Comprehensive Guide to Joint Discomfort: Causes, Symptoms, and Effective Treatment Strategies
This comprehensive article explores the causes, symptoms, and modern treatment options for joint discomfort. It emphasizes the importance of early diagnosis and personalized care plans involving medication, physiotherapy, lifestyle adjustments, and surgical options. The guide aims to help individuals understand their joint pain and seek effective solutions to restore mobility and reduce discomfort, ultimately enhancing their quality of life.
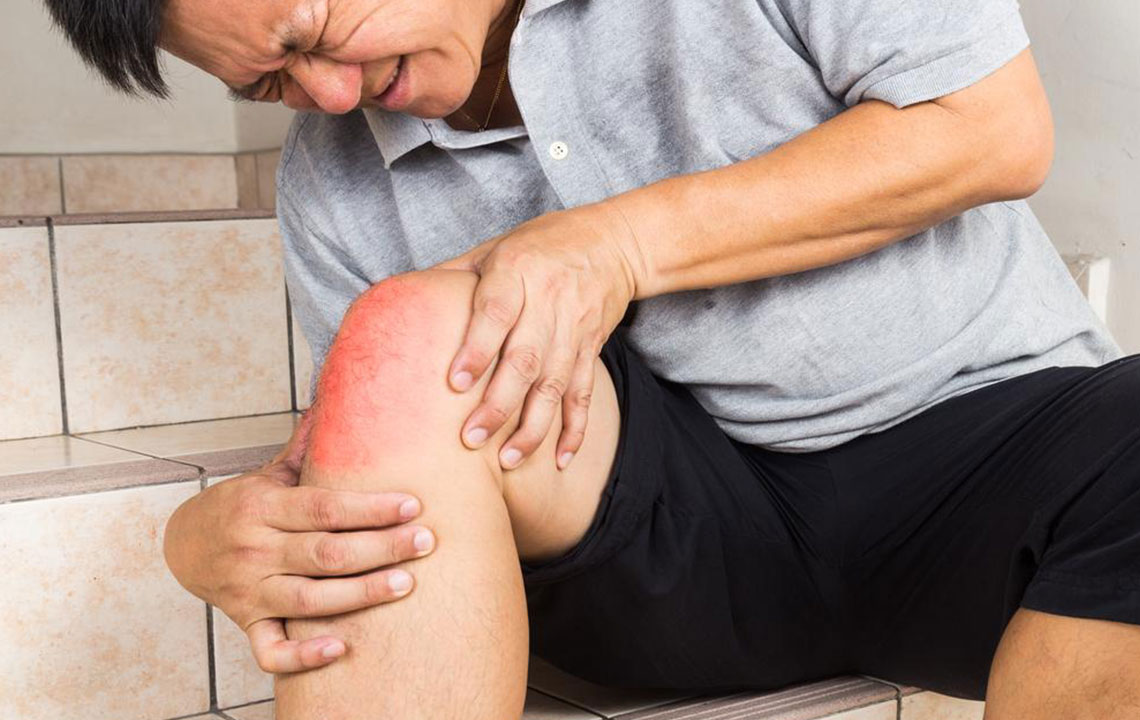
Comprehensive Guide to Joint Discomfort: Causes, Symptoms, and Effective Treatment Strategies
Joint discomfort is a widespread health issue that can significantly hinder daily life, restrict mobility, and diminish overall well-being. Whether experienced as dull aches, sharp pains, or persistent inflammation, joint pain affects people across all age groups and backgrounds. Understanding the root causes of joint discomfort is crucial for selecting the most appropriate treatment options and improving quality of life. This extensive guide explores the primary causes of joint pain, their symptoms, and a variety of treatment strategies—from medical interventions to lifestyle adjustments—to help individuals manage and overcome joint-related issues effectively.
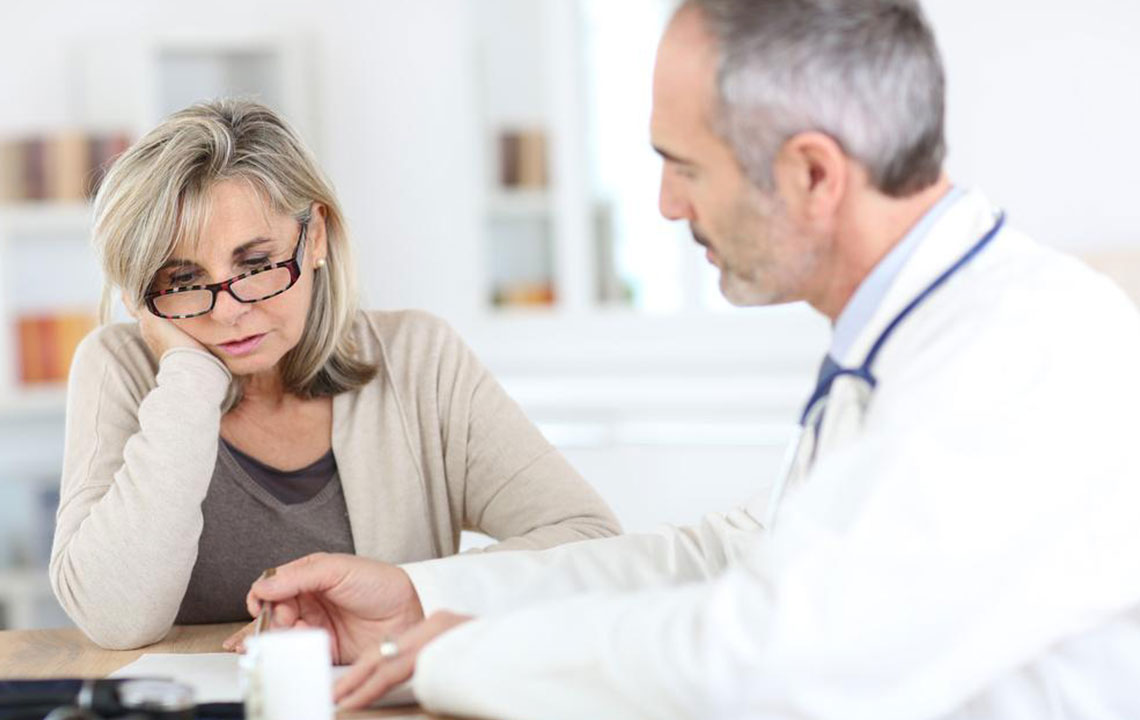
Before initiating any treatment, it is vital to consult healthcare professionals for precise diagnosis. Self-diagnosing or neglecting symptoms can lead to worsening conditions or chronic pain. Armed with proper medical advice, individuals can adopt targeted therapies and lifestyle changes that can relieve pain, reduce inflammation, and restore joint function. Let’s delve deeper into the common causes of joint discomfort, associated symptoms, prevention strategies, and contemporary treatment options.
Understanding the Causes of Joint Discomfort
Joint discomfort can be caused by a myriad of factors, each requiring specific management approaches. Recognizing these causes is the first step toward effective relief and improved joint health.
Arthritis: The Leading Cause of Chronic Joint Pain
Arthritis, a term encompassing several joint-related inflammatory conditions, is among the most common causes of persistent joint pain. The two primary types are osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis.
Osteoarthritis: This degenerative joint disease results from the wear and tear of cartilage, leading to bones rubbing against each other, causing pain, swelling, and reduced mobility. It predominantly affects older adults but can occur at any age due to injury or overuse.
Rheumatoid Arthritis: An autoimmune disorder where the immune system mistakenly attacks the synovial lining of joints, causing inflammation, swelling, and deformity. It often affects multiple joints symmetrically and requires prompt medical intervention.
Both conditions can significantly impair joint function if left untreated. Treatment aims to reduce inflammation, alleviate pain, and prevent further joint damage.
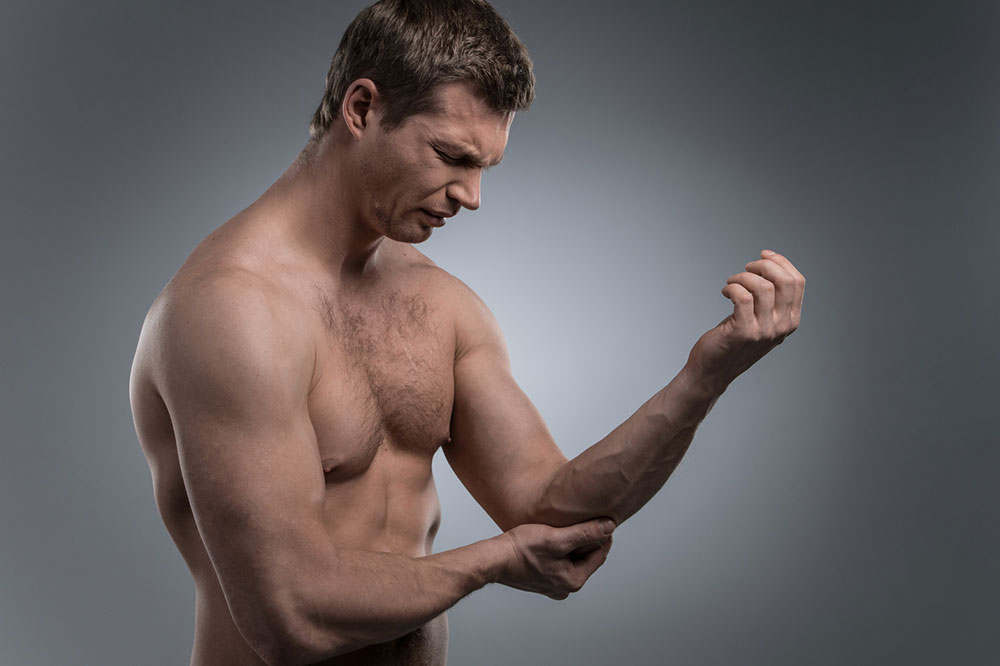
Injuries and Trauma
Sudden injuries such as sprains, strains, fractures, or dislocations are common causes of acute joint pain. These injuries often result from sports activities, accidents, or falls. Immediate management includes rest, applying ice packs, compression, and elevation (RICE protocol). Proper medical evaluation ensures proper healing and prevents chronic issues such as instability or arthritis later in life.
Chronic Fatigue Syndrome and Related Conditions
Chronic Fatigue Syndrome (CFS) is a complex disorder characterized by profound exhaustion that does not improve with rest. CFS often coexists with joint pain, muscle aches, and cognitive disturbances like memory issues. While the etiology of CFS is not fully understood, psychological factors such as stress and depression can influence its manifestation. Multidisciplinary approaches, including mental health support, physical therapy, and medication, can help alleviate symptoms.
Bursitis and Overuse Injuries
Bursae are small, fluid-filled sacs that cushion joints and facilitate smooth movement. Inflammation or rupture of bursae—bursitis—can cause localized pain, swelling, and stiffness. Commonly affected areas include shoulders, elbows, hips, and knees. Treatment involves rest, corticosteroid injections, physiotherapy, and in severe cases, surgical intervention.
Other Factors Contributing to Joint Discomfort
Apart from primary causes, other factors can contribute to joint pain, including:
Infections: Septic arthritis caused by bacterial, viral, or fungal infections can produce intense joint pain, swelling, and fever. Prompt antibiotic or antifungal treatment is essential.
Metabolic Disorders: Conditions like gout, pseudogout, and osteoporosis can lead to episodic or chronic joint pain due to crystal deposits or bone weakness.
Lifestyle and Environmental Factors: Sedentary lifestyles, obesity, poor posture, and repetitive movements increase joint strain and inflammation over time.
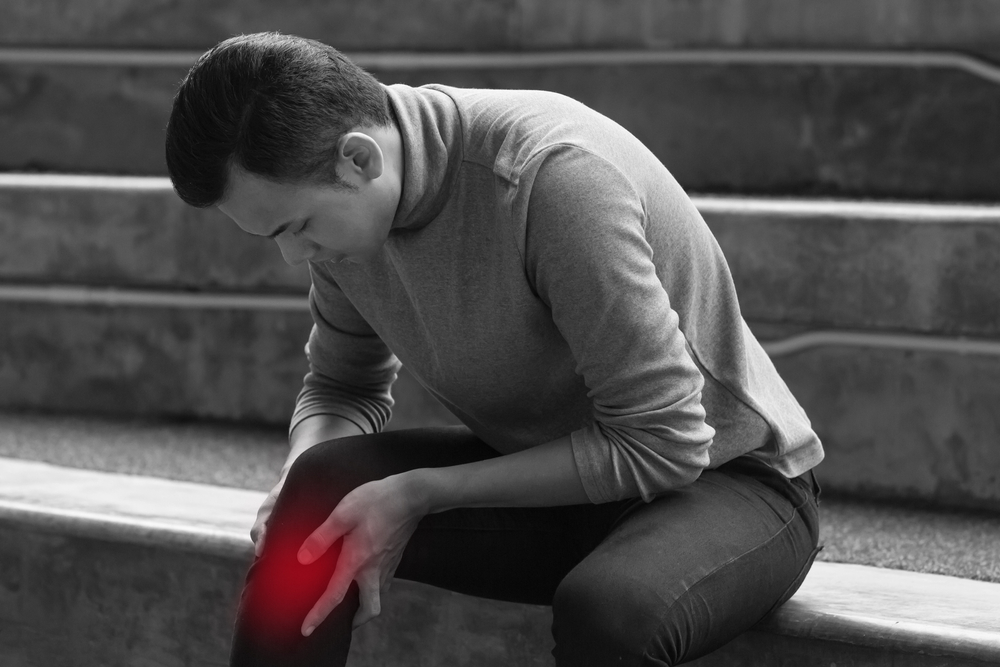
Recognizing Symptoms of Joint Discomfort
Joint pain can manifest in various ways, depending on the underlying cause. Key symptoms to watch for include:
Persistent aching or soreness in one or multiple joints
Swelling, tenderness, or warmth around the joint
Reduced range of motion or stiffness, especially after periods of inactivity
Deformity or visible abnormalities in the joint area
Radiating pain that worsens with activity or declines with rest
Modern Treatment Options for Joint Pain
Effective management of joint discomfort often requires a combination of approaches tailored to individual needs. The main treatment options include:
Medications
Medications are essential in managing joint inflammation and pain:
NSAIDs (Non-steroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs): Help reduce inflammation and alleviate pain (e.g., ibuprofen, naproxen).
Corticosteroids: Prescribed for short-term relief of severe inflammation through oral or injectable forms.
Disease-Modifying Anti-Rheumatic Drugs (DMARDs): Used in autoimmune conditions like rheumatoid arthritis to slow disease progression.
Analgesics: Such as acetaminophen, to relieve pain without affecting inflammation.
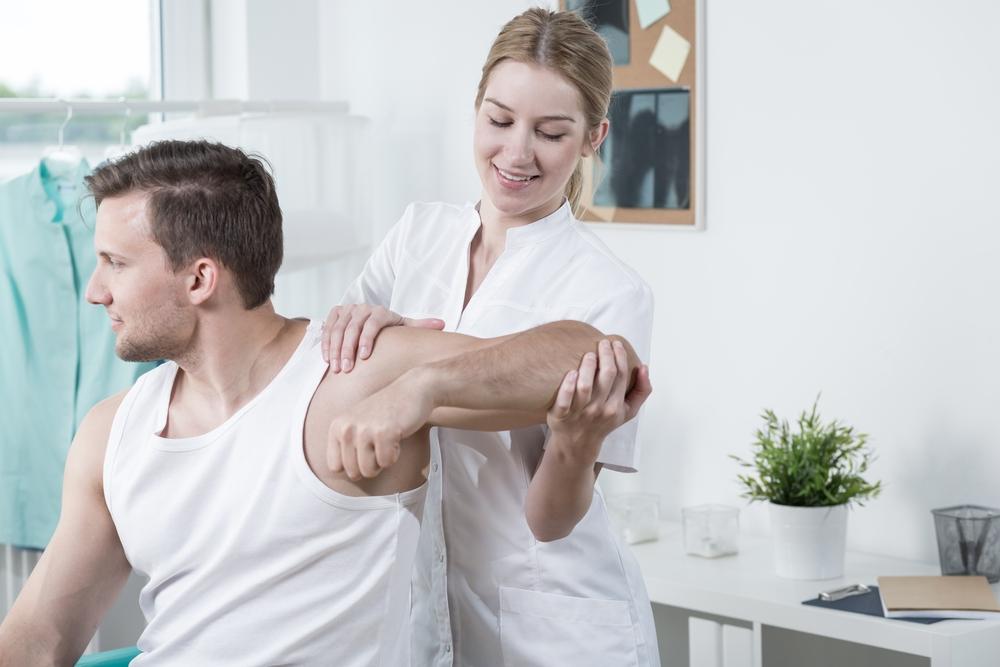
Physiotherapy and Rehabilitation
Targeted physiotherapy can strengthen surrounding muscles, improve joint flexibility, and reduce strain. Techniques include manual therapy, stretching, strengthening exercises, and hydrotherapy. Physiotherapists tailor programs to individual needs, promoting recovery and preventing further injury.
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
Adopting healthy habits can significantly improve joint health:
Maintain a healthy weight to reduce stress on weight-bearing joints.
Engage in low-impact exercises like swimming, walking, or cycling to strengthen muscles and boost joint function.
Use ergonomic supports and proper footwear to prevent undue strain.
Apply heat or cold therapy to reduce pain and inflammation.
Advanced and Surgical Treatments
In cases where conservative measures fail, surgical options such as joint replacement, arthroscopy, or realignment can restore function and relieve pain. Newer biologic therapies target specific inflammatory pathways, offering hope for chronic and severe cases.
Preventive Strategies and When to See a Doctor
Proactive measures can help prevent joint problems or catch issues early:
Maintain a balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods like omega-3 fatty acids, fruits, and vegetables.
Stay physically active to promote joint mobility and muscle strength.
Avoid repetitive stress and improper techniques during sports or work activities.
Seek medical advice if experiencing persistent or worsening joint symptoms, especially with swelling, deformity, or loss of function.
In summary, joint discomfort is a multifaceted condition with numerous causes. Proper diagnosis, combined with personalized treatment strategies—including medication, physiotherapy, lifestyle changes, and surgical interventions—can significantly improve outcomes. Empowering yourself with knowledge about joint health and promptly addressing symptoms will help maintain mobility, reduce pain, and enhance overall quality of life.