Complete Guide to Managing and Alleviating Joint Discomfort
This comprehensive guide explores joint discomfort, highlighting its causes, symptoms, and the latest treatment options. Learn how to manage and prevent joint pain to improve mobility and quality of life through effective strategies and medical advances.

Understanding Joint Discomfort: Causes, Symptoms, and Effective Treatments
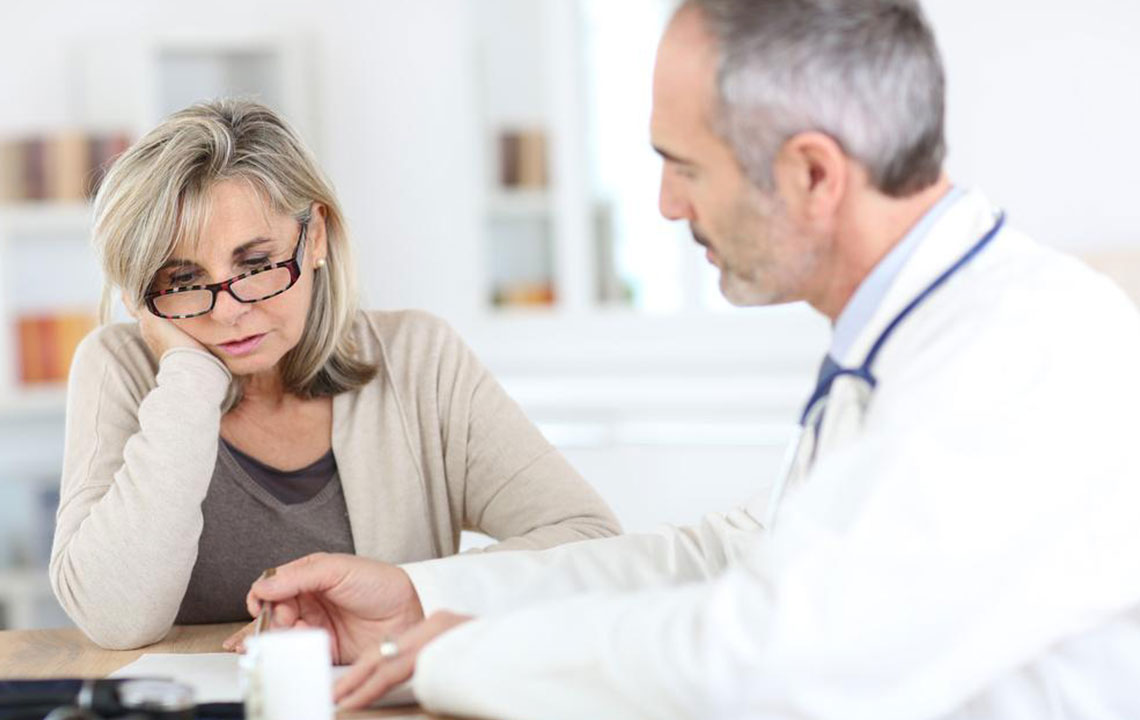
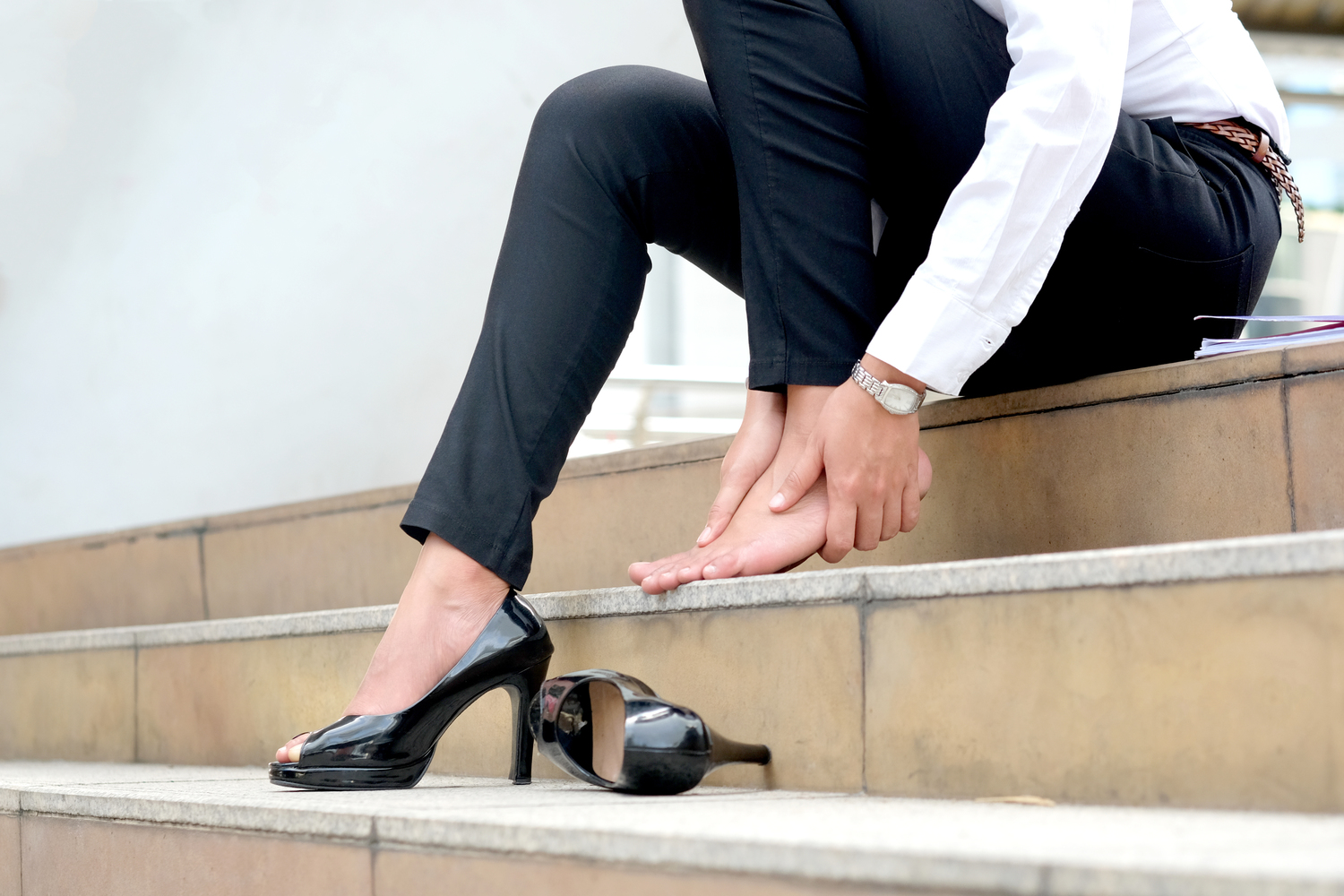
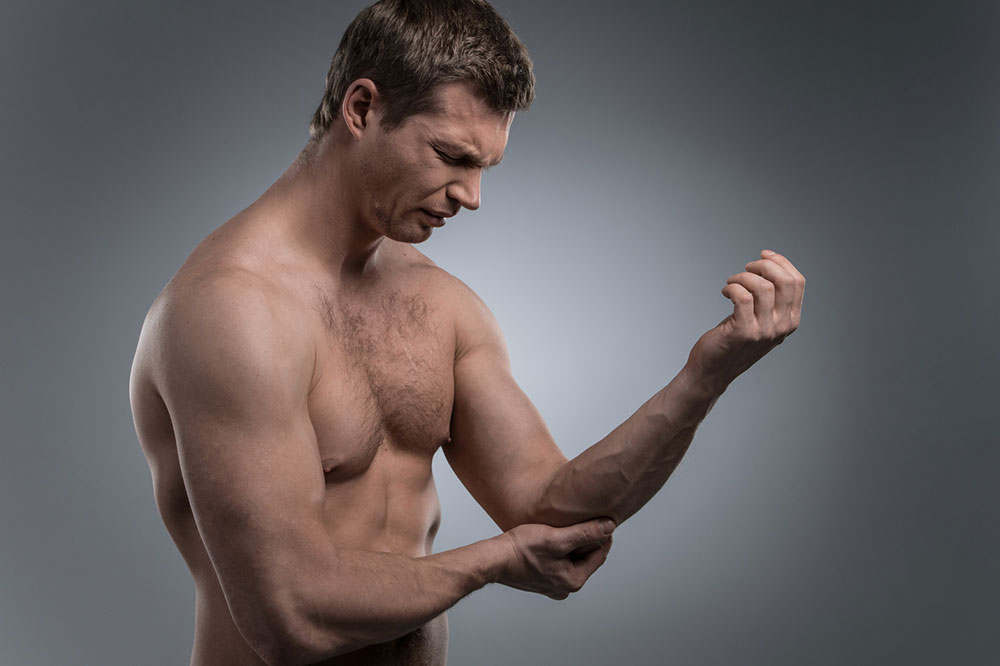
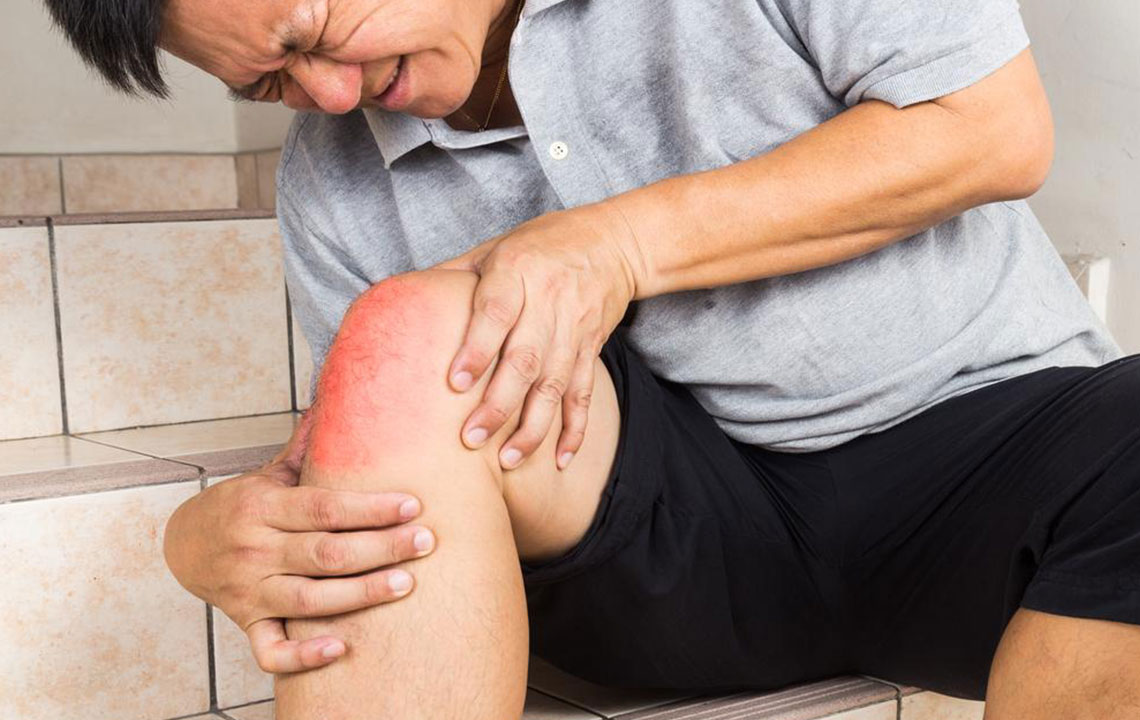
Joint discomfort, a common health concern affecting millions worldwide, manifests as pain, swelling, stiffness, and sometimes inflammation in various parts of the body's joints. These joints include critical parts such as the knees, hips, shoulders, elbows, and wrists, which facilitate our movement and daily activities. When these joints are compromised, it can significantly impact mobility, independence, and quality of life. Understanding the intricacies of joint discomfort, including its causes, symptoms, and treatments, is essential for effective management and improved well-being.
Joint pain, medically known as arthralgia, and joint diseases like arthritis are prevalent, especially among the aging population. According to recent health surveys, approximately 33% of adults experience some form of joint discomfort at some stage of their life. The severity can range from mild, occasional stiffness to persistent, debilitating pain that hampers everyday activities. The joints are complex structures that connect bones, allowing for smooth movements and weight support. When these supports are damaged or inflamed, pain ensues, which can be a warning sign of underlying health issues.
One of the most common conditions associated with joint discomfort is osteoarthritis, a degenerative joint disease characterized by the breakdown of cartilage that cushions the ends of bones. As cartilage wears down, bones may rub against each other, causing pain and deformity. Rheumatoid arthritis, an autoimmune disorder where the immune system attacks joint linings, leads to inflammation, swelling, and potential joint destruction if untreated. Other causes include ankylosing spondylitis, which causes chronic inflammation of the spine and large joints, avascular necrosis that results from blood supply loss to bones, and traumatic injuries like dislocations and bursitis.
Each underlying cause presents with distinct symptoms and requires tailored treatment approaches. Often, joint discomfort is accompanied by redness, warmth, swelling, stiffness, or visible deformities. These symptoms can worsen over time if not addressed promptly. Many factors contribute to joint pain, including excessive strain, repetitive movements, obesity, aging, genetic predisposition, and certain illnesses. It’s crucial to recognize early warning signs and seek medical advice for proper diagnosis and management.
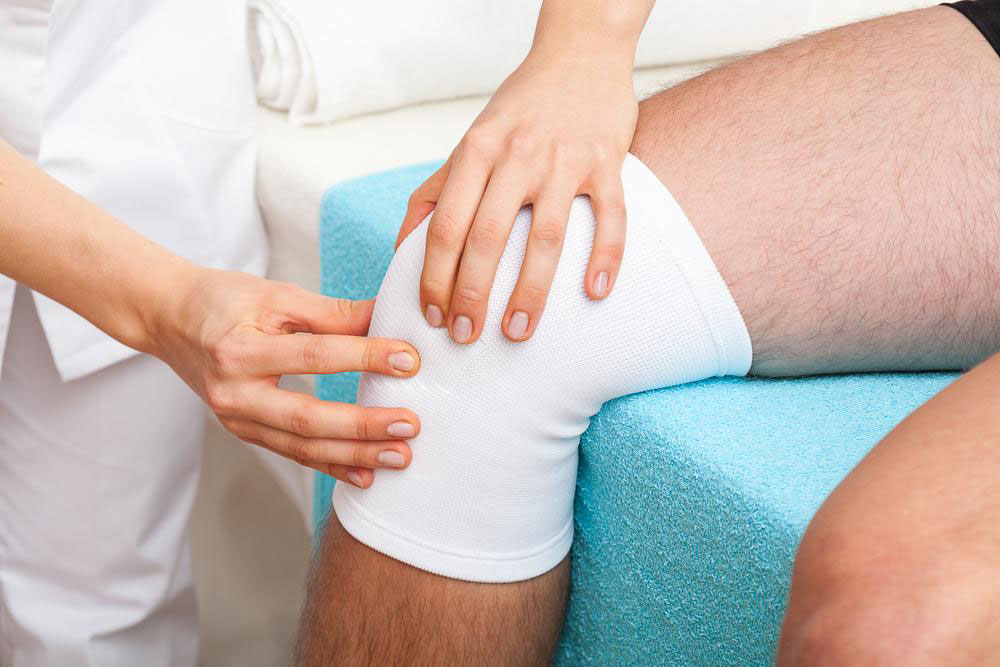
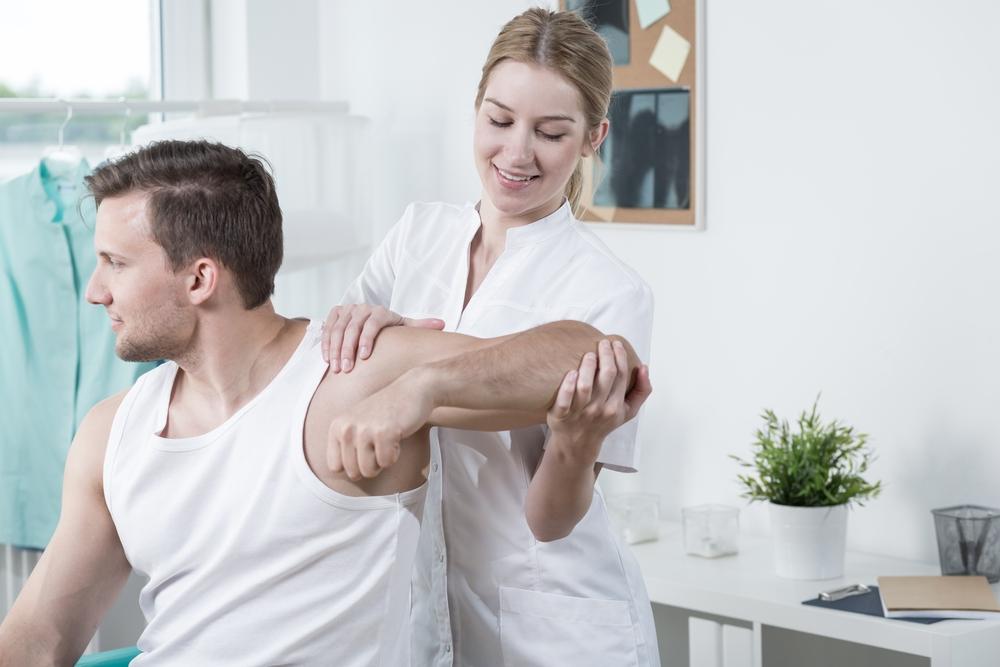
Treatment options for joint discomfort are diverse and depend on the specific cause, severity, and individual health conditions. Non-invasive strategies like rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE) can help alleviate symptoms during flare-ups. Over-the-counter medications, including non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), are commonly used to reduce pain and inflammation. Physical therapy plays a vital role in strengthening muscles around affected joints, improving flexibility, and preventing further deterioration. For some patients, lifestyle modifications such as weight loss, adopting low-impact exercises, and ergonomic adjustments prove beneficial in managing symptoms.
In cases where conservative treatments are insufficient, more advanced interventions may be necessary. These include corticosteroid injections to reduce severe inflammation, hyaluronic acid injections to improve joint lubrication, and surgical procedures like joint replacement or arthroscopy for severely damaged joints. Advances in regenerative medicine, such as stem cell therapy and platelet-rich plasma (PRP) injections, are emerging as alternative options to promote cartilage repair and joint regeneration. Early diagnosis and a comprehensive treatment plan are key to controlling joint discomfort and maintaining optimal mobility.