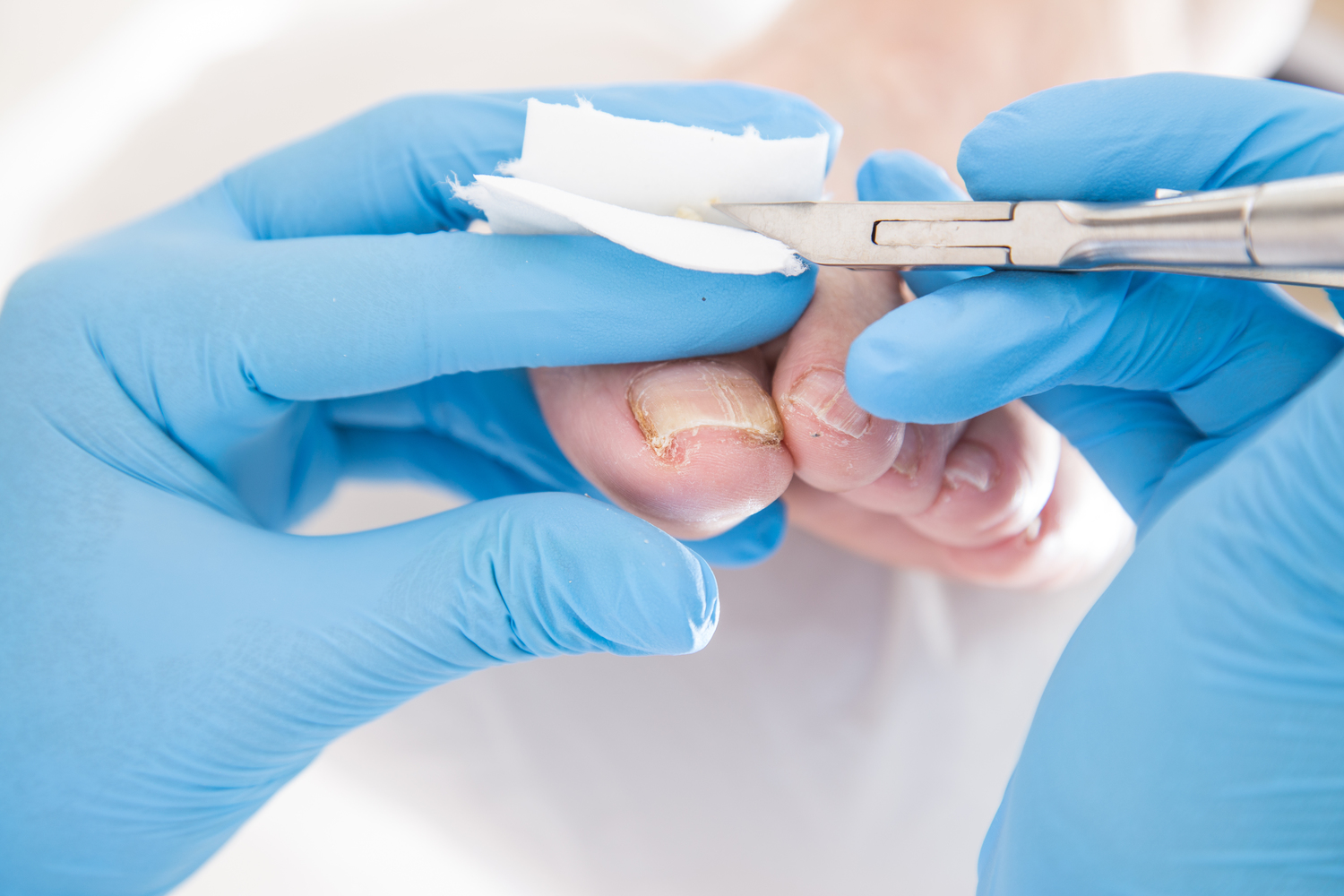
Early diagnosis and treatment are vital to prevent the infection from worsening and to preserve the appearance and health of the nails. If you notice persistent changes in your toenails, consult a healthcare professional for appropriate diagnostic testing and treatment options.
Understanding toenail fungal infections, their causes, symptoms, risk factors, and preventive measures empowers individuals to take proactive steps towards healthy nails. With proper care and attention, most fungal infections can be efficiently treated, restoring both nail health and confidence.