Comprehensive Guide to Recognizing Gout: Symptoms, Signs, and Early Indicators
This comprehensive guide explores the key symptoms and signs of gout, including sudden joint pain, tophi formation, warmth, redness, and skin changes. Recognizing these early indicators is vital for timely diagnosis and treatment to prevent joint damage and systemic complications. Learn about the typical presentation of gout and how to differentiate it from other joint conditions for better health management.
Comprehensive Guide to Recognizing Gout: Symptoms, Signs, and Early Indicators
Gout is a complex form of inflammatory arthritis that results from the accumulation of uric acid crystals in the joints. Recognizing its symptoms early is crucial for effective management and to prevent joint damage. Gout symptoms can vary significantly among individuals, often presenting as sudden and extremely painful episodes that may last anywhere from a few days to several weeks. Some individuals might experience persistent discomfort or low-grade symptoms, which can complicate diagnosis. Furthermore, because gout symptoms mimic those of other joint conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis or osteoarthritis, misdiagnosis is relatively common, emphasizing the importance of understanding the key signs and symptoms of this condition.
In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore the primary indicators of gout, including notable physical signs, typical pain patterns, and other manifestations that can help in early detection and treatment.
Understanding Gout and Its Symptoms
Gout is characterized by the deposition of monosodium urate crystals within the joint space. These crystals form when blood levels of uric acid become abnormally high, a condition known as hyperuricemia. While hyperuricemia alone does not always lead to gout, it significantly increases the risk, especially when uric acid levels fluctuate or rise rapidly. The symptoms of gout typically begin suddenly, often during the night or early morning, and can escalate quickly, causing intense discomfort.
Let's analyze the most common symptoms and signs associated with gout in detail to aid in early recognition and prompt medical intervention.
Major Signs and Symptoms of Gout
Nodules or Tophi Formation
One of the earliest indicators of gout is the appearance of tophi—chalky, yellowish deposits of uric acid crystals that develop under the skin. These nodules tend to form on prominent joints such as fingers, toes, elbows, or the cartilage of the ear. Typically, tophi precede other symptoms and can be felt as firm lumps, sometimes visible, which signal an ongoing imbalance of uric acid in the body. Their presence is a clear warning sign that gout has developed or is progressing, especially in individuals with chronic hyperuricemia.
Intense and Sudden Joint Pain
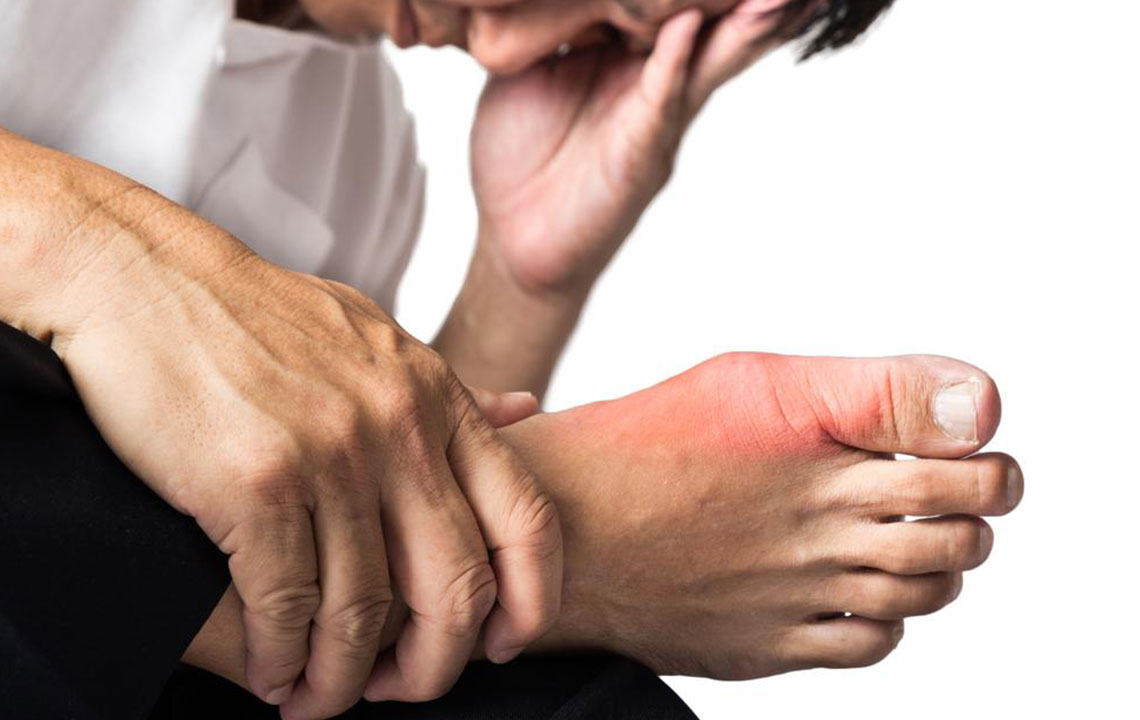
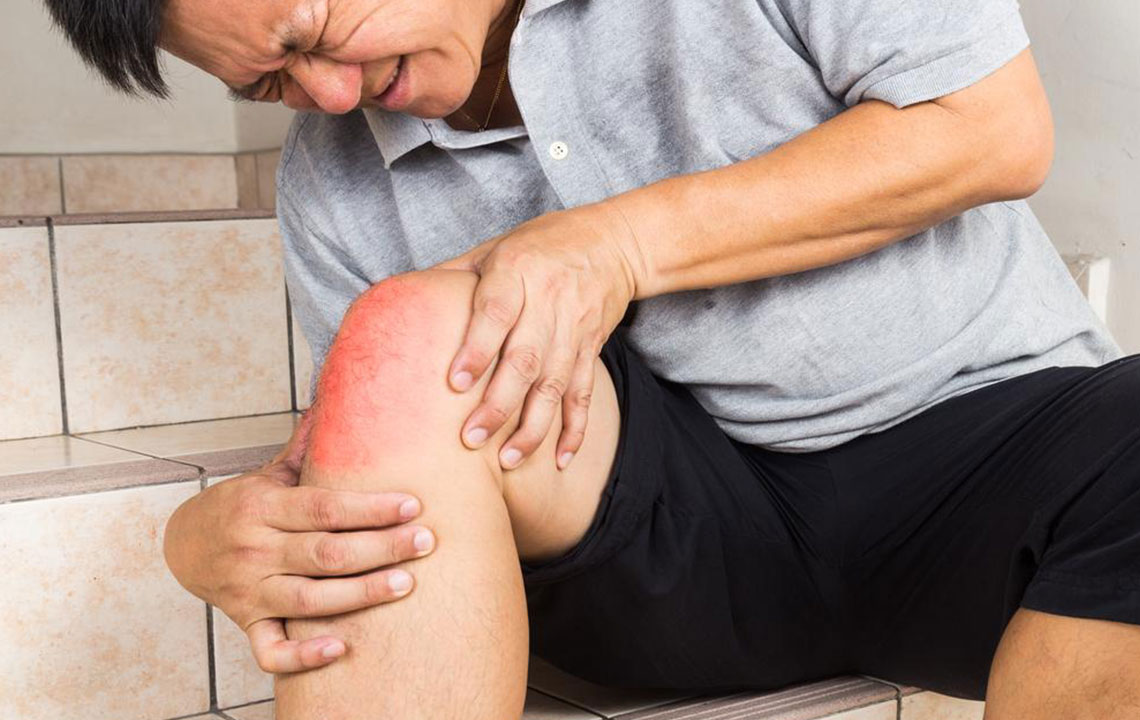
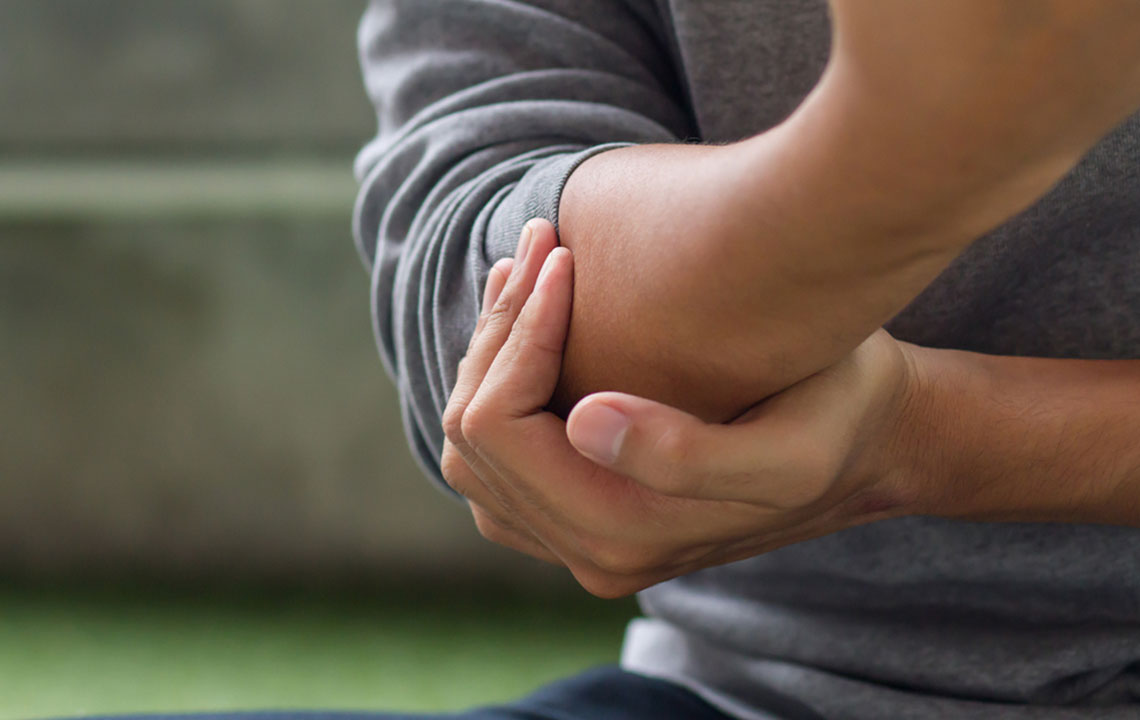
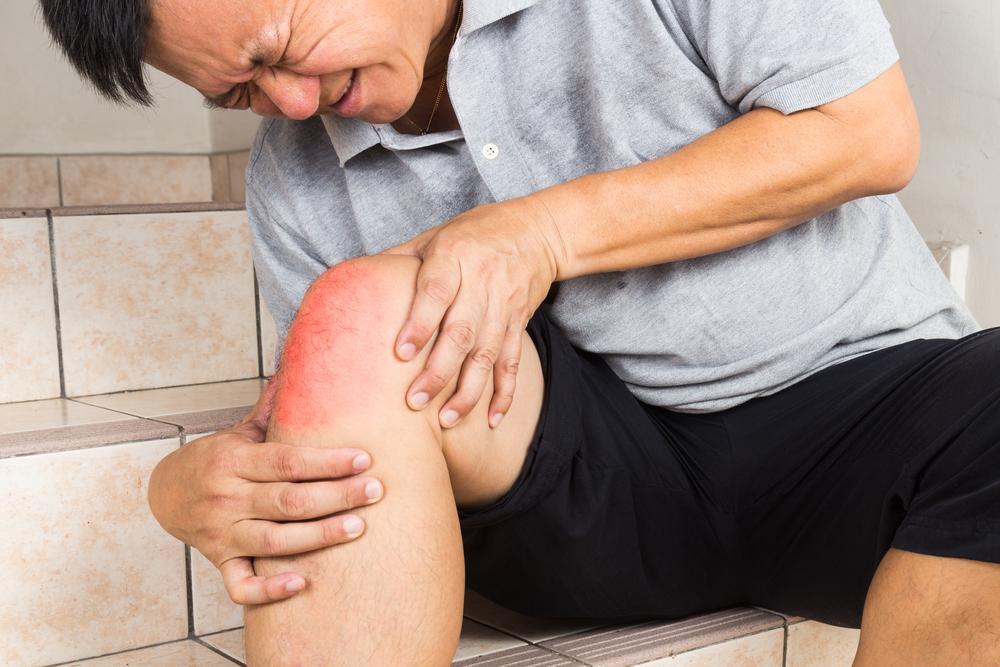
The hallmark of gout is a sudden, severe attack of joint pain that often reaches an excruciating level. The most commonly affected joint is the first metatarsophalangeal joint—the base of the big toe, a condition known as podagra. However, gout can also affect other joints such as the wrists, fingers, elbows, ankles, or knees. During a gout attack, the affected joint typically becomes extremely sensitive, making even the lightest touch unbearable. The pain usually develops rapidly, often within hours, and peaks within the first 24 hours.
Warmth, Redness, and Swelling
The inflamed joint during a gout flare-up appears visibly swollen and is often warm and reddened due to increased blood flow and inflammation. This swelling can limit movement and make everyday activities difficult. The inflammation results from the body’s immune response attempting to combat the uric acid crystals, which are perceived by the immune system as foreign invaders. The severity of swelling and redness correlates with the intensity of the attack.
Color Changes in the Skin
During intense attacks, the skin over the affected joint may change color, turning a shade of purple, deep red, or even mottled. This discoloration is caused by the inflammation and increased blood flow to the area. The affected skin may also become hot and shinier. Sometimes, the swelling may extend beyond the joint to surrounding tissues, adding to the visual signs of inflammation.
Itchy, Peeling, and Warm Skin
As the inflammation resolves, the affected skin often exhibits signs of peeling or flaking. Itchiness and warmth are common sensations experienced during and after a gout attack. These skin changes are temporary but can be alarming if not recognized as part of gout. Proper management and treatment can help reduce these symptoms and prevent further skin complications.
Additional Symptoms and Considerations
Beyond the primary signs outlined above, gout can sometimes present with other symptoms that may not be immediately associated with the condition. For example, systemic symptoms like fever and malaise can occasionally occur during severe attacks, especially if the inflammation is widespread. Recurrent gout attacks can lead to joint damage and deformities over time if untreated. Chronic gout may also result in the formation of large tophi, which can cause joint destruction and functional impairment.
It's also important to note that not everyone experiences all these signs equally. Some individuals might have mild symptoms or atypical presentations, such as isolated wrist or ankle involvement. Recognizing these variations is important for timely diagnosis and treatment.
To accurately diagnose gout, healthcare professionals often perform joint fluid analysis, blood tests for uric acid levels, and imaging techniques like ultrasound or dual-energy CT scans. Understanding the physical signs and symptoms is vital in guiding appropriate diagnostic testing and subsequent management strategies.
Why Early Recognition Matters
Early identification of gout symptoms allows for prompt treatment, which can significantly reduce the severity and duration of flare-ups. Effective management not only alleviates pain but also prevents long-term joint damage and systemic complications like kidney stones or chronic kidney disease associated with persistent hyperuricemia. Lifestyle modifications, dietary adjustments, medication regimens, and regular monitoring of uric acid levels form the cornerstone of gout management.
If you notice any signs of gout, such as sudden joint pain, swelling, redness, or visible nodules, consulting a healthcare professional promptly is essential. Early intervention can improve quality of life and reduce the risk of recurrent attacks.
Understanding the key symptoms and signs of gout can empower you to take early action and seek appropriate medical care. While gout can be challenging to diagnose due to its variable presentation, awareness of the hallmark features can lead to quicker diagnosis and better management outcomes. Remember, if left untreated, gout can lead to permanent joint damage and other serious health complications, making early recognition and treatment crucial.