Comprehensive Guide to Identifying Early Signs and Symptoms of Lupus
Lupus is a complex autoimmune disease with varied symptoms that can often be mistaken for other conditions. Recognizing early signs such as fatigue, fever, hair loss, skin rashes, and joint pain is essential for timely diagnosis and treatment. This comprehensive guide offers valuable insights into the symptoms of lupus, helping individuals and healthcare professionals identify the disease early to prevent severe complications and improve health outcomes.
Comprehensive Guide to Identifying Early Signs and Symptoms of Lupus
Lupus, formally known as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), is a multifaceted autoimmune disease characterized by the immune system’s improper attack on healthy tissues. Its causes remain not fully understood, but genetics, environmental factors, and hormonal influences all contribute to its development. As a chronic condition, lupus can affect multiple organ systems, leading to inflammation, tissue damage, and a variety of clinical symptoms. Recognizing the early signs of lupus is vital for early intervention and effective management.
This autoimmune disorder primarily targets the skin, joints, kidneys, heart, lungs, and blood vessels. Its presentation can vary greatly from person to person, making diagnosis challenging. Women are disproportionately affected, especially during childbearing years, but men and children can also develop lupus. Early detection of symptoms can significantly improve outcomes and help prevent irreversible organ damage.
Understanding the Symptoms of Lupus
Since lupus can mimic many other health conditions, awareness of its hallmark symptoms is crucial. These signs can develop gradually or appear suddenly, often fluctuating in severity. Below is a detailed overview of the most common early warning indicators that should prompt medical evaluation.
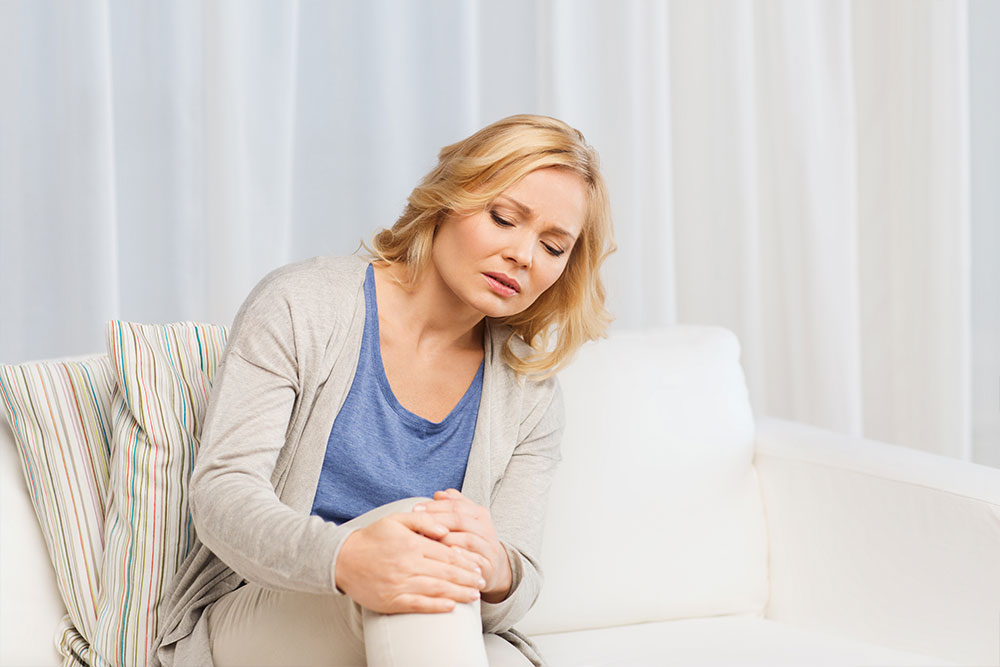
Profound Fatigue
Persistent exhaustion that doesn't improve with rest is one of the earliest and most common symptoms. Patients often describe feeling overwhelmingly tired, which interferes with daily activities. While fatigue can stem from various causes, in lupus, it often coincides with other systemic signs.
Low-grade fevers ranging between 98.5°F and 101°F that persist over weeks without any apparent infection are typical lupus symptoms. This constitutional sign reflects underlying inflammation and immune activity affecting multiple organs.
Hair Loss and Thinning
Patients may notice hair shedding, thinning, or brittle hair. The hair loss often occurs gradually but can sometimes happen abruptly in patches. This symptom results from skin inflammation and immune-mediated damage to hair follicles, especially on the scalp, eyebrows, or beard areas.
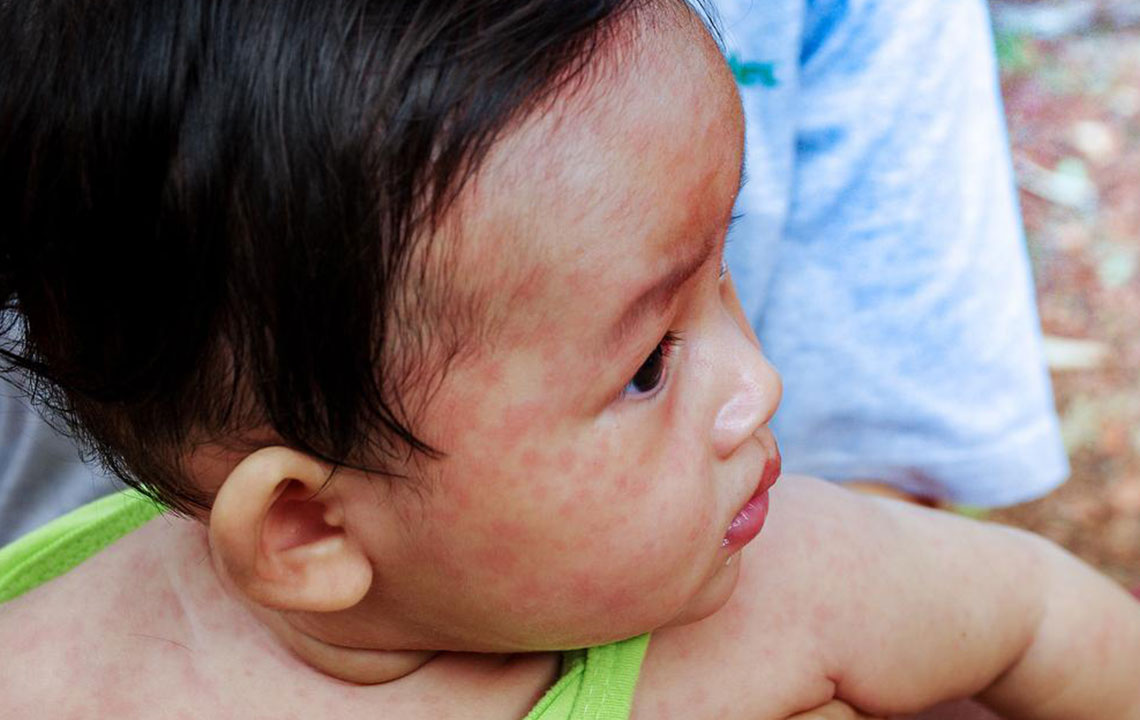
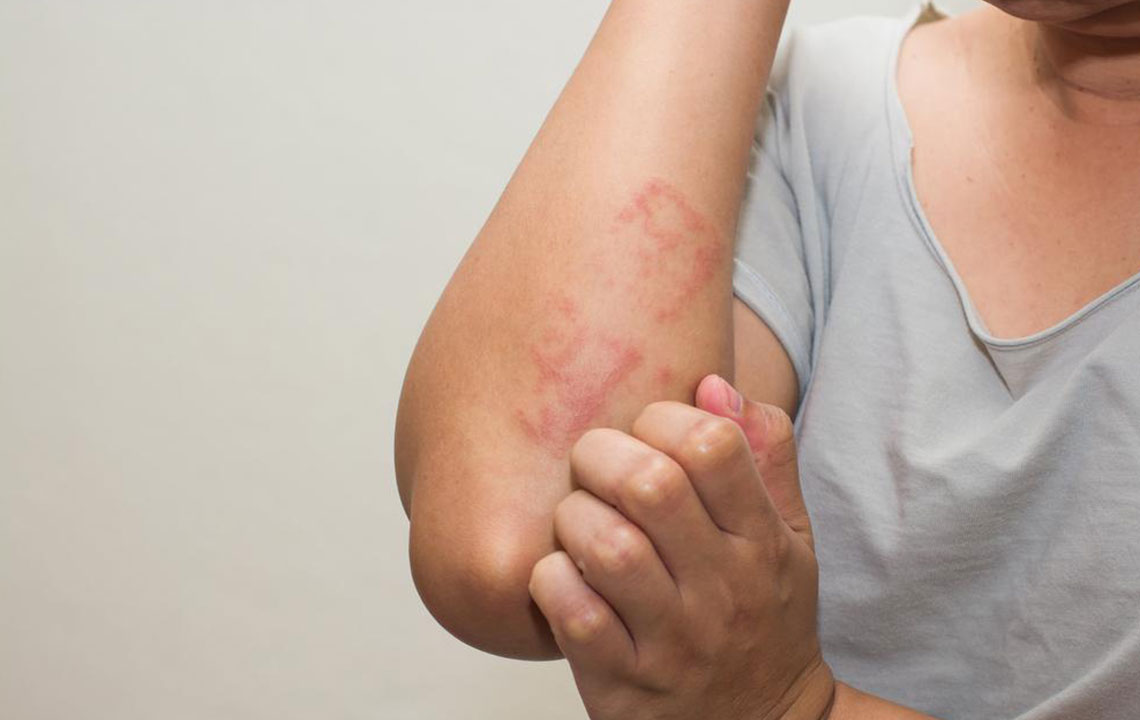
Skin Rash and Photosensitivity
The classic butterfly-shaped rash across the cheeks and bridge of the nose is highly indicative of lupus. Sun-exposed areas of skin often develop red, purple, or flaky patches, and patients frequently report skin sensitivities, leading to photosensitivity. These skin manifestations can flare when exposed to sunlight.
Nail Abnormalities
Changes in nails, such as discoloration, cracking, or even falling off, can be signs of lupus. Reddish spots or abnormal nail beds are also observed in some cases, often associated with inflammation of blood vessels or skin tissues.
Joint and Muscle Symptoms
Unexplained joint pain, swelling, stiffness, and warmth, especially in symmetrical joints like wrists, knees, or fingers, are prominent signs. These symptoms can come and go, sometimes leading to misdiagnosis as common arthritis, but in lupus, they are linked to immune-mediated joint inflammation.
Digestive and Oral Manifestations
Lupus can cause oral ulcers or sores in the mouth, often painless but sometimes tender. Gastrointestinal symptoms such as heartburn, acid reflux, difficulty swallowing, or stomach pain might also occur. Long-term complications include dry mouth, increases in dental cavities, or gastrointestinal motility issues.
Neurological Symptoms
Neuropsychiatric features include cognitive difficulties, memory lapses, headaches, seizures, or mood disturbances. Visual changes like blurred vision, dry eyes, or sensitivity to light can also occur, stemming from nervous system involvement.
Respiratory Concerns
Inflammation in the lungs (pleuritis or pneumonitis) can cause chest pain, shortness of breath, and decreased lung function. These respiratory issues tend to worsen with physical exertion or during active disease flares.
Understanding and recognizing these early signs are essential. If any of these symptoms persist or worsen, consulting a healthcare professional promptly becomes critical. Proper diagnosis typically involves blood tests, physical examinations, and sometimes biopsy to confirm lupus. Early diagnosis allows for tailored treatment plans that can manage symptoms effectively, prevent organ damage, and improve quality of life for individuals living with lupus.